Change of forced vital capacity-to-weight index and future trend forecasting among Chinese Han students aged 7-18 during 2000-2019
-
摘要:
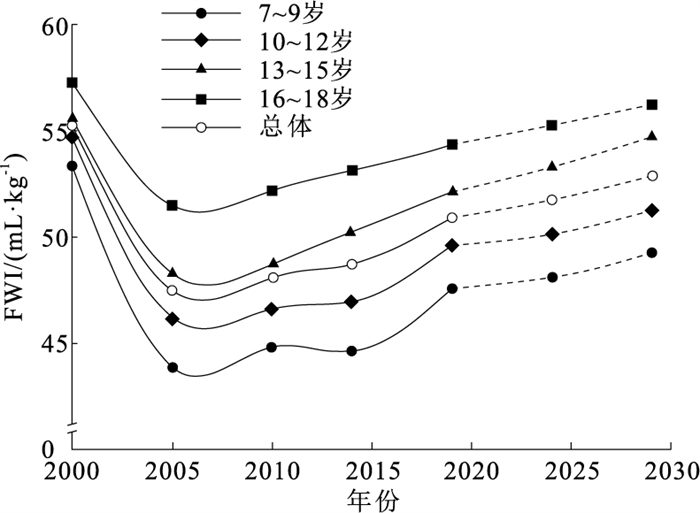
目的 探讨2000—2019年中国7~18岁汉族学生肺活量体重指数(FWI)的长期趋势并预测未来10年变化,为制定针对性的健康干预措施和学校卫生政策提供科学依据。 方法 基于2000—2019年5次全国学生体质与健康调研数据,分别纳入216 500,233 565,215 267,214 256,212 632名7~18岁汉族学生。分析学生FWI长期趋势,使用灰色模型GM(1, 1)预测未来10年的变化,并按照性别、年龄和城乡进行亚组分析。 结果 2000, 2005, 2010, 2014, 2019年中国7~18岁汉族学生FWI水平分别为(55.30±11.47)(47.43±11.92)(48.11±12.46)(48.75±12.81)(50.93±13.11)mL/kg。中国汉族学生2000—2019年FWI呈先降后升趋势,2006年左右降至最低点(约47.03 mL/kg),预测2029年恢复至52.88 mL/kg。2000—2019年男生各年及总体FWI水平均高于女生(t=72.58~304.66),且在2000—2005年的降低幅度(13.1%)小于女生(15.4%);但男女差距逐渐缩小,预测2029年缩至5.36 mL/kg。FWI随着年龄增加而增高,其中2014年7~9岁至16~18岁年龄组间增加最多(8.62 mL/kg)。2014年前城市男生FWI水平稍低于乡村男生,随后差异缩小,预计到2029年城乡男生FWI水平相近;城市女生FWI普遍高于乡村女生,且城乡差距有增大趋势,预计2029年13~15岁组城乡女生相差最大(7.74 mL/kg)。 结论 2000—2019年中国汉族学生FWI呈先降后升趋势,存在性别、年龄和城乡差异。需要加强对乡村女生呼吸健康状况的关注,采取有效措施缩小城乡差距。 Abstract:Objective To explore the long-term trend of forced vital capacity-to-weight index (FWI) among Chinese Han students aged 7-18 from 2000 to 2019, and to predict its changes over the next decade, so as to provide scientific evidences for targeted health interventions and school health policies. Methods Based on the data of the five Chinese National Surveys on Students' Constitution and Health conducted from 2000 to 2019, a total of 216 500, 233 565, 215 267, 214 256 and 212 632 Han students aged 7-18 were included, respectively. The long-term trend of FWI among students was analyzed, and the GM (1, 1) grey model was used to predict FWI changes over the next decade. Subgroup analyses were conducted by sex, age, and urban-rural residence. Results The FWI levels of Chinese Han students aged 7-18 were (55.30±11.47)(47.43±11.92)(48.11±12.46)(48.75±12.81)(50.93±13.11)mL/kg in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2014, and 2019, respectively. The FWI of Chinese Han students showed a decreasing-then-increasing trend from 2000 to 2019, reaching the lowest point of approximately 47.03 mL/kg around 2006, and was projected to recover to 52.88 mL/kg by 2029. Boys had higher FWI for each year and the total level than girls from 2000 to 2019(t=72.58-304.66), and the decline between 2000 and 2005 was smaller in boys (13.1%) than in girls (15.4%). However, the gender gap gradually narrowed and was projected to reduce to 5.36 mL/kg by 2029. FWI increased with age, with the largest difference observed in 2014 between the 7-9 and 16-18 age groups (8.62 mL/kg). Before 2014, urban boys had slightly lower FWI than rural boys; the gap narrowed thereafter, and their FWI levels were expected to become similar by 2029. Urban girls generally had higher FWI than rural girls, and the urban-rural gap showed an increasing trend. By 2029, the largest difference was projected to occur in the 13-15 age group, reaching 7.74 mL/kg. Conclusions The FWI of Chinese Han students showed a trend of initial decline followed by a gradual increase from 2000 to 2019, with notable differences across sex, age, and urban-rural residence. Greater attention should be paid to the respiratory health of rural girls, and effective measures should be taken to reduce urban-rural disparities. 1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 中国城乡不同性别7~18岁汉族学生各年份FWI水平(x±s,mL/kg)
Table 1. FWI level of Chinese Han students aged 7 to 18 years by urban-rural residence and sex in different years(x±s, mL/kg)
城乡 性别 2000年 2005年 2010年 2014年 2019年 总体 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 城市 男 54 387 58.63±12.04 59 081 50.70±12.58 53 822 51.30±13.00 53 575 52.31±13.68 53 776 54.28±13.94 274 641 53.44±13.05 女 54 394 51.65±10.98 58 510 43.61±11.64 53 740 44.82±11.95 53 618 45.72±12.32 52 892 48.30±12.62 273 154 46.82±11.90 乡村 男 53 833 59.62±11.66 58 277 52.04±12.37 53 840 52.00±12.94 53 596 52.24±13.31 52 879 53.93±13.54 272 425 53.97±12.76 女 53 886 51.17±11.20 57 697 43.39±11.08 53 865 44.34±11.95 53 467 44.71±11.90 53 085 47.22±12.35 272 000 46.17±11.70 合计 216 500 55.30±11.47 233 565 47.43±11.92 215 267 48.11±12.46 214 256 48.75±12.81 212 632 50.93±13.11 1 092 220 50.10±12.35 表 2 中国7~18岁不同性别与年龄组汉族学生各年份FWI水平比较(x±s,mL/kg)
Table 2. FWI level of Chinese Han students aged 7 to 18 years by sex and age in different years(x±s, mL/kg)
性别与年龄 选项 统计值 2000年 2005年 2010年 2014年 2019年 总体 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 人数 FWI 性别 男 108 220 59.13±11.85 117 358 51.37±12.48 107 662 51.65±12.97 107 171 52.28±13.50 106 655 54.11±13.74 547 066 53.71±12.91 女 108 280 51.41±11.09 116 207 43.50±11.36 107 605 44.58±11.95 107 085 45.22±12.11 105 977 47.76±24.97 545 154 46.50±11.80 t值 156.50 159.40 131.21 127.42 72.58 304.66 P值 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 年龄/岁 7~9 54 105 53.38±12.93 57 453 43.83±12.60 53 804 44.84±13.28 53 658 44.57±13.48 53 877 47.60±13.99 272 897 46.84±13.26 10~12 54 307 54.72±12.27 58 324 46.17±12.56 53 894 46.65±13.10 53 747 46.94±13.42 53 921 49.64±13.70 274 193 48.82±13.01 13~15 53 930 55.59±11.94 58 436 48.26±12.80 53 860 48.76±13.09 53 841 50.27±13.54 53 295 52.15±13.50 273 362 51.01±12.97 16~18 54 158 57.33±12.10 59 352 51.51±13.20 53 709 52.23±13.25 53 010 53.19±13.57 51 539 54.40±13.65 271 768 53.73±13.15 F值 977.90 3 397.25 3 117.37 4 173.97 2 458.73 13 906.13 P值 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 -
[1] 范明宽, 杨雷, 胡长虎. 某高职医学生体质指数与肺活量体重指数相关分析[J]. 职业卫生与病伤, 2021, 36(3): 164-166, 172.FAN M K, YANG L, HU C H. Body mass index and vital capacity weight index of medical students in a vocational college[J]. Occup Health Damage, 2021, 36(3): 164-166, 172. (in Chinese) [2] 万华喆. 江西省儿童青少年体质、青春发育及一般自我效能地域差异性研究[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学, 2015.WAN H Z. A study on regional differences of physical fitness, youth development and general self-efficacy of children and adolescents in Jiangxi Province[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University, 2015. (in Chinese) [3] WU T, SANTOS S, QUEZADA-PINEDO H G, et al. Body composition and respiratory outcomes in children: a population-based prospective cohort study[J]. Thorax, 2024, 79(5): 448-456. doi: 10.1136/thorax-2023-220014 [4] 舒文博. 在校大学生肺活量体重指数与脂肪分布的相关性分析: 以广西医科大学为例[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学, 2021.SHU W B. Correlation analysis of vital capacity index and fat distribution in college students: taking Guangxi Medical University as an example[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Medical University, 2021. (in Chinese) [5] MASANOVIC B, GARDASEVIC J, MARQUES A, et al. Trends in physical fitness among school-aged children and adolescents: a systematic review[J]. Front Pediatr, 2020, 8: 627529. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.627529 [6] 崔立志. 灰色预测技术及其应用研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010.CUI L Z. Grey forecast technology and its application research[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010. (in Chinese) [7] 查淑玲, 屈改珠, 王璇. 基于灰色模型的西安市人口数量预测分析[J]. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(6): 16-19.ZHA S L, QU G Z, WANG X. Population prediction analysis of Xi'an based on grey model[J]. J Cap Norm Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2023, 44(6): 16-19. (in Chinese) [8] 张亚慧, 张荣, 贾素红, 等. 灰色模型GM(1, 1)和残差自回归模型在中国孕产妇死亡率预测中的应用[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2023, 38(10): 1747-1752.ZHANG Y H, ZHANG R, JIA S H, et al. Application of grey model(1, 1) and autoregressive error model in predicting maternal mortality rate in China[J]. Matern Child Health Care China, 2023, 38(10): 1747-1752. (in Chinese) [9] 周浩, 刘文利, 于丽娅, 等. 2014—2019年辽宁省朝阳市城市居民肝癌死亡率年度趋势分析及灰色模型预测[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(7): 1293-1297.ZHOU H, LIU W L, YU L Y, et al. Annual trend analysis and grey model prediction of liver cancer mortality among urban residents in Chaoyang City, Liaoning, 2014-2019[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(7): 1293-1297. (in Chinese) [10] 文静, 殷成宇, 廖国伟, 等. 应用GM(1, 1)灰色模型预测全国甲状腺癌发病趋势[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022, 30(5): 899-902.WEN J, YIN C Y, LIAO G W, et al. Application of GM(1, 1) model in predicting the incidence trend of thyroid cancer in China[J]. J Mod Oncol, 2022, 30(5): 899-902. (in Chinese) [11] 寻鲁宁, 王冲, 沈成凤, 等. 1990—2019年中国结直肠癌发病趋势分析及预测模型比较[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2023, 32(4): 279-286.XUN L N, WANG C, SHEN C F, et al. Prediction of colorectal cancer incidence in China with three different models based on trends from 1990 to 2019[J]. China Cancer, 2023, 32(4): 279-286. (in Chinese) [12] 蔡红霞, 刘潇霞, 张文彬. 2011—2016年中国恶性肿瘤发病和死亡趋势分析及GM(1, 1)模型预测[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2023, 31(5): 931-936.CAI H X, LIU X X, ZHANG W B. Trend analysis and GM(1, 1) model prediction of the cancer incidence and mortality in China from 2011 to 2016[J]. J Mod Oncol, 2023, 31(5): 931-936. (in Chinese) [13] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2000年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002: 3-4.Research Group on Physical Fitness and Health of Chinese School Students. Report on the physical fitness and health surveillance of Chinese school students in 2000[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2002: 3-4. (in Chinese) [14] 中国学生体质与健康调研组. 2005年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007: 8-9.Research Group on Physical Fitness and Health of Chinese School Students. Report on the physical fitness and health surveillance of Chinese school students in 2005[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007: 8-9. (in Chinese) [15] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2010年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2012: 4-5.Research Group on Physical Fitness and Health of Chinese School Students. Report on the physical fitness and health surveillance of Chinese school students in 2010[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2012: 4-5. (in Chinese) [16] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2014年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2016: 4-5.Research Group on Physical Fitness and Health of Chinese School Students. Report on the physical fitness and health surveillance of Chinese school students in 2014[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2016: 4-5. (in Chinese) [17] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2019年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2021: 4-5.Research Group on Physical Fitness and Health of Chinese School Students. Report on the physical fitness and health surveillance of Chinese school students in 2019[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2021: 4-5. (in Chinese) [18] JI C Y, CHEN T J, . Empirical changes in the prevalence of overweight and obesity among Chinese students from 1985 to 2010 and corresponding preventive strategies[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2013, 26(1): 1-12. [19] DONG Y H, LAU P W C, DONG B, et al. Trends in physical fitness growth, and nutritional status of Chinese children and adolescents: a retrospective analysis of 1.5 million students from six successive national surveys between 1985 and 2014[J]. Lancet Child Adolesc Health, 2019, 3(12): 871-880. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(19)30302-5 [20] KIM S A, LIM K, LEE J K, et al. Metabolically healthy obesity and the risk of all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in a Korean population: a prospective cohort study[J]. BMJ Open, 2021, 11(9): e049063. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049063 [21] 宋源龙, 杨弋星, 董顺雨, 等. 1990—2019年中国伤害疾病负担变化趋势及预测[J]. 现代预防医学, 2024, 51(8): 1377-1383, 1419.SONG Y L, YANG Y X, DONG S Y, et al. Trends and predictions of the burden of three types of injury diseases, China, 1990-2019[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2024, 51(8): 1377-1383, 1419. (in Chinese) [22] FORNO E, HAN Y Y, MULLEN J, et al. Overweight, obesity, and lung function in children and adults: a Meta-analysis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2018, 6(2): 570-581.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.07.010 [23] YE H, ULLAH R, WANG J B, et al. Trends of obesity and overweight among children and adolescents in China[J]. World J Pediatr, 2023, 19(Suppl 3): 627529. [24] 胡小琪, 陈超, 张梅. 中国儿童青少年肥胖防控策略与挑战[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2021, 55(1): 7-12.HU X Q, CHEN C, ZHANG M. Strategies and challenges of obesity prevention and control among children and adolescents in China[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2021, 55(1): 7-12. (in Chinese) [25] 肖悦, 田永中, 许文轩, 等. 近10年中国空气质量时空分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(2): 243-252.XIAO Y, TIAN Y Z, XU W X, et al. Spatiotemporal pattern changes of air quality in China from 2005 to 2015[J]. Ecol Environ Sci, 2017, 26(2): 243-252. (in Chinese) [26] WEI J, LI Z, CHEN X, et al. Separating daily 1 km PM2.5 inorganic chemical composition in China since 2000 via deep learning integrating ground, satellite, and model data[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2023, 57(46): 18282-18295. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c00272 [27] WEI J, LI Z, WANG J, et al. Ground-level gaseous pollutants (NO2, SO2, and CO) in China: daily seamless mapping and spatiotemporal variations[J]. Atmos Chem Phys, 2023, 23(2): 1511-1532. doi: 10.5194/acp-23-1511-2023 [28] 沈续航, 苏时雨, 关静, 等. 城市与山村青少年肠道菌群及其代谢组学差异的研究[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2023, 58(11): 1952-1956.SHEN X H, SU S Y, GUAN J, et al. Study on the difference of gut microbiota and metabolites between urban and rural adolescents[J]. Acta Univ Med Anhui, 2023, 58(11): 1952-1956. (in Chinese) [29] 彭李奥, 柳鸣毅, 敬艳, 等. 中国儿童青少年身体活动的地区差异性[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(9): 1290-1293, 1299. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024288PENG L A, LIU M Y, JING Y, et al. Regional variations in physical activity among children and adolescents in China[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(9): 1290-1293, 1299. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024288 [30] 高萌, 魏玉虾, 吕筠, 等. 中国成年人代谢异常相关的体质指数和腰围切点研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40(12): 1533-1540.GAO M, WEI Y X, LV Y, et al. The cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference for predicting metabolic risk factors in Chinese adults[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2019, 40(12): 1533-1540. (in Chinese) [31] 伍晓艳, 陶舒曼, 张诗晨, 等. 中国12省份中小学生视屏时间及其影响因素分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2016, 50(6): 508-513.WU X Y, TAO S M, ZHANG S C, et al. Analysis on risk factors of screen time among Chinese primary and middle school students in 12 provinces[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2016, 50(6): 508-513. (in Chinese) [32] 杜艳艳, 陈俊虎, 杨朔. 广州市番禺区某中学2013—2015年学生体质指数与肺活量体重指数分析[J]. 华南预防医学, 2017, 43(6): 578-580.DU Y Y, CHEN J H, YANG S. Analysis of body mass index and lung capacity body mass index of students in a middle school in Panyu District, Guangzhou City, from 2013 to 2015[J]. South Chin J Prev Med, 2017, 43(6): 578-580. (in Chinese) [33] ZHANG H, SUN L, YU Y, et al. The associations between body composition and vital capacity index of medical students in Shenyang of China: a cross-sectional survey[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1): 373. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02176-8 [34] ZHANG F, BI C, YIN X, et al. Physical fitness reference standards for Chinese children and adolescents[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 4991. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84634-7 [35] LIU J. Highlights of the 2018 Chinese hypertension guidelines[J]. Clin Hypertens, 2020, 26(1): 8. doi: 10.1186/s40885-020-00141-3 -







 下载:
下载: