Cross-sectional and cross-lagged network analyses of Internet addiction among university students
-
摘要:
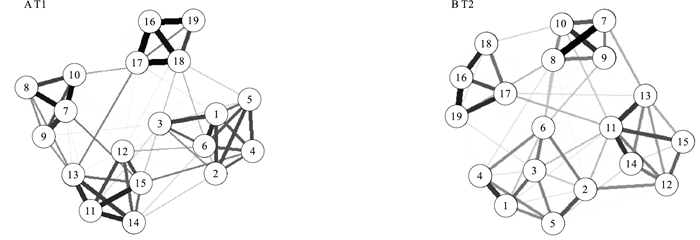
目的 了解大学生网络成瘾的动态时序演化路径并筛选出核心驱动节点,为精准实施靶向干预提供理论依据。 方法 采用方便整群抽样方法,从贵州、江西和广东省的3所高校抽取1 066名大一、大二年级的全日制在校本科生展开追踪调查(T1:2024年1—3月;T2:2025年1—3月)。运用网络成瘾量表(CIAS-R)对大学生网络成瘾状况进行测量,构建横断面与交叉滞后面板网络模型对大学生网络成瘾及其多维影响因素进行分析。 结果 T1网络有19个节点和114条非零边,T2网络有19个节点和126条非零边;横断面网络分析显示,“睡眠不足”与“白天疲乏”之间关联性最强;T1时期的核心节点为“早晨第一念头是上网”与“断网后情绪低落”(心理依赖特征),T2时期的核心节点为“健康受损”与“上网亢奋”(功能损害与成瘾性精神动力特征)。交叉滞后网络分析揭示,“休闲减少”可直接预测“压缩睡眠”,“需更多时间满足”与“学业下滑”之间存在双向影响。 结论 大学生网络成瘾呈现动态演化的特征。需要分阶段对核心驱动节点进行靶向干预,结合行为调控以及学业支持阻断恶性循环,提升现实需求契合能力。 Abstract:Objective To understand the dynamic temporal evolution pathways of Internet addiction among university students and to identify the core driving nodes, so as to provide theoretical evidences for the precise implementation of targeted interventions. Methods Using a convenient cluster sampling method, a total of 1 066 full-time freshmen and sophomores were recruited from three universities in Guizhou, Jiangxi, and Guangdong Provinces for a follow-up survey (T1:January-March 2024; T2:January-March 2025). The Revised Chen Internet Addiction Scale (CIAS-R) was employed to assess the status of Internet addiction among university students, and cross-sectional as well as cross-lagged panel network models were constructed to analyze Internet addiction and its multidimensional influencing factors. Results The T1 network comprised 19 nodes and 114 non-zero edges, while the T2 network comprised 19 nodes and 126 non-zero edges. Cross-sectional network analysis revealed the strongest association between "insufficient sleep" and "daytime fatigue"; the core nodes were "first thought upon waking for going online" and "feeling low after disconnection" (characteristics of psychological dependence) at T1, while the core nodes shifted to "impaired health" and "excitement when online" (characteristics of functional impairment and addictive psychodynamic features) at T2. Cross-lagged network analysis further indicated that "reduced leisure" directly predicted "sleep compression", and a bidirectional relationship was observed between "needing more time to achieve satisfaction" and "academic decline". Conclusions Internet addiction among university students exhibits dynamic evolutionary characteristics. Stage-specific targeted interventions focusing on core driving nodes are needed, integrating behavioral regulation and academic support to break the vicious cycle and enhancing the ability to cope with real-life demands. -
Key words:
- Internet /
- Behavior, addictive /
- Mental health /
- Cross-over studies /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
图 3 大学生网络成瘾交叉滞后网络
注:线条越粗表示相关性越强。1~6为强迫症状,分别表示早晨第一念头是上网、无网络则生活无趣、断网怕错过信息、断网后情绪低落、上网亢奋、下网后又忍不住再连;7~10为耐受症状,分别表示上网时长递增、每周上网时间暴增、计划短时间但难停下、需更多时间满足;11~15为人际与健康问题,分别表示健康受损、社交疏离、学业下滑、休闲减少、身体不适;16~19为时间管理问题,分别表示睡眠不足、压缩睡眠、被劝时长、白天疲乏。
Figure 3. Cross-lagged network of Internet addiction among university students
-
[1] 马清泽, 陈瑶, 魏淑华. 青少年网络游戏成瘾防范机制的国外实践及启示[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(9): 1221-1226. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024271MA Q Z, CHEN Y, WEI S H. International practice and implications of preventive measures for adolescent online game addiction[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(9): 1221-1226. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024271 [2] TAYLOR K. The social diagnoses of digital addictions: technophobic am-bivalences, the limits of the natural and imperatives of self-governance in the information age[J]. Soc Health Illn, 2024, 46(S1): 18-36. doi: 10.1111/1467-9566.13624 [3] 袁琳琳, 张喆, 周欣怡, 等. 上海市中学生压力与网络成瘾的关联性[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(12): 1757-1760, 1765. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024369YUAN L L, ZHANG Z, ZHOU X Y, et al. Correlation between stress and Internet addiction among middle school students in Shanghai[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(12): 1757-1760, 1765. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024369 [4] 付晓丽, 徐小青, 秦洁琼, 等. 家庭结构对初中生网络成瘾的影响: 基于有调节的中介模型[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2025, 60(2): 190-194.FU X L, XU X Q, QIN J Q, et al. Impact of family structure on Internet addiction among junior high school students: a moderated mediation model[J]. J Zhengzhou Univ (Med Sci), 2025, 60(2): 190-194. (in Chinese) [5] DUC T Q, CHI V T Q, HUYEN N T H, et al. Growing propensity of Internet addiction among Asian college students: Meta-analysis of pooled prevalence from 39 studies with over 50 000 participants[J]. Public Health, 2024, 227: 250-258. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2023.11.040 [6] HASSAN T, ALAM M M, WAHAB A, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of Internet addiction among young adults in Bangladesh[J]. J Egypt Public Health Assoc, 2020, 95(1): 3. doi: 10.1186/s42506-019-0032-7 [7] BATURAY M H, TOKER S. Internet addiction among college students: some causes and effects[J]. Educ Inf Technol, 2019, 24(5): 2863-2885. doi: 10.1007/s10639-019-09894-3 [8] DU Z, WANG T, SUN Y, et al. The influence of physical activity on Internet addiction among Chinese college students: the mediating role of self-esteem and the moderating role of gender[J]. BMC Public Health, 2024, 24(1): 935. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18474-1 [9] ZHANG Y, ZHOU J, WANG F, et al. The impact of cyberbullying victimization on Internet gaming addiction among college students: the mediating roles of basic psychological need satisfaction and frustration, and the moderating role of parental autonomy support[J]. Psychol Res Behav Manag, 2024, 17: 4105-4118. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S486250 [10] YAO L, LIANG K, HUANG L, et al. Longitudinal associations between healthy eating habits, resilience, insomnia, and Internet addiction in Chinese college students: a cross-lagged panel analysis[J]. Nutrients, 2024, 16(15): 2470. doi: 10.3390/nu16152470 [11] 肖皓月, 张杉, 郝海平, 等. 高中生网络成瘾与未来时间洞察力的纵向关系: 抑郁的中介作用[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2024, 22(5): 673-681.XIAO H Y, ZHANG S, HAO H P, et al. The longitudinal relationship between Internet addiction and future time perspective among high school students: the mediating role of depression[J]. Stud Psychol Behav, 2024, 22(5): 673-681. (in Chinese) [12] MISIAK B, PYTEL A, STAÑCZYKIEWICZ B. A systematic review of studies using network analysis to assess dynamics of psychotic-like experiences in community samples[J]. Psychol Med, 2025, 55: e54. doi: 10.1017/S0033291725000261 [13] FUNKHOUSER C J, CHACKO A A, CORREA K A, et al. Unique longitudinal relationships between symptoms of psychopathology in youth: a cross-lagged panel network analysis in the ABCD study[J]. J Child Psychol Psychiatry, 2021, 62(2): 184-194. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13256 [14] 白羽, 樊富珉. 大学生网络依赖测量工具的修订与应用[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2005, 21(4): 99-104.BAI Y, FAN F M. A study on the Internet dependence of college students: the revising and applying of a measurement[J]. Psychol Dev Educ, 2005, 21(4): 99-104. (in Chinese) [15] WILLIAMS D R, RHEMTULLA M, WYSOCKI A C, et al. On nonregularized estimation of psychological networks[J]. Multivariate Behav Res, 2019, 54(5): 719-750. doi: 10.1080/00273171.2019.1575716 [16] DEMIN D, POSKOTINOVA L. Neurophysiologic reactions during heart rate variability biofeedback session in adolescents with different risk of Internet addiction[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(5): 2759. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19052759 [17] BENER A, YILDIRIM E, TORUN P, et al. Internet addiction, fatigue, and sleep problems among adolescent students: a large-scale study[J]. Int J Ment Health Addict, 2019, 17(4): 959-969. doi: 10.1007/s11469-018-9937-1 [18] BAI W, CAI H, WU S, et al. Internet addiction and its association with quality of life in patients with major depressive disorder: a network perspective[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2022, 12(1): 138. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-01893-2 [19] FABIO R A, STRACUZZI A, LO FARO R. Problematic smartphone use leads to behavioral and cognitive self-control deficits[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(12): 7445. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127445 [20] TOMASO C C, JOHNSON A B, NELSON T D. The effect of sleep deprivation and restriction on mood, emotion, and emotion regulation: three Meta-analyses in one[J]. Sleep, 2021, 44(6): zsaa289. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsaa289 [21] 曹美, 陈段段, 杨海波. 问题性社交网络使用大学生对社交信息注意偏向的特异性[J]. 心理科学, 2025, 48(2): 346-358.CAO M, CHEN D D, YANG H B. Specificity of attentional bias information in college students with problematic social networking use[J]. J Psychol Sci, 2025, 48(2): 346-358. (in Chinese) [22] 陈雪莲, 苏宇涵, 张钊. 自我效能感与大学生网络成瘾: 自我控制的中介作用[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2024, 32(2): 371-373.CHEN X L, SU Y H, ZHANG Z. Self-efficacy and Internet addiction: the mediating role of self-control[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2024, 32(2): 371-373. (in Chinese) [23] 魏华, 李倩, 周宗奎, 等. 中庸思维与大学生网络成瘾: 同伴冲突和性别的作用[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2021, 37(5): 668-674.WEI H, LI Q, ZHOU Z K, et al. Zhong-yong thinking style and Internet addiction of college students: the role of peer conflict and gender[J]. Psychol Dev Educ, 2021, 37(5): 668-674. (in Chinese) [24] OTSUKA Y, KANEITA Y, ITANI O, et al. The association between Internet usage and sleep problems among Japanese adolescents: three repeated cross-sectional studies[J]. Sleep, 2021, 44(12): zsab175. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab175 [25] 陈晨. 熬夜: 青年的时间嵌入与脱嵌[J]. 中国青年研究, 2021(8): 29-35.CHEN C. Staying up late: temporal embedding and disembedding in youth[J]. China Youth Study, 2021(8): 29-35. (in Chinese) [26] BAKER T B, PIPER M E, MCCARTHY D E, et al. Addiction motivation reformulated: an affective processing model of negative reinforcement[J]. Psychol Rev, 2004, 111(1): 33-51. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.111.1.33 [27] 李科, 杨昆鹏, 张姗姗. 多感官刺激干预对网络成瘾大学生心理状态与神经生物学及电生理指标的影响[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(4): 539-543, 548. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024102LI K, YANG K P, ZHANG S S. Impact of multi-sensory stimulation intervention on the psychological state, neurobiology, and neuroelectro-physiological indicators of college students with Internet addiction[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(4): 539-543, 548. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024102 [28] LADRÓN DE G R M, LOPEZ-AGUDO L A, PRIETO-LATORRE C, et al. Internet use and academic performance: an interval approach[J]. Educ Inf Technol, 2022, 27(8): 11831-11873. doi: 10.1007/s10639-022-11095-4 [29] 尹霞云, 赵温也, 陈剑峰, 等. 父母行为控制和心理控制对青少年网络游戏成瘾影响的独立效应及其机制[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2023, 31(5): 1063-1069.YIN X Y, ZHAO W Y, CHEN J F, et al. Independent effect and mechanism of parental behavior control and psychological control on adolescents Internet gaming addiction[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2023, 31(5): 1063-1069. (in Chinese) [30] ÖZPARLAK A, KARAKAYA D. The associations of cognitive distortions with Internet addiction and Internet activities in adolescents: a cross-sectional study[J]. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nurs, 2022, 35(4): 322-330. doi: 10.1111/jcap.12385 [31] 公娜, 黄巧敏, 张孟思, 等. 深圳市初中生网络成瘾3年追踪研究[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2021, 42(12): 1833-1837. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.12.018GONG N, HUANG Q M, ZHANG M S, et al. A three-year longitudinal study on Internet addiction among junior high school students in Shenzhen City[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2021, 42(12): 1833-1837. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.12.018 -







 下载:
下载: