Performance of four simplified screening methods of elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents
-
摘要:
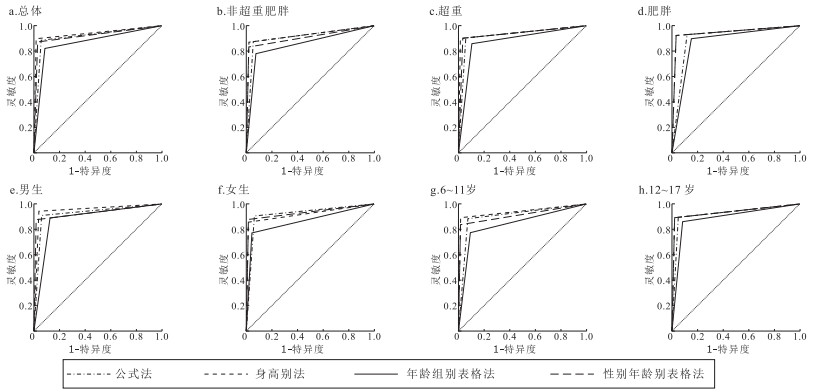
目的 根据中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)对儿童青少年血压偏高常用的4种简化筛查方法进行效果评价,为儿童青少年血压异常的早期识别提供参考依据。 方法 于2021年10—11月,采用分层整群随机抽样方法对山西省某市5 211名儿童青少年进行体质监测,将中国高血压防治指南作为金标准,分别计算公式法、身高别法、年龄组别表格法和性别年龄别表格法筛查血压偏高的灵敏度、特异度、曲线下面积(AUC)和Kappa值等指标评价筛检效果。 结果 金标准、公式法、身高别法、年龄组别表格法和性别年龄别表格法筛查儿童青少年血压偏高率分别为21.9%,24.0%,21.1%,24.5%和20.2%。公式法、性别年龄别表格法与金标准判定结果差异均无统计学意义(χ2值分别为1.12,1.41,P值均>0.05),而身高别法和年龄组别表格法与金标准判定结果差异均有统计学意义(χ2值分别为20.39,67.09,P值均<0.05)。身高别法AUC最大,为0.94(95%CI=0.93~0.95);年龄组别表格法AUC最小,为0.87(95%CI=0.86~0.88)。身高别法和性别年龄别表格法的Kappa值分别为0.89,0.89,均大于0.85,与金标准的筛查效果更吻合。分性别、年龄和体质量指数(BMI)情况比较时,男生、6~11岁和非超重肥胖组的筛查效果与总体一致,而女生、12~17岁、超重组和肥胖组的筛查效果与总体不同。年龄组别表格法的AUC(0.87)、Kappa值(0.71)和灵敏度(82.33%)均最低,筛查效果最差。 结论 身高别法筛查儿童青少年血压异常效果更好,该方法适用于儿童青少年血压异常的早期识别和自我检测。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the performance of four simplified screening methods of elevated blood pressure commonly used among children and adolescents according to Chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension (revised in 2018), so as to provide a reference for the early detection of the elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents. Methods Stratified cluster random sampling method was used to monitor the physical fitness of 5 211 children and adolescents in a city of Shanxi Province from October to November 2021. Chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension was considered as gold standard, and sensitivity, specificity, area under the curve (AUC) and Kappa value were calculated to evaluate the screening effectiveness of formula method, height-specific method, age group-specific method, sex and age-specific method for screening elevated blood pressure. Results The detection rates of elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents screened by gold standard, formula method, height-specific method, age group-specific method, sex and age-specific method were 21.9%, 24.0%, 21.1%, 24.5% and 20.2%, respectively. There was no significant difference between prevalence of elevated blood pressure screened by formula method, sex and age-specific method and gold standard(χ2=1.21, 1.41, P>0.05), whereas height-specific method and age group-specific method had significant differences with gold standard (χ2=20.39, 67.09, P < 0.05). AUC was the largest for height-specific method [0.94(95%CI=0.93-0.95)], and the smallest for age group-specific method [0.87(95%CI=0.86-0.88)]. The Kappa values of height-specific method (0.89) and sex and age-specific method (0.89) were both greater than 0.85, which were more consistent with the screening effectiveness of gold standard. When comparing by sex, age and body mass index (BMI), the screening effectivenesses were consistent with the overall in boys, 6-11 years and normal body weight groups, while the screening effectivenesses were different in girls, 12-17 years, overweight and obese groups. The AUC (0.87), Kappa value (0.71) and sensitivity (82.33%) of age group-specific method were the lowest and the screening effectiveness was the worst. Conclusion Height-specific method is more effective and can be used for early identification and self-detection of blood pressure abnormalities among children and adolescents. -
Key words:
- Blood pressure /
- Reference standards /
- Area under curve /
- Child /
- Adolescent
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 不同性别儿童青少年基本特征比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of basic characteristics among children and adolescents by sex (x±s)
性别 人数 身高/cm 体重/kg BMI/
(kg·m-2)SBP/
mmHgDBP/
mmHg男 2 627 150.4±17.7 47.3±18.3 20.1±4.3 110.0±14.1 68.7±8.8 女 2 584 147.1±14.4 44.2±14.7 19.8±4.0 105.6±12.4 69.1±8.5 t值 188.60 98.46 5.36 38.02 -3.06 P值 <0.01 <0.01 0.02 <0.01 0.08 注:1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。 表 2 4种简化方法与金标准筛检儿童青少年血压偏高检出率
Table 2. Detection rates of elevated blood pressure in children and adolescents by four simplified methods and gold standard
性别 人数 金标准 公式法 身高别法 年龄组别表格法 性别年龄别表格法 男 2 627 590(22.5) 648(24.7) 620(23.6) 772(29.4) 547(20.8) 女 2 584 553(21.4) 605(23.4) 478(18.5) 507(19.6) 504(19.5) 合计 5 211 1 143(21.9) 1 253(24.0) 1 098(21.1) 1 279(24.5) 1 051(20.2) 注:()内数字为检出率/%。 表 3 不同性别儿童青少年4种简化方法筛检血压偏高的效果比较
Table 3. Comparion of effect of four simplified methods for screening elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents by sex
性别 方法 AUC值(95%CI) 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 阳性预测值/% 阴性预测值/% Kappa值 男 公式法 0.92(0.91~0.94) 90.00 94.26 81.94 97.02 0.81 (n=2 627) 身高别法 0.95(0.94~0.96) 93.56 96.66 89.03 98.11 0.89 年龄组别表格法 0.88(0.86~0.90) 88.14 87.63 67.36 96.23 0.68 性别年龄别表格法 0.93(0.92~0.95) 87.97 98.63 94.88 96.49 0.89 女 公式法 0.92(0.90~0.93) 88.61 94.34 80.99 96.82 0.80 (n=2 584) 身高别法 0.92(0.90~0.94) 84.63 99.51 97.91 95.96 0.89 年龄组别表格法 0.86(0.84~0.88) 76.13 95.77 83.04 93.65 0.74 性别年龄别表格法 0.93(0.91~0.94) 86.44 98.72 94.84 96.39 0.88 合计 公式法 0.92(0.91~0.93) 89.33 94.30 81.48 96.92 0.81 (n=5 211) 身高别法 0.94(0.93~0.95) 89.24 98.08 92.90 97.01 0.89 年龄组别表格法 0.87(0.86~0.88) 82.33 91.69 73.57 94.86 0.71 性别年龄别表格法 0.93(0.92~0.94) 87.23 98.67 94.86 96.49 0.89 表 4 不同年龄组儿童青少年4种简化方法筛检儿童青少年血压偏高的效果比较
Table 4. Comparion of effect of four simplified methods for screening elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents by age
年龄/岁 方法 AUC值(95%CI) 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 阳性预测值/% 阴性预测值/% Kappa值 6~11 公式法 0.91(0.89~0.93) 89.27 95.81 76.43 97.04 0.77 (n=2 368) 身高别法 0.94(0.93~0.96) 89.68 98.56 94.26 97.31 0.90 年龄组别表格法 0.85(0.82~0.87) 78.14 91.20 70.05 94.06 0.67 性别年龄别表格法 0.92(0.90~0.94) 85.02 98.93 95.46 96.16 0.88 12~17 公式法 0.93(0.91~0.94) 89.37 95.62 85.80 96.82 0.84 (n=2 843) 身高别法 0.93(0.92~0.95) 88.91 97.68 91.88 96.75 0.88 年龄组别表格法 0.89(0.87~0.91) 85.52 92.12 76.24 95.56 0.74 性别年龄别表格法 0.94(0.92~0.95) 88.91 98.45 94.44 96.77 0.89 表 5 不同BMI组儿童青少年4种简化方法筛查儿童青少年血压偏高效果比较
Table 5. Comparion of effect of four simplified methods for screening elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents by BMI
BMI 方法 AUC值(95%CI) 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 阳性预测值/% 阴性预测值/% Kappa值 非超重肥胖组 公式法 0.91(0.90~0.93) 87.52 95.06 79.48 97.21 0.79 (n=3 530) 身高别法 0.93(0.92~0.95) 87.68 98.48 92.65 97.34 0.88 年龄组别表格法 0.86(0.84~0.88) 78.04 93.23 71.59 95.11 0.69 性别年龄别表格法 0.91(0.90~0.93) 83.73 98.93 94.47 96.53 0.87 超重组 公式法 0.93(0.90~0.95) 90.61 94.86 86.38 96.56 0.84 (n=926) 身高别法 0.94(0.92~0.96) 90.20 97.65 93.25 96.52 0.89 年龄组别表格法 0.88(0.85~0.91) 85.71 90.02 75.54 94.60 0.73 性别年龄别表格法 0.95(0.92~0.97) 90.20 98.97 96.93 96.56 0.91 肥胖组 公式法 0.91(0.88~0.93) 92.45 88.98 81.94 95.61 0.79 (n=755) 身高别法 0.94(0.92~0.96) 92.08 96.33 93.13 95.74 0.89 年龄组别表格法 0.87(0.84~0.90) 89.43 84.90 76.21 93.69 0.72 性别年龄别表格法 0.95(0.93~0.97) 92.83 96.74 93.89 96.15 0.90 -
[1] 国家心血管病中心. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022[M]. 北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社, 2023.National Center for Cardiovascular Disease. China cardiovascular health and disease report 2022[M]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press, 2023. (in Chinese) [2] MOZAFFARIAN D, BENJAMIN E J, GO A S, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2015, 131(4): e299-e322. [3] HAO G, WANG X, TREIBER F A, et al. Blood pressure trajectories from childhood to young adulthood associated with cardiovascular risk: results from the 23-year longitudinal Georgia stress and heart study[J]. Hypertension, 2017, 69(3): 435-442. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08312 [4] DONG B, MA J, WANG H J, et al. The association of overweight and obesity with blood pressure among Chinese children and adolescents[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2013, 26(6): 437-444. [5] 席波, 宋逸, 马军. 预防成年人心血管疾病应重视儿童期危险因素防控[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(9): 1428-1432.XI B, SONG Y, MA J. Prevention of cardiovascular disease in adulthood should attach importance to related risk factors in childhood[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2020, 41(9): 1428-1432. (in Chinese) [6] DONG Y, MA J, SONG Y, et al. Secular trends in blood pressure and overweight and obesity in Chinese boys and girls aged 7 to 17 years from 1995 to 2014[J]. Hypertension, 2018, 72(2): 298-305. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11291 [7] 范晖, 闫银坤, 米杰. 中国3~17岁儿童性别、年龄别和身高别血压参照标准[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2017, 25(5): 428-435. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201705010.htmFAN H, YAN Y K, MI J. Updating blood pressure references for Chinese children aged 3-17 years[J]. Chin J Hypertens, 2017, 25(5): 428-435. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201705010.htm [8] National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents[J]. Pediatrics, 2004, 114(2): 555-576. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.2.S2.555 [9] LURBE E, AGABITI-ROSEI E, CRUICKSHANK J K, et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents[J]. J Hypertens, 2016, 34(10): 1887-1920. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001039 [10] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会, 高血压联盟(中国), 中华医学会心血管病学分会, 等. 中国高血压防治指南2018年修订版[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2019, 19(1): 1-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-816X.2019.01.001Chinese Hypertension Prevention and Treatment Guidelines Revision Committee, Hypertension Alliance (China), Chinese Medical Association Cardiovascular Branch, et al. Chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension revised in 2018[J]. Prev Treat Cardiovasc Dis, 2019, 19(1): 1-44. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-816X.2019.01.001 [11] CHIOLERO A, PARADIS G, SIMONETTI G D, et al. Absolute height-specific thresholds to identify elevated blood pressure in children[J]. J Hypertens, 2013, 31(6): 1170-1174. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32836041ff [12] SOMU S, SUNDARAM B, KAMALANATHAN A N. Early detection of hypertension in general practice[J]. Arch Dis Child, 2003, 88(4): 302. doi: 10.1136/adc.88.4.302 [13] MA C, KELISHADI R, HONG Y M, et al. Performance of eleven simplified methods for the identification of elevated blood pressure in children and adolescents[J]. Hypertension, 2016, 68(3): 614-620. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07659 [14] STABOULI S, NIKA T, KOLLIOS K, et al. Performance of simplified tables for high blood pressure screening in a European pediatric population[J]. J Hypertens, 2019, 37(5): 917-922. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001972 [15] MOURATO F A, LIMA FILHO J L, MATTOS SDA S. Comparison of different screening methods for blood pressure disorders in children and adolescents[J]. J Pediatr (Rio J), 2015, 91(3): 278-283. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2014.08.008 [16] 孟玲慧, 侯冬青, 单馨影, 等. OMRON HEM-7012电子血压计测量儿童青少年血压的准确性评价[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2013, 21(2): 158-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201302023.htmMENG L H, HOU D Q, SHAN X Y, et al. Accuracy evaluation of OMRON HEM-7012 electronic sphygmomanometers in measuring blood pressure of children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Hypertens, 2013, 21(2): 158-162. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201302023.htm [17] 范晖, 闫银坤, 米杰. 中国3~17岁儿童血压简化标准的研制[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2017, 25(5): 436-440. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201705011.htmFAN H, YAN Y K, MI J. Establishing the user-friendly screening criteria for elevated blood pressure in Chinese children aged 3-17 years[J]. Chin J Hypertens, 2017, 25(5): 436-440. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201705011.htm [18] 侯亚苹, 刘琴, 羊柳, 等. 儿童青少年身高别高血压筛查界值简化表的制定与验证[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2019, 53(7): 701-705.HOU Y P, LIU Q, YANG L, et al. Development and validation of a simplified height-specific blood pressure cutoffs table for screening hypertension in Chinese children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2019, 53(7): 701-705. (in Chinese) [19] 米杰, 王天有, 孟玲慧, 等. 中国儿童青少年血压参照标准的研究制定[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2010, 5(1): 4-14.MI J, WANG T Y, MENG L H, et al. Development of blood pressure reference standard for Chinese children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Evid-Based Pediatr, 2010, 5(1): 4-14. (in Chinese) [20] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查: WS/T 586—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC. Screening for overweight and obesity among school-age children and adolescents: WS/T 586-2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018. (in Chinese) [21] HU J, DING Z, HAN D, et al. Prevalence of hypertension and related risk factors among children and adolescents at three separate visits: a large school-based study in China[J]. Front Pediatr, 2022, 10: 976317. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.976317 [22] SONG P, ZHANG Y, YU J, et al. Global prevalence of hypertension in children: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2019, 173(12): 1154-1163. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.3310 [23] WANG L, SONG L, LIU B, et al. Trends and status of the prevalence of elevated blood pressure in children and adolescents in China: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Curr Hypertens Rep, 2019, 21(11): 88. doi: 10.1007/s11906-019-0992-1 [24] 胡佳, 韩迪, 海波, 等. 基于中国高血压防治指南的简化方法筛查苏州市儿童青少年血压偏高的效果[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 5(6): 739-744. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ202106021.htmHU J, HAN D, HAI B, et al. Evaluation of simplified methods based on Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension for screening high blood pressure among children and adolescents in Suzhou[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2021, 5(6): 739-744. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ202106021.htm [25] 张媛媛, 杨丽丽, 席波. 济南市城区年龄6~17岁儿童青少年血压偏高现状[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2018, 26(1): 72-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201801029.htmZHANG Y Y, YANG L L, XI B. Prevalence of elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents aged 6-17 years in urban region of Jinan[J]. Chin J Hypertens, 2018, 26(1): 72-77. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ201801029.htm [26] 黄贵民, 侯冬青, 高爱钰, 等. 北京市6~16岁儿童青少年睡眠状况与高血压的关联分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2018, 52(11): 1136-1139.HUANG G M, HOU D Q, GAO A Y, et al. The analysis of the association of sleep with high blood pressure among children and adolescents aged 6-16 years in Beijing[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2018, 52(11): 1136-1139. (in Chinese) [27] 吉晓理, 罗江宾, 吉晓天, 等. 三亚地区儿童青少年高血压患病现状及其相关因素分析[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 19(10): 1731-1733. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202110034.htmJI X L, LUO J B, JI X T, et al. Analysis of the current status of hypertension among children and adolescents in Sanya and its related factors[J]. Chin J Integr Med Cardio-Cerebrovasc Dis, 2021, 19(10): 1731-1733. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202110034.htm [28] REGNAULT N, KLEINMAN K P, RIFAS-SHIMAN S L, et al. Components of height and blood pressure in childhood[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2014, 43(1): 149-159. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyt248 [29] CHEN X, WANG Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: a systematic review and Meta-regression analysis[J]. Circulation, 2008, 117(25): 3171-3180. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.730366 [30] LIANG Y, HOU D, SHAN X, et al. Cardiovascular remodeling relates to elevated childhood blood pressure: Beijing blood pressure cohort study[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2014, 177(3): 836-839. [31] LURBE E. Hypertension and target organ damage in children and adolescents[J]. J Hypertens, 2007, 25(10): 1998-2000. [32] MIR S, SOZERI B, DEVECI M, et al. Cardiovascular functional and structural changes in children with primary hypertension[J]. Minerva Pediatr, 2016, 68(1): 27-35. [33] FULY J T, GIOVANINNI N P, MARCATO D G, et al. Evidence of underdiagnosis and markers of high blood pressure risk in children aged 6 to 13 years[J]. J Pediatr(Riol), 2014, 90(1): 65-70. -







 下载:
下载: