Association of latent profiles of mobile phone dependence and self-control with physical exercise among junior high school students
-
摘要:
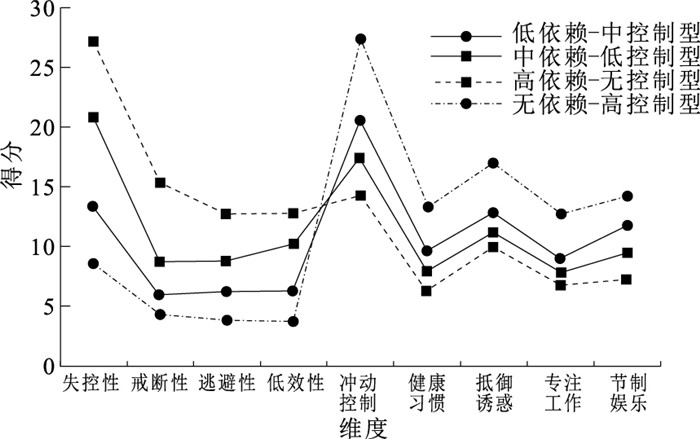
目的 探讨初中生手机依赖和自我控制的潜在类别与体育锻炼的关联,为预防初中生手机依赖和提高自我控制水平提供参考。 方法 于2024年4—5月,采用分层随机整群抽样法,选取湖南省湘西自治州3所公立中学初一至初三共计2 311名学生进行调查。采用潜在剖面分析初中生手机依赖与自我控制的类别,运用Pearson相关分析手机依赖与自我控制的相关性,χ2检验分析不同人口学特征青少年潜在剖面类别分布的差异,采用多元Logistic回归分析初中生手机依赖和自我控制与体育锻炼的关系。 结果 初中生手机依赖和自我控制的潜在剖面分为低依赖-中控制型(885名,38.3%)、中依赖-低控制型(910名,39.4%)、高依赖-无控制型(232名,10.0%)和无依赖-高控制型(284名,12.3%)4个类别;不同性别、年级、独生情况在不同类别上的分布差异均有统计学意义(χ2值分别为10.85,35.72,13.85,P值均 < 0.05)。Logistic回归分析结果显示,控制人口学变量后,以低依赖-中控制组为参照,体育锻炼与中依赖-低控制组(OR=0.79)、高依赖-无控制组(OR=0.81)均呈负相关,与无依赖-高控制组(OR=1.58)呈正相关(P值均 < 0.01)。 结论 体育锻炼对初中生不同手机依赖与自我控制的潜在剖面类别的影响存在差异。学校和家庭应针对不同类别初中生加强体育锻炼,促进身心健康发展。 Abstract:Objective To explore the association of latent profiles of mobile phone dependence and self-control with physical exercise among junior high school students, so as to provide references for the prevention of mobile phone dependence and the improvement of self-control among junior high school students. Methods From April to May 2024, a stratified random cluster sampling method was used to select a total of 2 311 students from grade 7 to grade 9 in three public junior high schools in Xiangxi Autonomous Prefecture, Hunan Province. Latent profile analysis was conducted to identify the latent profiles of mobile phone dependence and self-control among junior high school students. Pearson correlation analysis was used to examine the correlation between mobile phone dependence and self-control, and Chi-square test was used to analyze the distribution differences of latent profiles of adolescents across different demographic characteristics. Multiple Logistic regression analysis was applied to explore the association between mobile phone dependence, self-control, and physical exercise. Results Four latent profiles of mobile phone dependence and self-control were identified: low dependence-moderate self-control group (n=885, 38.3%), moderate dependence-low self-control group (n=910, 39.4%), high dependence-no self-control group (n=232, 10.0%), and no dependence-high self-control group (n=284, 12.3%). Significant differences were observed in the distribution of latent profiles across gender, grade and only-child status (χ2=10.85, 35.72, 13.85, P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that, after controlling for demographic variables, compared with the low dependence-moderate self-control group, physical exercise was negatively associated with the moderate dependence-low self-control group (OR=0.79) and the high dependence-no self-control group (OR=0.81), while positively associated with the no dependence-high self-control group (OR=1.58) (P < 0.01). Conclusions The influence of physical exercise on junior high school students' different potential profile types of mobile phone dependence and self-control is different. Schools and families should adopt targeted physical exercise interventions based on the characteristics of different profiles to promote the physical and mental health of junior high school students. -
Key words:
- Cellular phone /
- Behavior, addictive /
- Ego /
- Mental health /
- Exercise movement techniques /
- Regression analysis /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 初中生手机依赖与自我控制量表得分相关性分析(r值,n=2 311)
Table 1. Analysis of correlation between mobile phone dependence and self-control scale scores among junior high school students(r, n=2 311)
变量 失控性 戒断性 逃避性 低效性 冲动控制 健康习惯 抵御诱惑 专注工作 戒断性 0.57 逃避性 0.53 0.57 低效性 0.73 0.56 0.57 冲动控制 -0.46 -0.37 -0.37 -0.43 健康习惯 0.50 -0.34 -0.33 -0.48 0.57 抵御诱惑 -0.50 -0.32 -0.32 -0.48 0.48 0.51 专注工作 -0.50 -0.32 -0.32 -0.48 0.55 0.58 0.55 节制娱乐 -0.52 -0.41 -0.35 -0.46 0.64 0.59 0.47 0.49 注: P值均 < 0.01。 表 2 初中生手机依赖与自我控制的潜在剖面模型拟合指标
Table 2. Potential profile model fitting indicators of mobile phone dependence and self-control
类别 条目 AIC值 BIC值 aBIC值 Entropy值 LMR值 BLRT值 类别概率 1 18 113 602.07 113 705.49 113 648.30 — — — 1.00 2 28 107 764.80 107 925.67 107 836.71 0.85 0 0 0.45/0.56 3 38 105 437.31 105 655.64 105 534.90 0.86 < 0.01 0 0.15/0.33/0.53 4 48 104 355.61 104 631.39 104 478.89 0.86 < 0.01 0 0.12/0.10/0.39/0.38 5 58 103 869.35 104 202.59 104 018.31 0.84 0.26 0 0.13/0.09/0.15/0.25/0.39 表 3 不同人口学特征初中生手机依赖和自我控制的潜在类别分布比较
Table 3. Comparison of the status quo of potential categories of mobile phone dependence and self-control among middle school students in different demographic characteristics
人口学指标 选项 人数 低依赖-中控制 中依赖-低控制 高依赖-无控制 无依赖-高控制 χ2值 P值 性别 男 1 162 457(39.3) 431(37.1) 110(9.5) 164(14.1) 10.85 0.01 女 1 149 428(37.2) 479(41.7) 122(10.6) 120(10.4) 年级 初一 807 289(37.5) 76(35.8) 139(9.4) 303(17.2) 35.72 < 0.01 初二 774 312(40.3) 326(42.1) 76(9.8) 60(7.8) 初三 730 270(37.0) 295(40.4) 80(11.0) 85(11.6) 独生子女 是 331 108(32.6) 156(47.1) 38(11.5) 29(8.8) 13.85 < 0.01 否 1 980 777(39.2) 754(38.1) 194(9.8) 255(12.9) 注: ()内数字为构成比/%。 -
[1] WANG A, GUO S, CHEN Z, et al. The chain mediating effect of self-respect and self-control on the relationship between parent-child relationship and mobile phone dependence among middle school students[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 30224. [2] 中国互联网络信息中心发布第53次《中国互联网络发展状况统计报告》[J]. 国家图书馆学刊, 2024, 33(2): 104.China Internet Network Information Center released the 53rd Statistical Report on the Development of China's Internet Network[J]. Nation Library J, 2024, 33(2): 104. (in Chinese) [3] LIU Y, TAN D, WANG P, et al. Physical activity moderated the mediating effect of self-control between bullying victimization and mobile phone addiction among college students[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 20855. [4] 石利娟, 郑瑶, 黎兆康, 等. 大学生分裂特质和孤独特质的潜在剖面类型及情绪智力和共情比较[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2023, 31(5): 1102-1106.SHI L J, ZHENG Y, LI Z K, et al. Latent profile types of college students' schizotypal and loneliness traits and a comparison of emotional intelligence and empathy[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2023, 31(5): 1102-1106. (in Chinese) [5] 詹鋆, 任俊. 自我控制与自我控制资源[J]. 心理科学进展, 2012, 20(9): 1457-1466.ZHAN Y, REN J. Self-control and self-control resources[J]. Adv Psychol, 2012, 20(9): 1457-1466. (in Chinese) [6] HAGGER M S, WOOD C, STIFF C, et al. Ego depletion and the strength model of self-control: a Meta-analysis[J]. Psychol Bull, 2010, 136(4): 495-525. [7] 徐涛, 周县委, 张天成, 等. 学校联结与初中生危害健康行为共存的交叉滞后分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(11): 1565-1569. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024335XU T, ZHOU X W, ZHANG T C, et al. Cross-lagged analysis of school connection and the co-occurrence of health-harming behaviors among junior high school students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(11), 1565-1569. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024335 [8] GERDTHAM U G, WENGSTRÖM E, WICKSTRÖM Ö L. Trait self-control, exercise and exercise ambition: evidence from a healthy, adult population[J]. Psychol Health Med, 2020, 25(5): 583-592. [9] CASPERSEN C J, POWELL K E, CHRISTENSON G M. Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: definitions and distinctions for health-related research[J]. Public Health Rep, 1985, 100(2): 126-131. [10] LEUNG L. Linking psychological attributes to addiction and improper use of the mobile phone among adolescents in Hong Kong[J]. J Children Med, 2008, 2: 93-113. [11] 吕行, 张璠, 朱传林, 等. 父母低头与青少年手机依赖及体育活动所调节的中介机制[J]. 现代预防医学, 2023, 50(22): 4088-4093.LÜ X, ZHANG F, ZHU C L, et al. Parental smartphone use and adolescent smartphone addiction: mediating mechanisms moderated by physical activity[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2023, 50(22), 4088-4093. (in Chinese) [12] 刘诗洁, 刘亚女, 王林. 运动干预和团体认知疗法对大学生手机依赖的实证研究[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2022, 43(6): 825-829. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.06.007LIU S J, LIU Y N, WANG L. An empirical study on the effects of exercise intervention and group cognitive therapy on mobile phone addiction among college students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2022, 43(6), 825-829. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.06.007 [13] 谭树华, 郭永玉. 大学生自我控制量表的修订[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2008, 16(5): 468-470.TAN S H, GUO Y Y. Revision of the Self-control Scale for College Students[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2008, 16(5): 468-470. (in Chinese) [14] 胡凤姣, 陈贵, 蔡太生. 自我控制量表在中学生中的试用[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2012, 20(8): 1183-1184.HU F J, CHEN G, CAI T S. Trial of the Self-control Scale among middle school students[J]. Chin J Health Psychol, 2012, 20(8): 1183-1184. (in Chinese) [15] 梁德清. 高校学生应激水平及其与体育锻炼的关系[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 1994, 8(1): 5-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.1994.01.020LIANG D Q. Stress levels of college students and their relationship with physical exercise[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 1994, 8(1): 5-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.1994.01.020 [16] 王澳伦, 张天成, 徐涛, 等. 武陵山区大学生危害健康行为潜在类别及其与校园欺凌的关联[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2023, 44(5): 751-755. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.05.025WANG A L, ZHANG T C, XU T, et al. Potential categories of unhealthy behavior among college students in the Wuling Mountain Area and their association with school bullying[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2023, 44(5): 751-755. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.05.025 [17] 张天成, 周县委, 徐涛, 等. 武陵山区青少年危害健康行为潜在类别及与学校联结的关联[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(4): 509-513. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024127ZHANG T C, ZHOU X W, XU T, et al. Potential categories of health-harming behaviors among adolescents in the Wuling Mountain Area and their association with school connection[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(4): 509-513. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024127 [18] 来枭雄, 黄顺森, 张彩, 等. 中小学生手机成瘾与人际关系主观幸福感和学校认同感的关联[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2020, 41(4): 613-616. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.04.036LAI X X, HUANG S S, ZHANG C, et al. Association between mobile phone addiction and interpersonal relationships, subjective well-being, and school identity among primary and middle school students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2020, 41(4): 613-616. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.04.036 [19] 王慧慧, 王孟成, 吴胜齐. 不同手机成瘾类型对大学生人际关系和孤独感的影响: 基于潜剖面分析的结果[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2015, 23(5): 881-885.WANG H H, WANG M C, WU S Q. The impact of different types of mobile phone addiction on interpersonal relationships and loneliness among college students: results based on latent profile analysis[J]. Chin J Clinic Psychol, 2015, 23(5): 881-885. (in Chinese) [20] 宋明华, 陈晨, 刘燊, 等. 父母教养方式对初中生攻击行为的影响: 越轨同伴交往和自我控制的作用[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2017, 33(6): 675-682.SONG M H, CHEN C, LIU S, et al. The influence of parenting styles on aggressive behavior in junior high school students: the role of deviant peer affiliation and self-control[J]. Psychol Dev Educ, 2017, 33(6): 675-682. (in Chinese) [21] 田玉环, 黎晓钧, 李国兴, 等. 初中生解释水平与手机依赖的关系: 奖励敏感性和自我控制的链式中介作用[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2022, 30(7): 1060-1065.TIAN Y H, LI X J, LI G X, et al. The relationship between junior high school students' construal level and mobile phone addiction: a chain mediating effect of reward sensitivity and self-control[J]. Chin J Health Psychol, 2022, 30(7): 1060-1065. (in Chinese) [22] MARSHALL A T, ADISE S, KAN E C, et al. Longitudinal mapping of cortical change during early adolescence associated with prenatal tobacco and/or alcohol exposure in the adolescent brain cognitive development study[J]. Preprint Server Biol, 2024, 30: 2024.8.29.610335. [23] SAHU M, GANDHI S, SHARMA M K. Mobile phone addiction among children and adolescents: a systematic review[J]. J Addict Nurs, 2019, 30(4): 261-268. doi: 10.1097/JAN.0000000000000309 [24] 陈萍. 初中生自我控制训练的实验研究[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2015, 36(2): 217-220. http://www.cjsh.org.cn/article/id/zgxxws201502016CHEN P. An experimental study on self-control training for junior high school students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2015, 36(2): 217-220. (in Chinese) http://www.cjsh.org.cn/article/id/zgxxws201502016 [25] XU X, HAN W, LIU Q. Peer pressure and adolescent mobile social media addiction: moderation analysis of self-esteem and self-concept clarity[J]. Front Public Health, 2023, 11: 1115661. [26] 田录梅, 刘玲玲, 袁竞驰, 等. 家庭功能对青少年冒险行为的影响: 自我控制能力与不良同伴交往的序列中介效应[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2018, 34(3): 361-368.TIAN L M, LIU L L, YUAN J C, et al. The impact of family function on adolescent risk-taking behavior: a sequential mediating effect of self-control ability and negative peer interaction[J]. Psychol Dev Educ, 2018, 34(3): 361-368. (in Chinese) [27] ZHANG Y, LI Y, XIA M, et al. The relationship between loneliness and mobile phone addiction among Chinese college students: the mediating role of anthropomorphism and moderating role of family support[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(4): e0285189. [28] LI Y S, LI Y L, CHEN G, et al. Being an only child and children's prosocial behaviors: evidence from rural China and the role of parenting styles[J]. Human Soc Sci Commun, 2024, 11(1): 1-14. [29] WANG Q, CHEN Y, LI L. Effects of physical activity and self-control on mobile phone addiction in college students: a cross-lagged study in China[J]. Front Psychol, 2024, 15: 1417379. [30] ZHUANG S S. The effects of physical activity on adolescent psychological sub-health: chain-mediated effects of self-control and mobile phone addiction[J]. BMC Psychol, 2025, 13(1): 98. [31] 徐久阳, 朱峣, 朱昊, 等. 初中生攻击行为体育锻炼和学习成绩关联的交叉滞后分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(8): 1091-1095. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024244XU J Y, ZHU Y, ZHU H, et al. The cross-lagged analysis of aggressive behavior, physical exercise, and academic performance among junior high school students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(8): 1091-1095. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2024244 -







 下载:
下载: