Systematic evaluation of eye tracking characteristics of emotional face in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder
-
摘要:
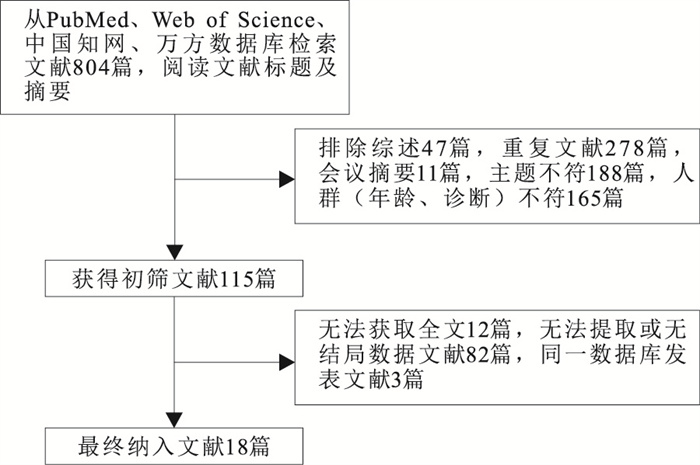
目的 应用眼动技术测量孤独症谱系障碍(ASD)儿童青少年对情绪面孔的注视时间,为ASD的诊断及干预提供潜在的客观指标。 方法 以PubMed、Web of Science、中国知网、万方数据为检索数据库,检索时间为建库至2024年4月1日,根据检索策略,检索3~18岁儿童青少年ASD的情绪面孔相关病例-对照研究,采用纽卡斯尔-渥太华量表(NOS)评估文献质量,使用State 17.0软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入18篇文献,研究样本包括ASD组361例,对照组413例,NOS评分均≥6分,研究质量较高。与对照组相比,ASD组对某些情绪面孔的注视时间更短(P值均<0.01),包括自制情绪面孔及同人种情绪面孔范式下高兴面孔的注视时间(SMD值分别为-1.05,-1.16),国内文献条件下中性面孔的注视时间(SMD=-1.00),临床诊断标准下生气面孔(SMD=-1.73)和悲伤面孔的注视时间(SMD=-1.29)及中国精神障碍分类与诊断标准第3版(CCMD-Ⅲ)标准下恐惧面孔的注视时间(SMD=-1.51)。 结论 ASD儿童青少年对某些情绪面孔的眼动指标存在异常,提示这些眼动指标可能是ASD诊断的预警指标。 Abstract:Objective To apply eye-tracking technology to measure the fixation duration of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) towards emotional faces, so as to provide potential objective indicators for the diagnosis and intervention of ASD. Methods Case-control studies related to emotional faces in ASD children and adolescents aged 3-18 years were searched in PubMed, Web of Science, CNKI and Wanfang, with a search period spanning from the inception of the databases to April 1, 2024. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was employed to assess the quality of the retrieved articles, and a Meta-analysis was conducted by Stata 17.0 software. Results A total of 18 articles were included, encompassing 361 participants in the ASD group and 413 in the control group. All studies scored ≥6 on the NOS, indicating high research quality. Compared to the control group, the ASD group demonstrated significantly shorter fixation duration (P < 0.01) towards specific emotional faces, including happy faces under the paradigm of self-made and same-ethnicity emotional faces (SMD=-1.05, -1.16), neutral faces in domestic literature (SMD= -1.00), angry and sad faces under clinical diagnosis criteria (SMD=-1.73, -1.29), and fearful faces under Chinese Classification and Diagnostic Criteria of Mental Disorders, Version 3 (CCMD-Ⅲ) (SMD=-1.51). Conclusion Children and adolescents with ASD exhibit abnormal eye-tracking indicators towards certain emotional faces, which may serve as early warning indicators for the diagnosis of ASD. -
Key words:
- Autistic disorder /
- Emotions /
- Face /
- Mental health /
- Meta-analysis /
- Child /
- Adolescent
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 1. Basic characteristics of included literature
第一作者及年份 国家 人数 年龄/岁 ASD诊断方法 眼动追踪装置 刺激材料 情绪面孔 NOS评分 病例组 对照组 病例组 对照组 Wieckowski(2017)[8] 美国 20 20 14.65±1.79 13.75±1.59 临床诊断/ADOS-2 Tobii T60 XL VT-KFER数据集 生气、厌恶、恐惧、悲伤、高兴、惊喜 8 Sahuquillo-Leal(2022)[9] 西班牙 27 25 12.81±2.79 13.05±4.41 DSM-IV SMI RED250 IAPS 高兴、悲伤、中性 8 Chien(2022)[10] 中国 3 14 4.75±1.76 4.89±1.24 DSM-V/ICD-10 Tobii X2-30 自制情绪识别游戏 悲伤、高兴、惊喜 7 Van Der Donck(2021)[11] 比利时 20 20 10.40±1.40 10.50±1.50 DSM-IV-TR/DSM-V Tobii X3-120 情绪识别任务 生气、厌恶、恐惧、悲伤、高兴、惊喜 9 Van Der Geest(2002)[12] 荷兰 17 17 12.60±2.10 10.10±1.30 DSM-IV/ADI-R SensoMotoric JAC-Fee和JACNeuf数据集 生气、高兴、惊喜、中性 9 马伟娜(2014)[13] 中国 15 15 13.80±1.42 12.90±0.46 临床诊断 Tobii 120 中国化情绪图片系统 生气、恐惧、悲伤、高兴 7 李丹丹(2021)[14] 中国 27 36 7.60±0.49 7.50±1.45 临床诊断 SMI iView X 中国化情绪图片系统 生气、悲伤、高兴、中性 6 李琳(2020)[15] 中国 30 30 4.98±1.17 5.20±0.50 DSM-V Tobii 4C 自制情绪视频 悲伤、高兴 7 林云强(2022)[16] 中国 15 15 11.07±1.83 5.50±0.82 DSM-V Tobii Pro X3-120 EPU 自制情绪面孔 生气、悲伤、高兴 8 余宥依(2019)[17] 中国 22 25 8.14±1.07 8.11±0.71 临床诊断/CARS SMI Iview X 自制情绪面孔 生气、恐惧、高兴 7 王广帅(2018)[18] 中国 31 51 4.37±2.00 5.02±0.63 DSM-V Tobii Eye Tracker 4C BU-3DFE数据库 恐惧、高兴 8 林云强(2014)[19] 中国 28 28 12.15±1.89 5.39±0.43 临床诊断 Tobii X120 自制情绪面孔 生气、高兴 7 陈晖(2012)[20] 中国 35 35 11.91±2.10 5.33±0.46 DSM-IV Tobii X120 自制情绪面孔 生气、高兴、中性 8 魏玲(2023)[21] 中国 21 23 8.11±1.03 8.19±0.69 临床诊断 SMI Iview X 自制情绪面孔 生气、恐惧、高兴 7 龙细连(2015)[22] 中国 6 6 一至四年级 一至四年级 临床诊断 Tobii 120 CFAPS 生气、厌恶、恐惧、悲伤、惊喜 6 胡清莹(2013)[23] 中国 25 27 9.16±2.90 8.41±1.42 CCMD-Ⅲ Tobii 120 自制情绪面孔 恐惧、高兴、中性 7 龙细连(2012)[24] 中国 6 6 8.83±1.72 7.83±1.17 CCMD-Ⅲ Tobii 120 CFAPS 中性 8 陈顺森(2011)[25] 中国 13 20 8.69±0.97 8.45±0.97 CCMD-Ⅲ Tobii 120 CFAPS 恐惧、高兴、中性 7 注: ADOS-2为第2版孤独症诊断观察时间表,DSM-IV为《诊断和统计手册》第4版,DSM-IV-TR为《诊断和统计手册》第4版修订版,DSM-V为《诊断和统计手册》第5版,ICD-10为《国际疾病分类》第10版,ADI-R为孤独症诊断访谈量表(修订版),CARS为儿童孤独症评定量表,CCMD-Ⅲ为中国精神障碍分类与诊断标准第3版。 -
[1] Ameican Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and satistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5[M]. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2013. [2] ZHOU H, XU X, YAN W, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in China: a nationwide multi-center population-based study among children aged 6 to 12 years[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2020, 36(9): 961-971. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00530-6 [3] MAENNER M J, WARREN Z, WILLIAMS A R, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years: autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2020[J]. MMWR Surveill Summ, 2023, 72(2): 1-14. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7202a1 [4] RAYNER K. Eye movements in reading and information processing[J]. Psychol Bull, 1978, 85(3): 618-660. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.85.3.618 [5] TREVISAN D A, BIRMINGHAM E. Are emotion recognition abilities related to everyday social functioning in ASD? A Meta-analysis[J]. Res Autism Spectr Disord, 2016, 32: 24-42. doi: 10.1016/j.rasd.2016.08.004 [6] ÄSBERG JOHNELS J, HOVEY D, ZÜRCHER N, et al. Autism and emotional face-viewing[J]. Autism Res, 2017, 10(5): 901-910. doi: 10.1002/aur.1730 [7] 艾飞玲, 胡葵茹, 石钰霖, 等. 基于纽卡斯尔-渥太华量表对中国吸烟队列研究文献的质量评价[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25(6): 722-729.AI F L, HU K R, SHI Y L, et al. Quality assessment of cohort studies literature on Chinese smoking by using Newcastle-Ottawa-Scale[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2021, 25(6): 722-729. (in Chinese) [8] WIECKOWSKI A T, WHITE S W. Eye-Gaze analysis of facial emotion recognition and expression in adolescents with ASD[J]. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol, 2017, 46(1): 110-124. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2016.1204924 [9] SAHUQUILLO-LEAL R, NAVALÓN P, MORENO-GIMÉNEZ A, et al. Attentional biases towards emotional scenes in autism spectrum condition: an eye-tracking study[J]. Res Dev Disabil, 2022, 120: 104124. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2021.104124 [10] CHIEN Y L, LEE C H, CHIU Y N, et al. Game-based social interaction platform for cognitive assessment of autism using eye tracking[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng, 2022. DOI: 10.109/TNSRE.2022.3232369. [11] VAN DER DONCK S, VETTORI S, DZHELYOVA M, et al. Investigating automatic emotion processing in boys with autism via eye tracking and facial mimicry recordings[J]. Autism Res, 2021, 14(7): 1404-1420. doi: 10.1002/aur.2490 [12] VAN DER GEEST J N, KEMNER C, VERBATEN M N, et al. Gaze behavior of children with pervasive developmental disorder toward human faces: a fixation time study[J]. J Child Psychol Psychiatry, 2002, 43(5): 669-678. doi: 10.1111/1469-7610.00055 [13] 马伟娜, 朱蓓蓓. 孤独症儿童的情绪共情能力及情绪表情注意方式[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(4): 528-539.MA W N, ZHU B B. Emotional empathy in children with autism spectrum disorder: evidence from biofeedback measurement and eye movements[J]. Acta Psychol Sinca, 2014, 46(4): 528-539. (in Chinese) [14] 李丹丹. 自闭症谱系障碍患者社会认知损伤特点及其rTMS靶向干预的机制研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2021.LI D D. A study of the characteristics of the social cognitive impairment and its mechanism of targeted rTMS intervention for autism spectrum disorder[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2021. (in Chinese) [15] 李琳. 不同情绪刺激下自闭症儿童视觉注意特点研究[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2020.LI L. Study on the visual attention characteristics of children with autism spectrum disorder in different emotional stimulation[D]. Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2020. (in Chinese) [16] 林云强, 申灵钰, 李良秀. 孤独症儿童对动态情境中面孔表情社交定向的警觉与维持特征[J]. 中国特殊教育, 2022(9): 66-76.LIN Y Q, SHEN L Y, LI L X. The characteristics of alertness and maintenance of social orientation of facial expressions in children with autism in dynamic situations[J]. Chin J Spec Educ, 2022(9): 66-76. (in Chinese) [17] 余宥依. 自闭症谱系障碍儿童对同龄和异龄面孔加工差异的眼动研究[D]. 福州: 福建医科大学, 2019.YU Y Y. The difference of face processing between the same age and different age face in children with autism spectrum disorder: an eye movement study[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Medical University, 2019. (in Chinese) [18] 王广帅, 陈靓影, 张坤. 基于多重因素混合设计和眼动追踪的自闭症谱系障碍儿童情绪面孔识别[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(31): 3204-3216.WANG G S, CHEN L Y, ZHANG K. The perception of emotional facial expressions by children with autism using hybrid multiple factorial design and eye-tracking[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2018, 63(31): 3204-3216. (in Chinese) [19] 林云强, 刘宝根, 陈冠杏. 面孔方向对自闭症儿童表情视觉搜索影响的眼动研究[J]. 中国特殊教育, 2014(5): 12, 25-32.LIN Y Q, LIU B G, CHEN G X. On the eye movement involving the effect of face directions on the visual expression search in children with autism[J]. Chin J Spec Educ, 2014(5): 12, 25-32. (in Chinese) [20] 陈晖. 自闭症儿童对社交信息选择性注意的实验研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2012.CHEN H. An experimental study of selective attention to social information in children with autism[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2012. (in Chinese) [21] 魏玲, 王静, 余宥依, 等. 自闭症谱系障碍儿童对面孔加工的同龄偏向效应[J]. 心理科学, 2023, 46(1): 72-81.WEI L, WANG J, YU Y Y, et al. The own-age bias in face processing in children with ASD[J]. J Psych Sci, 2023, 46(1): 72-81. (in Chinese) [22] 龙细连, 陈顺森, 白学军. 自闭症儿童对负性情绪面孔的注视特点[J]. 牡丹江师范学院学报(哲学社会科学版), 2015(1): 120-124.LONG X L, CHEN S S, BAI X J. Gaze characteristics of autistic children on negative emotional faces[J]. J Mudanjiang Norm Univ(Soc Sci Edit), 2015(1): 120-124. (in Chinese) [23] 胡清莹, 陈顺森, 龙细连, 等. 自闭症谱系障碍儿童对情绪面孔视觉加工的时程分析[J]. 漳州师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2013, 26(4): 127-132.HU Q Y, CHEN S S, LONG X L, et al. Time course of emotional faces visual processing in children with autism spectrum disorder[J]. J Zhangzhou Norm Univ(Natl Sci), 2013, 26(4): 127-132(in Chinese) [24] 龙细连. 自闭症儿童社交面孔加工特点研究[D]. 漳州: 漳州师范学院, 2012.LONG X L. A study on the characters of social face process in children with autism[D]. Zhangzhou: Zhangzhou Normal University, 2012. (in Chinese) [25] 陈顺森, 白学军, 沈德立, 等. 7~10岁自闭症谱系障碍儿童对情绪面孔的觉察与加工[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2011, 27(5): 449-458.CHEN S S, BAI X J, SHEN D L, et al. Emotional faces detection and processing of individuals with autism spectrum disorder aged 7-10[J]. Psychol Dev Educ, 2011, 27(5): 449-458. (in Chinese) [26] 孙文芳, 王馨悦, 王长生, 等. 专家运动员的视觉搜索特征: 基于眼动研究的Meta分析[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2018, 33(4): 321-328.SUN W F, WANG X Y, WANG C S, et al. Visual search feature of expert athletes: a Meta-analysis of eye-tracking studies[J]. J Tianjin Univ Sport, 2018, 33(4): 321-328. (in Chinese) [27] SATO W, KOCHIYAMA T, UONO S, et al. Atypical amygdala-neocortex interaction during dynamic facial expression processing in autism spectrum disorder[J]. Front Hum Neurosci, 2019, 13: 351. [28] VOLKMAR F R, LORD C, BAILEY A, et al. Autism and pervasive developmental disorders[J]. J Child Psychol Psychiatry, 2004, 45(1): 135-170. [29] LI Y, TSE C S. Interference among the processing of facial emotion, face race, and face gender[J]. Front Psychol, 2016, 7: 1700. [30] HUDAC C M, SANTHOSH M, CELERIAN C, et al. The role of racial and developmental experience on emotional adaptive coding in autism spectrum disorder[J]. Dev Neuropsychol, 2021, 46(2): 93-108. [31] 陈倩, 静进. 孤独症谱系障碍面孔情绪识别的研究进展[J]. 教育生物学杂志, 2021, 9(5): 341-346.CHEN Q, JING J. Advances in facial emotion recognition in autism spectrum disorder[J]. J Bio Educ, 2021, 9(5): 341-346. (in Chinese) [32] NAYAR K, KANG X, WINSTON M, et al. A cross-cultural study of visual attention in autism spectrum disorder[J]. Child Neuropsychol, 2023, 29(3): 413-444. [33] 杜美玲, 郭岚敏, 邢晓, 等. 孤独症谱系障碍成年期转归及影响因素的研究进展[J]. 中华精神科杂志, 2023, 56(4): 311-316.DU M L, GUO L M, XING X, et al. Progress in the adult outcome and influencing factors of autism spectrum disorder[J]. Chin J Psychiatry, 2023, 56(4): 311-316. (in Chinese) [34] LOTT-SANDKAMP L L, SPENGLER F B, HEINRICHS M. Impairment in reading negative social cues extends beyond the face in autism[J]. J Psychiatr Res, 2023, 164: 350-356. [35] THABTAH F, PEEBLES D. Early autism screening: a comprehensive review[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2019, 16(18): 3502. -







 下载:
下载: