Association between 24 h movement behaviors and fundamental motor skills of children with autism spectrum disorder in Jinan
-
摘要:
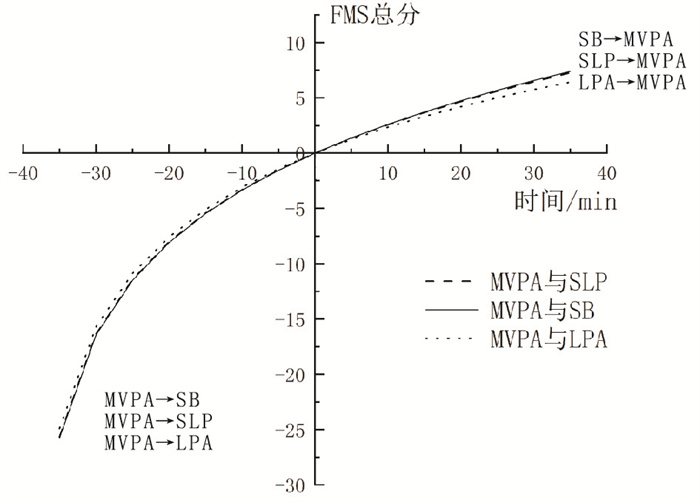
目的 使用成分数据分析法探究孤独症谱系障碍(ASD)儿童24 h活动与基本动作技能(FMS)的相关性,以及各活动等时替代后FMS的预期变化,为提高ASD儿童FMS水平提供参考依据。 方法 2023年10月至2024年4月,采用整群随机抽样方法,抽取济南市7所特殊教育学校301名6~10岁ASD儿童,使用加速度计和粗大肌肉动作发展测试调查其24 h活动和FMS水平,使用R软件对成分数据进行描述性统计、多元线性回归和等时替代效益分析。 结果 ASD儿童中高强度体力活动(MVPA)时间占比与FMS总分、移动技能和物体控制技能得分均呈正相关(β值分别为12.42,6.32,6.10,P值均 < 0.01)。将15 min MVPA替代睡眠(SLP),ASD儿童的FMS总分、移动技能和物体控制技能得分分别增加3.66,1.91,1.75分;将15 min MVPA替代久坐行为(SB),ASD儿童的FMS总分、移动技能和物体控制技能得分分别增加3.72,1.88,1.83分;将15 min MVPA替代低强度体力活动(LPA),ASD儿童的FMS总分、移动技能和物体控制技能得分分别增加3.32,1.57,1.74分(P值均 < 0.05)。此外,将15 min LPA替代SB,ASD儿童的移动技能得分增加0.28分(P < 0.05)。“剂量-效应”分析显示,MVPA替代SLP、SB、LPA均可提升ASD儿童的FMS水平,且MVPA与SLP、SB、LPA的相互替代效应具有不对称性;LPA替代SB可提升ASD儿童的移动技能水平。 结论 24 h活动中,MVPA、LPA时间对ASD儿童基本动作技能增加有积极作用。学校和家庭应优化ASD儿童24 h活动时间分配,以促进ASD儿童FMS水平的提升。 Abstract:Objective To study the association between 24 h activities and Fundamental Motor Skills (FMS) among children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using compositional data analysis, and the expected changes in FMS after isochronous substitution of each activity, in order to provide reference basis for improving FMS levels in children with ASD. Methods From October 2023 to April 2024, a total of 301 children with ASD aged 6-10 from 7 special education schools in Jinan, were investigated by cluster random sampling, and 24 h movement behaviors were calculated based on accelerator data. Test of Gross Motor Development-2 was used to assess FMS. R software was used to perform the descriptive statistical, multiple linear regression and isochronous substitution analyses. Results The proportion of moderate-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) in children with ASD was positively related with FMS scores, locomotor, and object control skills (β=12.42, 6.32, 6.10, P < 0.01). Reallocating 15 min from sleep (SLP) to MVPA resulted in respective increases of 3.66, 1.91, and 1.75 points in FMS scores, locomotor skills, and object control skills (P < 0.05). Reallocating 15 min from sedentary behavior (SB) to MVPA resulted in respective increases of 3.72, 1.88, and 1.83 points in FMS scores, locomotor skills, and object control skills (P < 0.05). Reallocating 15 min from light physical activity (LPA) to MVPA resulted in respective increases of 3.32, 1.57, and 1.74 points in FMS scores, locomotor skills, and object control skills (P < 0.05). Moreover, reallocating 15 min from SB to LPA resulted in an increase of 0.28 points in locomotor skills (P < 0.05). Dose-response analysis revealed that substitution of MVPA for SLP, SB, and LPA in children with ASD enhanced their FMS levels, and their substitution was asymmetrical; and substitution of LPA for SB enhanced locomotor skills level. Conclusions Among the 24 h movement behaviors, increasing the time spent on MVPA and LPA have positive impacts on the FMS of children with ASD. Schools and families should optimize the allocation of 24 h activity time in children with ASD, so as to promote the improvement of FMS levels of children with ASD. -
Key words:
- Motor activity /
- Autistic disorder /
- Motor skills /
- Child
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。2) 丁佳宁和原雅青为共同第一作者 -
表 1 济南市ASD儿童24 h活动时间与FMS的线性回归分析(β值,n=301)
Table 1. Linear regression analysis on 24 h activity time and FMS among children with ASD in Jinan(β, n=301)
自变量 FMS总分 移动技能 物体控制技能 SLP -6.58 -5.55 -1.02 SB -8.86 -3.97 -4.89 LPA 3.02 3.20 -0.18 MVPA 12.42** 6.32** 6.10** R2值 0.47 0.40 0.44 模型P值 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 注:**P<0.01。 表 2 济南市ASD儿童24 h活动时间15 min等时替代的FMS预测值变化[β值(95%CI),n=301]
Table 2. Changes in FMS prediction values of 15-minute isochronous substitution for 24 h activity time among children with ASD in Jinan[β(95%CI), n=301]
增加 减少 FMS总分 移动技能 物体控制技能 SLP SB 0.05(-0.67~0.78) -0.03(-0.47~0.41) 0.08(-0.28~0.45) SLP LPA -0.34(-1.08~0.39) -0.33(-0.78~0.11) -0.01(-0.38~0.36) SLP MVPA -5.42(-8.01~-2.82)* -2.80(-4.38~-1.22)* -2.61(-3.93~-1.29)* SB SLP -0.04(-0.77~0.68) 0.03(-0.41~0.48) -0.08(-0.45~0.28) SB LPA -0.39(-0.87~0.08) -0.30(-0.59~-0.01)* -0.09(-0.33~0.15) SB MVPA -5.47(-7.96~-2.97)* -2.77(-4.29~-1.25)* -2.69(-3.96~-1.42)* LPA SLP 0.33(-0.38~1.05) 0.32(-0.11~0.76) 0.01(-0.35~0.37) LPA SB 0.38(-0.07~0.84) 0.28(0.01~0.56)* 0.09(-0.13~0.33) LPA MVPA -5.09(-7.80~-2.37)* -2.48(-4.14~-0.83)* -2.60(-3.98~-1.22)* MVPA SLP 3.66(1.88~5.45)* 1.91(0.82~3.00)* 1.75(0.84~2.66)* MVPA SB 3.72(2.04~5.40)* 1.88(0.85~2.90)* 1.83(0.98~2.69)* MVPA LPA 3.32(1.39~5.24)* 1.57(0.40~2.74)* 1.74(0.76~2.72)* 注:*P<0.05。 -
[1] 五彩鹿自闭症研究院. 中国孤独症教育康复行业发展状况报告[M]. 北京: 华夏出版社, 2024.Wucai Deer Autism Research Institute. Report on the development of autism education and rehabilitation industry in China[M]. Beijing: Huaxia Publishing House, 2024. (in Chinese) [2] GANDOTRA A, KOTYUK E, SZEKELY A, et al. Fundamental movement skills in children with autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review[J]. Res Autism Spect Dis, 2020, 78: 1-14. [3] 原雅青, 王美娟, 原维佳, 等. 健康促进视角下智力障碍儿童基本动作技能干预研究进展[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2023, 49(6): 129-138.YUAN Y Q, WANG M J, YUAN W J, et al. Research progress on fundamental movement skill intervention studies in children with intellectual disability from health promotion perspective[J]. J Chengdu Sport Univ, 2023, 49(6): 129-138. (in Chinese) [4] 邱艳平, 王丽娟, 周玉兰, 等. 基于成分数据分析的24 h活动与儿童基本动作技能的关系[J]. 体育学刊, 2023, 30(1): 137-144.QIU Y P, WANG L J, ZHOU Y L, et al. The association between 24 h movement behaviors and fundamental motor skills of children based on compositional data analyses[J]. J Phys Educ, 2023, 30(1): 137-144. (in Chinese) [5] 原雅青, 刘洋, 丁佳宁. 布尼氏动作熟练度测试(BOT-2)在智力障碍儿童动作发展评估中的应用及对我国的启示[J]. 中国体育科技, 2019, 55(6): 14-20.YUAN Y Q, LIU Y, DING J N. Application of Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency-second edition (BOT-2) in assessing motor development among children with intellectual disability and its enlightenment to China[J]. China Sport Sci Technol, 2019, 55(6): 14-20. (in Chinese) [6] 尹龙, 李芳, 孙明云. 幼儿24 h活动行为对基本动作技能影响的成分等时替代效益[J]. 上海体育学院学报, 2023, 47(3): 90-100.YIN L, LI F, SUN M Y. Compositional isochronous substitution effect of 24-hour movement behaviors on fundamental movement skills of preschool children[J]. J Shanghai Univ Sport, 2023, 47(3): 90-100. (in Chinese) [7] THOMAS S, BARNETT L M, PAPADOPOULOS N, et al. How do physical activity and sedentary behaviour affect motor competence in children with autism spectrum disorder compared to typically developing children: a pilot study[J]. J Autism Dev Disord, 2021, 52(8): 3443-3455. [8] KETCHESON L, HAUCK J L, ULRICH D. The levels of physical activity and motor skills in young children with and without autism spectrum disorder, aged 2-5 years[J]. Autism, 2018, 22(4): 414-423. doi: 10.1177/1362361316683889 [9] TAYLOR S L, DOWNS S J, RUDD J, et al. Associations between motor competence and physical activity levels of children with intellectual disabilities and/or autism spectrum disorder: movement matters[J]. J Intellect Disabil, 2023: 17446295231203764. doi: 10.1177/17446295231203764 [10] DUMUID D, STANFORD T E, MARTIN-FERNÁNDEZ J A, et al. Compositional data analysis for physical activity, sedentary time and sleep research[J]. Stat Methods Med Res, 2018, 27(12): 3726-3738. [11] TALARICO R, JANSSEN I. Compositional associations of time spent in sleep, sedentary behavior and physical activity with obesity measures in children[J]. Int J Obes(Lond), 2018, 42(8): 1508-1514. [12] CHOI L, LIU Z, MATTHEWS C E, et al. Validation of accelerometer wear and nonwear time classification algorithm[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2011, 43(2): 357-364. [13] BARREIRA T V, SCHUNA J M, MIRE E F, et al. Identifying children's nocturnal sleep using 24 h waist accelerometry[J]. Med Sci Sport Exer, 2015, 47(5): 937-943. [14] EVENSON K R, CATELLIER D J, GILL K, et al. Calibration of two objective measures of physical activity for children[J]. J Sport, 2008, 26(14): 1557-1565. [15] PALMER K K, CHINN K M, SCOTT-ANDREWS K Q, et al. An intervention-related comparison of preschoolers' scores on the TGMD-2 and TGMD-3[J]. Percept Motor Skill, 2021, 128(4): 1354-1372. [16] 任园春, 李亚梦, 张茜, 等. 小学一年级学生动作发展测评方法探索[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2017, 38(8): 1248-1251. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2017.08.038REN Y C, LI Y M, ZHANG Q, et al. Exploration of evaluation methods for motor development of first-grade primary school students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2017, 38(8): 1248-1251. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2017.08.038 [17] 孟雪. 低年级智力障碍学生粗大动作技能学习的研究[D]. 北京: 北京体育大学, 2012.MENG X. A study on the learning of gross motor skills among lower grade students with intellectual disabilities[D]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University, 2012. (in Chinese) [18] DUMUID D, WAKE M, CLIFFORD S, et al. The association of the body composition of children with 24-hour activity composition[J]. J Pediatr, 2019, 2(8): 43-49. [19] 梁果, 王丽娟, 陈欢, 等. 24 h活动时间分布及替代与儿童身体质量指数的关系研究: 基于成分分析模型[J]. 体育科学, 2022, 42(3): 77-84.LIANG G, WANG L J, CHEN H, et al. The association of the body mass index of children with 24-hour activity composition and isotemporal substitution: compostional data analysis[J]. China Sport Sci, 2022, 42(3): 77-84. (in Chinese) [20] 张云婷, 马生霞, 陈畅, 等. 中国儿童青少年身体活动指南[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2017, 12(6): 401-409.ZHANG Y T, MA S X, CHEN C, et al. Physical activity guideline for Chinese children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Evid Based Pediatr, 2017, 12(6): 401-409. (in Chinese) [21] YUAN Y Q, DING J N, BI N, et al. Physical activity and sedentary behavior among children and adolescents with intellectual disabilities during the COVID-19 lockdown in China[J]. J Intell Disabil Res, 2021, 66(12): 913-923. [22] YIN J, SCHAAF C P. Autism genetics: an overview[J]. Prenat Diag, 2017, 37(1): 14-30. [23] STODDEN D F, GOODWAY J D, LANGENDORFER S J, et al. A developmental perspective on the role of motor skill competence in physical activity: an emergent relationship[J]. Quest, 2008, 60(2): 290-306. [24] BHAT A N, LANDA R J, GALLOWAY J C. Current perspectives on motor functioning in infants, children, and adults with autism spectrum disorders[J]. Phys Ther, 2011, 91(7): 1116-1129. [25] FÜZÉKI E, ENGEROFF T, BANZER W. Health benefits of light-intensity physical activity: a systematic review of accelerometer data of the national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES)[J]. Sport Med, 2017, 7(9): 1769-1793. -







 下载:
下载: