Executive functions of obese adolescents
-
摘要:
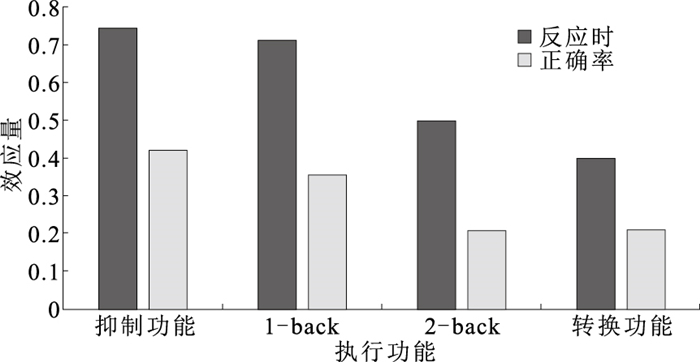
目的 探究肥胖青少年执行功能表征状况, 为肥胖青少年执行功能提升的干预提供参考依据。 方法 于2023年3—4月在太原市的2所中学选取1 227名13~18岁的青少年作为方便样本。采用Flanker任务、N-back任务和More-odd shifting任务分别对61名肥胖青少年和70名正常体重青少年的执行功能各子功能(刷新功能、转移功能、抑制功能)进行比较。采用独立样本t检验进行组间比较, 使用Cohen's d检验计算两组青少年执行功能的组间差异。 结果 与体重正常组相比, 肥胖组的抑制功能、刷新功能和转换功能的反应时均高于体重正常组(t值分别为4.26, 4.06, 1.92, 2.26);抑制功能(0.91±0.09)和1-back(0.73±0.24)的正确率也均低于体重正常组(0.94±0.05, 0.83±0.21), 差异有均统计学意义(t值分别为-2.04, -2.04, P值均 < 0.05)。肥胖青少年在抑制功能和刷新功能1-back中表现出中等缺陷效应量(d值分别为0.746, 0.712), 在2-back和转换功能中表现出较小的缺陷效应量(d值分别为0.497, 0.398)。 结论 肥胖青少年具有明显的执行功能缺陷, 但各子功能的缺陷程度不同, 其中抑制功能是肥胖青少年执行功能核心缺陷成分。 Abstract:Objective To explore of executive function in obese adolescents, so as to provide a reference for executive function enhancement intervention in obese adolescents. Methods A convenience sample of 1 227 adolescents aged 13-18 years was selected from 2 secondary schools in Taiyuan City during March-April 2023. The Flanker task, N-back task and More-odd shifting task was used to compare the different subfunctions of executive function (refreshing function, shifting function, inhibiting function) of 61 obese adolescents and 70 normal-weight adolescents. Independent samples t-tests was used for between-group comparisons and Cohen's d-tests was used to calculate between-group differences in executive function between the two groups of adolescents. Results Compared with the group of normal weight, time responses of the inhibitory function, the refreshing function and the shifting function in the obese group were significantly longer than those in the normal weight group (t=4.26, 4.06, 1.92, 2.26, P < 0.05); inhibitory function (0.91±0.09) and 1-back (0.73±0.24) were also significantly less correct than in the normal weight group (0.94±0.05, 0.83±0.21) (t=-2.04, -2.04, P < 0.05). Obese adolescents showed moderate adverse effect sizes in the inhibition function (d=0.746, 0.712) and the refresh function 1-back, and smaller adverse effect sizes in the refresh function 2-back and the conversion function(d=0.497, 0.398). Conclusion Obese adolescents have significant executive function deficits, but the degree of adverse varies across sub-functions, with inhibitory function being the core deficit component of executive function in obese adolescents. -
Key words:
- Obesity /
- Executive function /
- Mental health /
- Adolescent
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 肥胖组和体重正常组青少年的抑制功能比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of inhibitory function performance of adolescents in the obese and normal weight groups(x±s)
组别 人数 反应时/ms 正确率 不一致 一致 抑制功能 不一致 一致 抑制功能 体重正常组 70 555.12±70.09 540.26±71.09 14.86±20.27 0.94±0.06 0.94±0.06 0.94±0.05 肥胖组 61 552.28±57.27 522.55±56.20 29.73±19.55 0.92±0.09 0.91±0.10 0.91±0.09 t值 0.25 1.57 -4.26 1.95 1.88 2.04 P值 0.80 0.12 <0.01 0.05 0.06 0.04 表 2 肥胖组和体重正常组青少年的刷新功能比较(x±s)
Table 2. Comparison of refreshment function performance of adolescents in the obese and normal weight groups(x±s)
组别 人数 反应时/ms 正确率 1-back 2-back 1-back 2-back 体重正常组 70 888.38±286.57 1 126.20±287.43 0.81±0.21 0.64±0.19 肥胖组 61 1 088.75±275.76 1 285.44±355.16 0.73±0.24 0.60±0.20 t值 -4.06 -1.92 2.04 1.22 P值 <0.01 0.06 0.04 0.23 表 3 肥胖组和体重正常组青少年的转换功能比较(x±s)
Table 3. Comparison of shifting function performance of adolescents in the obese and normal weight groups(x±s)
组别 人数 反应时/ms 正确率 不转换 转换 转换功能 不转换 转换 转换功能 体重正常组 70 660.41±118.02 990.75±211.37 323.12±134.71 0.93±0.07 0.85±0.13 0.89±0.09 肥胖组 61 679.69±113.13 1 002.80±168.82 380.34±153.18 0.92±0.08 0.82±0.15 0.87±0.10 t值 0.95 0.36 -2.26 1.30 1.05 1.29 P值 0.34 0.72 0.03 0.20 0.30 0.20 -
[1] AHMED S F, KUHFELD M, WATTS T W, et al. Preschool executive function and adult outcomes: a developmental cascade model[J]. Dev Psychol, 2021, 57(12): 2234-2249. doi: 10.1037/dev0001270 [2] DEER L K, HASTINGS P D, HOSTINAR C E. The role of childhood executive function in explaining income disparities in long-term academic achievement[J]. Child Dev, 2020, 91(5): e1046-e1063. [3] LOWE C J, MORTON J B, REICHELT A C. Adolescent obesity and dietary decision making-a brain-health perspective[J]. Lancet Child Adolesc Health, 2020, 4(5): 388-396. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(19)30404-3 [4] RONAN L, ALEXANDER-BLOCH A, FLETCHER P C. Childhood obesity, cortical structure, and executive function in healthy children[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2020, 30(4): 2519-2528. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhz257 [5] PAN X F, WANG L, PAN A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2021, 9(6): 373-392. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00045-0 [6] MUST A, STRAUSS R S. Risks and consequences of childhood and adolescent obesity[J]. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord, 1999, 23(Suppl 2): S2-S11. [7] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查: WS/T 586—2018[S]. 2018-08-01.Nation Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC. Screening for overweight and obesity among school-age children and adolescents: WS/T 586-2018[S]. 2018-08-01. (in Chinese) [8] LIU Y, ZHANG F, GAN L, et al. Associations between waist circumference and executive function among Chinese Tibetan adolescents living at high altitude[J]. Front Nutr, 2023, 10: 996785. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.996785 [9] SULLIVAN G M, FEINN R. Using effect size-or why the p value is not enough[J]. J Grad Med Educ, 2012, 4(3): 279-282. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-12-00156.1 [10] MEO S A, ALTUWAYM A A, ALFALLAJ R M, et al. Effect of obesity on cognitive function among school adolescents: a cross-sectional study[J]. Obes Facts, 2019, 12(2): 150-156. doi: 10.1159/000499386 [11] 解淳, 张育恺, 崔晨, 等. 肥胖青少年多层面认知功能特点的研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2017, 32(1): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY201701012.htmXIE C, ZHANG Y K, CUI C, et al. A study of multifaceted cognitive function characteristics in obese adolescents[J]. J Tianjin Sports Inst, 2017, 32(1): 68-72. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY201701012.htm [12] 李焕玉, 陈爱国, 李卫东, 等. 小学生体质量指数对执行功能的影响[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2016, 37(12): 1834-1836, 1840. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2016.12.023LI H Y, CHEN A G, LI W D, et al. Effects of body mass index on executive function in elementary school students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2016, 37(12): 1834-1836, 1840. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2016.12.023 [13] GABAY A, LONDON S, YATES K F, et al. Does obesity-associated insulin resistance affect brain structure and function of adolescents differentially by sex?[J]. Psychiatry Res Neuroimag, 2022, 319: 111417. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2021.111417 [14] LIZARBE B, CAMPILLO B, GUADILLA I, et al. Magnetic resonance assessment of the cerebral alterations associated with obesity development[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2020, 40(11): 2135-2151. doi: 10.1177/0271678X20941263 [15] LEE S H, ZABOLOTNY J M, HUANG H, et al. Insulin in the nervous system and the mind: functions in metabolism, memory, and mood[J]. Mol Metab, 2016, 5(8): 589-601. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2016.06.011 [16] RHEA E M, SALAMEH T S, LOGSDON A F, et al. Blood-brain barriers in obesity[J]. AAPS J, 2017, 19(4): 921-930. doi: 10.1208/s12248-017-0079-3 [17] MORENO-LOPEZ L, CONTRERAS-RODRIGUEZ O, SORIANO-MAS C, et al. Disrupted functional connectivity in adolescent obesity[J]. Neuroimag Clin, 2016, 12: 262-268. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.07.005 [18] LIKHITWEERAWONG N, LOUTHRENOO O, BOONCHOODUANG N, et al. Bidirectional prediction between weight status and executive function in children and adolescents: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of longitudinal studies[J]. Obes Rev, 2022, 23(8): e13458. doi: 10.1111/obr.13458 [19] GUXENS M, MENDEZ M A, JULVEZ J, et al. Cognitive function and overweight in preschool children[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2009, 170(4): 438-446. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwp140 [20] LISTER N B, BAUR L A, FELIX J F, et al. Child and adolescent obesity[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2023, 9(1): 24. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00435-4 [21] LIANG J, MATHESON B, KAYE W, et al. Neurocognitive correlates of obesity and obesity-related behaviors in children and adolescents[J]. Int J Obes, 204, 38(4): 494-506. [22] LIN Q, JIANG Y, SUN X, et al. Weight spectrum and executive function in adolescents: the moderating role of negative emotions[J]. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health, 2022, 16(1): 34. doi: 10.1186/s13034-022-00468-9 [23] MAMROT P, HANĈ T. The association of the executive functions with overweight and obesity indicators in children and adolescents: a literature review[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2019, 107: 59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.08.021 [24] GROPPE K, ELSNER B. Executive function and weight status in children: a one-year longitudinal perspective[J]. Child Neuropsychol, 2017, 23(2): 129-147. doi: 10.1080/09297049.2015.1089981 [25] WESTWATER ML, VILAR-LÓPEZ R, ZIAUDDEEN H, et al. Combined effects of age and BMI are related to altered cortical thickness in adolescence and adulthood[J]. Dev Cogn Neurosci, 2019, 40: 100728. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2019.100728 [26] 刘培飞, 张乾一, 王琇, 等. 抑制控制的理论研究概述[J]. 教育观察, 2019, 8(9): 25-26, 34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGN201909009.htmLIU P F, ZHANG Q Y, WANG X, et al. An overview of theoretical research on inhibitory control[J]. Survey Educ, 2019, 8(9): 25-26, 34. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGN201909009.htm -







 下载:
下载: