Effects of physical activities on cognitive flexibility of Chinese children and adolescents: a Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
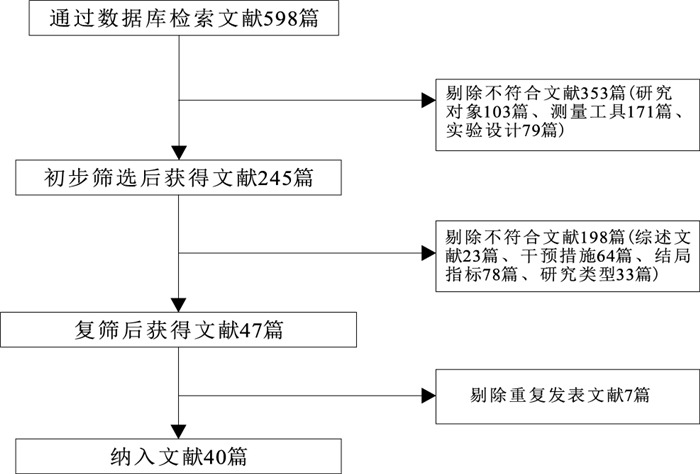
目的 系统评价体育活动对中国儿童青少年认知灵活性的影响,为中国学校体育和健康教育领域的相关研究工作提供循证依据。 方法 检索中国知网数据库、维普数据库、万方数据库,Web of ScienceTM核心合集、SPORTDiscus数据库、PubMed数据库、Springer link数据库、Science Direct数据库,收集数据库建库至2021年6月1日的所有文献,共纳入40篇文献。 结果 纳入文献共包括3 262个研究样本,其中实验组1 674人,对照组1 588人。Meta分析结果显示,文献总效应WMD值为121.11,Z=12.37,95%CI=101.91~140.30(P<0.01);学龄儿童亚分组包括32篇文献,合并效应WMD值为126.05,Z=10.42,95%CI=102.34~149.76(P<0.01);青少年亚分组包括8篇文献,合并效应WMD值为104.00,Z=9.72,95%CI=83.02~124.98(P<0.01),体育活动对中国儿童青少年的认知灵活性具有正向影响。采用Meta回归法对学龄儿童组的异质性来源进行检验,结果显示儿童类型t=12.77,95%CI=28.79~39.74(P < 0.01),不同儿童类型是Meta分析学龄儿童亚分组异质性的来源,可解释55.39%的异质性来源。Egger回归分析结果显示,t=0.47,95%CI=-1.48~2.37(P=0.64),纳入的文献不存在发表偏倚。 结论 儿童青少年时期是认识灵活性发展的灵敏期,在此期间进行的体育活动对儿童青少年认知灵活性具有显著的促进作用。 Abstract:Objective The purpose of this paper is to systematically review the impact of physical activities on cognitive flexibility of children and adolescents in China, and to provide evidence-based evidence for relevant research on improving cognitive flexibility of children and adolescents by using physical activities. Methods CNKI, VIP, Wanfang Data, Web of Science, SPORTDiscus, PubMed, Springer link and Science Direct database were searched. The time span of 40 articles collected in this study was from the establishment of the database to December 31, 2020. Results A total of 3 262 research samples were included in 40 articles, including 1 674 in the experimental group and 1 588 in the control group. Meta-analysis showed that the total effect WMD value of literature was 121.11, Z=12.37, 95%CI=101.91-140.30 (P < 0.01); the sub group of school-age children included 32 literatures, and the combined effect WMD value was 126.05, Z=10.42, 95%CI=102.34-149.76 (P < 0.01); the sub group of adolescents included 8 literatures, the combined effect WMD value was 104.00, Z=9.72, 95%CI=83.02-124.98 (P < 0.01). Compared with the control group, physical activity had a significant positive effect on the cognitive flexibility of Chinese children and adolescents. The source of heterogeneity in school-age children group was tested by meta-regression method. The results showed that the type of children t=12.77, 95%CI=28.79-39.74(P < 0.01) was the primary source of heterogeneity in Meta-analysis. The results of egger regression analysis showed that t=0.47, 95%CI=-1.48-2.37(P=0.64), and there was no publication bias. Conclusion Adolescence is the sensitive period for development of cognitive flexibility, and physical activities have a significant positive impact on the cognitive flexibility of children and adolescents. -
Key words:
- Motor activity /
- Cognition /
- Health education /
- Meta-analysis /
- Child /
- Adolescent
-
表 1 纳入文献基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of literatures
第一作者与年份 样本量 年龄/岁 运动方案 运动项目 质量评价 实验组 对照组 强度 时间/min 频率 周期/周 Chen[10](2014) 44 43 9~11 (220-年龄)×(60%~70%)HRmax 25 1次 — 慢跑 A 陈爱国[11](2014) 40 40 9~10 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 — 篮球 A (220-年龄)×(70%~79%) HRmax 颜军[12](2014) 62 61 9 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 — 健美操 A 赵中艳[13](2014) 38 39 9~10 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 — 跳绳 B 冯磊[14](2014) 64 62 9~10 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 — 篮球 B 赵莉[15](2014) 55 53 9~10 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 — 篮球 B (220-年龄)×(70%~79%) HRmax 吉晓海[16](2014) 110 60 9~10 (220-年龄)×(50%~70%) HRmax 20 1次 — 乒乓球 B 殷恒婵[17](2014) 108 108 9~11 (220-年龄)×(40%~80%) HRmax 30 5次/周 20 花样跑步 A 殷恒婵[18](2015) 86 72 9~11 (220-年龄)×(40%~80%) HRmax 30 3次/周 10 武术、跳绳、8字跑 A 陈爱国[19](2015) 18 15 11~12 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 40 3次/周 8 花样跳绳 A 王源[20](2015) 52 51 10~11 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 — 健美操 B 丁莉[21](2015) 24 25 9~11 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 12 恰恰舞 B 马冬静[22](2015) 40 44 10~12 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 20 3次/周 12 武术操 B 卫静[23](2015) 30 27 9~11 130~150次/min 30 1次 — 体育游戏 B 陈爱国[24](2015) 38 39 8~10 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 — 跳绳 A 陈爱国[25](2016) 24 22 9~10 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次 — 篮球 A 梁洪英[26](2016) 20 20 9~11 中低强度 40 3次/周 8 身心运动 B 傅建[27](2016) 49 50 14~17 130~160次/min 27 3次/周 8 体育课教学 A 张浩[28](2016) 42 43 10~12 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 3次/周 8 新思维体育游戏 B 刘丽丽[29](2016) 21 22 9~11 中等强度 30 2次/周 8 花样跳绳 B 刘坚[30](2016) 50 50 14~17 130~160次/min 45 3次/周 8 体育课教学 B 黄玲玲[31](2016) 33 37 15~18 (220-年龄)×(40%~60%) HRmax 27 2次/周 8 体育课教学 B 余婷婷[32](2016) 29 22 9~12 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 3次/周 10 篮球 B 张佩佩[33](2016) 37 40 10~11 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 40 2次/周 8 软式棒垒球 B 潘家礼[34](2016) 36 23 8~12 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 3次/周 10 合作游戏、武术操、花样踢毽 A 潘家礼[35](2016) 48 45 8~12 120~140次/min 30 3次/周 10 篮球 A 李捷良[36](2016) 20 20 9~11 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 45 5次/周 16 支架式网球 B 陈丽萍[37](2016) 30 30 9~10 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 40 2次/周 8 足球 A 陈爱国[38](2017) 41 40 8~10 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 40 2次/周 8 足球 A 缪海红[39](2017) 16 17 9~13 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 40 3次/周 12 足球 A 邹楠[40](2017) 54 54 7~12 (220-年龄)×(70%~80%) HRmax 30 3次/周 12 篮球、田径、武术 C 杨红[41](2017) 44 44 13 (220-年龄)×(60%~70%) HRmax 60 2次/周 12 篮球、健美操 B 王叶琼[42](2018) 16 18 10~11 中等强度 90 2次/周 12 健美操 C 白阔天[43](2018) 30 30 9~11 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 2次/周 8 篮球 B 张凯[44](2019) 17 15 15~17 (220-年龄)×(70%~80%) HRmax 90 2次/周 10 五体球 B 张立敏[45](2019) 33 33 7~12 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 45 1次 — 足球 C 许庆[46](2020) 74 72 13~14 (220-年龄)×(64%~85%) HRmax 10 4次/周 10 课间健身操 B 蔡春先[47](2020) 32 32 8~9 (220-年龄)×(80%~90%) HRmax 30 3次/周 8 跳绳 B (220-年龄)×(65%~75%) HRmax 张哲[48](2020) 49 50 13~15 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 30 1次/周 10 灵敏性训练 B 李亚鲁[49](2020) 20 20 7~8 (220-年龄)×(60%~69%) HRmax 40 2次/周 8 乒乓球 B 注: HRmax为最大心率。 表 2 不同研究特征对研究间异质性影响的Meta回归分析(n=32)
Table 2. Meta-regression analysis of the influence of different study characteristics on inter-study heterogeneity(n=32)
变量 β值 标准误 t值 P值 WMD值95%CI 总异质性I2占比/% 发表年份 -12.55 8.21 -1.53 0.14 -29.31~4.21 7.62 运动强度 -6.98 42.45 -0.16 0.87 -93.68~79.72 4.50 运动时间 -47.74 24.03 -1.99 0.06 -96.82~1.34 15.19 儿童类型 34.26 2.68 12.77 0.00 28.79~39.74 55.39 -
[1] DIAMOND A, CARLSON S M, BECK D M. Preschool children's performance in task switching on the dimensional change card sort task: separating the dimensions aids the ability to switch. Devel Neuropsychol, 2005, 28(2): 689-729. doi: 10.1207/s15326942dn2802_7 [2] CARTWRIGHT K B. Fostering flexibility and comprehension in elementary students. Reading Teach, 2006, 59(7): 628-634. doi: 10.1598/RT.59.7.2 [3] 王湃, 刘爱书, 郝洋, 等. 某高校大学生儿童期忽视对认知灵活性的影响. 中国学校卫生, 2020, 41(6): 871-873. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.06.019WANG B, LIU A S, HAO Y, et al. Effect of childhood neglect experience on cognitive flexibility. Chin J Sch Health, 2020, 41(6): 871-873. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.06.019 [4] CARTWRIGHT K B, COPPAGE E A, LANE A B, et al. Cognitive flexibility deficits in children with specific reading comprehension difficulties. Contemp Educ Psychol, 2016, 44(6): 50-54. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000038695831910_fad3.html [5] 彭杜宏, 廖渝, 苏蕙. 5~6岁幼儿认知灵活性的发展特征与个体差异. 学前教育研究, 2017, 24(4): 37-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XQJY201704006.htmPENG D H, LIAO Y, SU H. Research on the developmental feature and individual differences of 5 to 6 years old children's cognitive flexibility. Stud Early Childhood Educ, 2017, 24(4): 37-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XQJY201704006.htm [6] KIM C, JOHNSON N F, CILLES S E, et al. Common and distinct mechanisms of cognitive flexibility in prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci, 2011, 31(13): 4771-4779. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5923-10.2011 [7] MOHER D, LIBERATI A, TETZLAFF J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and Meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med, 2009, 6(7): 1-6. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC2707010/?lang=fr [8] 刘鸣. 系统评价、meta分析设计与实施方法. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2011: 48-49.LIU M. System evaluation, Meta-analysis design and implementation method. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2011: 48-49. [9] HIGGINS J P T, GREEN S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions V5.20. New Jersey: Tohn Wiley and Sons, 2011. [10] CHEN A G, YAN J, YIN H C, et al. Effects of acute aerobic exercise on multiple aspects of executive function in preadolescent children. Psychol Sport Exerc, 2014, 15(6): 627-636. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2014.06.004 [11] 陈爱国, 赵莉, 李焕玉, 等. 不同强度短时篮球运球训练对小学生执行功能的影响. 天津体育学院学报, 2014, 29(4): 352-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0000.2014.04.015CHEN A G, ZHAO L, LI H Y, et al. Effects of acute basketball dribbling training of different intensity on executive function of primary students. J Tianjin Univ Sport, 2014, 29(4): 352-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0000.2014.04.015 [12] 颜军, 王源, 陈爱国, 等. 短时中等强度不同类型运动对小学生执行功能的影响. 体育与科学, 2014, 24(6): 94-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4590.2014.06.017YAN J, WANG Y, CHEN A G, et al. Empirical study of the impact of various short-term physical activity of moderate intensity on the executive function of children in their preadolescence. Sports Sci, 2014, 24(6): 94-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4590.2014.06.017 [13] 赵中艳. 不同类型跳绳对小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2014.ZHAO Z Y. Experimental study on the effect of different types of rope skipping on the executive function of primary school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2014. [14] 冯磊. 不同运动持续时间对小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2014.FENG L. Experimental study on the effect of different exercise duration on the executive function of primary school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2014. [15] 赵莉. 不同强度篮球运动对小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2014.ZHAO L. An experimental study on the effect of basketball with different intensity on the executive function of primary school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2014. [16] 吉晓海. 不同运动项目训练小学生执行功能的差异性研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2014.JI X H. Study on the differences of executive function of primary school students trained by different sports. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2014. [17] 殷恒婵, 陈爱国, 马铮, 等. 两种运动干预方案对小学生执行功能影响的追踪研究. 体育科学, 2014, 34(3): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX201403003.htmYIN H C, CHEN A G, MA Z, et al. A follow-up study on two kinds of exercise intervention programs for children's executive functions. China Sport Sci, 2014, 34(3): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX201403003.htm [18] 殷恒婵, 李鑫楠, 陈爱国, 等. 5种运动干预方案对小学生脑执行功能影响的试验研究. 天津体育学院学报, 2015, 30(1): 7-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY201501003.htmYIN H C, LI X N, CHEN A G, et al. Experimental study on the effects of five kinds of exercise intervention programs on brain executive functions of primary students. J Tianjin Univ Sport, 2015, 30(1): 7-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY201501003.htm [19] 陈爱国, 蒋任薇, 吉晓海, 等. 8周中等强度的花样跳绳运动对聋哑儿童执行功能的影响. 体育与科学, 2015, 36(4): 105-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4590.2015.04.017CHEN A G, JIANG R W, JI X H, et al. Effects of 8-week moderate fancy rope skipping training on executive function in preadolescent deaf children: a school-based experimental study. Sports Sci, 2015, 36(4): 105-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4590.2015.04.017 [20] 王源. 不同类型短时中等强度运动对小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015.WANG Y. Empirical study of the impact of various short-term physical activity of moderate intensity on the executive function of children in their preadolescence. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2015. [21] 丁莉. "Poker Face"恰恰舞对小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015.DING L. An experimental study on the effect of "poker face" dance on the executive function of primary school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2015. [22] 马冬静. 中等运动强度武术操对小学五年级学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015.MA D J. An experimental study on the influence of medium intensity Wushu exercises on the executive function of the fifth grade primary school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2015. [23] 卫静. "心灵大比拼"体育游戏对儿童执行功能影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015.WEI J. An experimental study on the influence of "soul competition" sports games on children's executive function. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2015. [24] 陈爱国, 赵忠艳, 颜军. 不同组织形式短时跳绳运动对儿童执行功能的影响. 中国运动医学杂志, 2015, 34(9): 886-890. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX201509013.htmCHEN A G, ZHAO Z Y, YAN J. Effects of rope skipping with different forms of organization on the executive function of preadolescent children: a school-based experimental study. Chin J Sports Med, 2015, 34(9): 886-890. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX201509013.htm [25] 陈爱国, 冯磊, 朱丽娜, 等. 不同持续时间的中等强度篮球运动对儿童执行功能的影响. 首都体育学院学报, 2016, 27(3): 223-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BTSF201503007.htmCHEN A G, FENG L, ZHU L N, et al. Effects of medium-intensity basketball dribbling training of different durations on children' executive function. J Capit Univ Physic Educ Sports, 2016, 27(3): 223-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BTSF201503007.htm [26] 梁洪英. BAMS身心运动改善留守儿童执行功能的实践研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016.LIANG H Y. A practical study on the improvement of left behind children's executive function by physical and mental exercise. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. [27] 傅建, 范亚荣. 不同时间中等强度体育锻炼对初中生执行功能和学业成绩影响的实验研究. 体育与科学, 2016, 44(6): 110-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYYK201606016.htmFU J, FAN Y R. The Experimental study about impact of different moderate intensity exercise time on executive function and academic achievementof junior high school students. Sports Sci, 2016, 44(6): 110-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYYK201606016.htm [28] 张浩. 新思维体育游戏促进小学生执行功能发展的实践研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016.ZHANG H. Practical research on the development of primary school students' executive function promoted by new thinking sports games. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. [29] 刘丽丽. 8周花样跳绳运动对小学生执行功能影响的实践研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016.LIU L L. A practical study on the effect of 8-week rope skipping on the executive function of primary school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. [30] 刘坚. 不同时间中等强度体育锻炼对初中生执行功能与学习行为影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016.LIU J. An experimental study on the effects of moderate-intensity physical exercise at different times on executive function and learning behavior of junior high school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. [31] 黄玲玲. 不同时间中等强度体育锻炼对高中生执行功能和学业成绩影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016.HUANG L L. An experimental study on the effects of moderate-intensity physical exercise at different times on executive function and academic achievement of senior high school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. [32] 余婷婷. 篮球运动干预对学习困难小学生执行功能及学业成绩影响的实验研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016.YU T T. Experimental Study on the Influence of Basketball Intervention on Executive Function and Academic Achievement of Primary School Students with Learning Disabilities. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. [33] 张佩佩. 软式棒垒球运动方案影响小学生执行功能、学业成绩的实践研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016.ZHANG P P. A practical study on the influence of softball program on the executive function and academic performance of primary school students. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. [34] 潘家礼, 殷恒婵, 陈爱国, 等. 运动干预对数学学习困难小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 中国特殊教育, 2016, 191(5): 54-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDTJ201605009.htmPAN J L, YIN H C, CHEN A G, et al. An experimental study of the effect of exercise intervention on the executive function of primary school students with math learning difficulties. Chin J Spec Educ, 2016, 191(5): 54-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDTJ201605009.htm [35] 潘家礼, 殷恒婵, 陈爱国, 等. 运动干预对学习困难、正常小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 体育科学, 2016, 36(6): 84-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3624.2016.06.020PAN J L, YIN H C, CHEN A G, et al. An experimental study on the effect of exercise intervention on the executive functions of primary students with and without learning difficulties. Chin Sport Sci, 2016, 36(6): 84-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3624.2016.06.020 [36] 李捷良. 支架式网球教学对小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2016.LI J L. Experimental study on the effect of tennis teaching on the executive function of primary school students. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2016. [37] 陈丽萍. 足球运动方案影响农村留守儿童执行功能的实践研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016.CHEN L P. The practice research on the effect of football program on the executive function of rural left behind children. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. [38] 陈爱国, 陈丽萍, 颜军. 8周足球运动改善留守儿童执行功能的实验研究. 山东体育学院学报, 2017, 33(1): 85-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TIRE201701016.htmCHEN A G, CHEN L P, YAN J. Exepeimental study on the effect of eight-week football program on executive function among left-behind children. J Shandong Sport Univ, 2017, 33(1): 85-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TIRE201701016.htm [39] 缪海红, 丁璇, 吉晓海. 12周中等强度的足球运动对聋哑儿童执行功能的影响. 当代体育科技, 2017, 7(14): 248-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYKJ201714151.htmMIAO H H, DING X, JI X H. Effects of 12 weeks of moderate intensity football on executive function of deaf-mute children. Contemp Sports Technol, 2017, 7(14): 248-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYKJ201714151.htm [40] 邹楠, 陈晓娅. 运动干预方案对小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 当代体育科技, 2017, 7(18): 253-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYKJ201718141.htmZHOU N, CHEN X Y. Experimental study on the effect of exercise intervention program on the executive function of primary school students. Contemp Sports Technol, 2017, 7(18): 253-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYKJ201718141.htm [41] 杨红. 不同运动项目训练对初一学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2017.YANG H. An experimental study on the effect of different sports training on the executive function of junior high school students. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2017. [42] 王叶琼, 宋鑫平. 健美操锻炼对小学生执行功能的影响. 体育世界(学术版), 2018, 78(11): 116-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYSJ201811082.htmWANG Y Q, SONG X P. The influence of aerobics exercise on the executive function of primary school students. Sports World (Scholarly), 2018, 78(11): 116-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYSJ201811082.htm [43] 白阔天. 三种篮球基本技术训练对小学生执行功能影响的实验研究. 北京: 北京体育大学, 2018.BAI K T. Experimental study on the effects of three basic basketball skills training on executive function of primary school students. Beijing: Beijing Sport University, 2018. [44] 张凯. 10周五体球运动干预对高中生执行功能及体育学习兴趣的影响. 广州: 广州体育学院, 2019.ZHANG K. Ten weeks wutiball sports intervention for high school students executive function and the influence of sports learning interest. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Sport University, 2019. [45] 张立敏, 喻青, 查圣祥. 中等强度足球锻炼对小学生执行功能的影响. 体育成人教育学刊, 2019, 35(3): 74-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYHS201903017.htmZHANG L M, YU Q, ZHA S X. Influence of medium intensity football exercise on primary school students' executive function. J Sports Adult Educ, 2019, 35(3): 74-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYHS201903017.htm [46] 许庆. 10周大课间健身操运动对初中生体质及执行功能的影响. 上海: 上海体育学院, 2020.XU Q. The Effect of 10-week aerobics during the recess on fitness and executive function of middle school students. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Sport, 2020. [47] 蔡春先. 不同强度间歇运动干预对儿童执行功能的影响及其时程效益研究. 天津: 天津体育学院, 2020.CAI C X. Study on the effect of different intensity intermittent exercise intervention on children's executive function and its time course benefit. Tianjin: Tianjin Institute of Physical Education, 2020. [48] 张哲. 灵敏性训练对男性中学生执行功能的影响研究. 北京: 中央民族大学, 2020.ZHANG Z. Effect of sensitivity training on executive function of male middle school students. Beijing: Minzu University of China, 2020. [49] 李亚鲁. 乒乓球运动干预对儿童执行功能影响的研究. 天津: 天津体育学院, 2020.LI Y L. Research on the influence of table tennis intervention on children's executive function. Tianjin: Tianjin Institute of Physical Education, 2020. [50] 解超, 金成吉, 张自云, 等. 中等强度有氧运动对我国学龄儿童执行功能影响的Meta分析. 中国学校卫生, 2017, 38(1): 65-68, 71. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2017.01.020XIE C, JIN C J, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Meta-analysis of effects of moderate intensity aerobic exercise on executive functions of school-aged children in China. Chin J Sch Health, 2017, 38(1): 65-68, 71. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2017.01.020 [51] 王积福, 漆昌柱, 韦晓娜. 身体活动对执行功能影响的元分析. 首都体育学院学报, 2019, 31(4): 375-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BTSF201904017.htmWANG J F, QI C Z, WEI X N. Effects of physical activity on executive function: a Meta-analysis. Capit Univ Physi Educ Sports, 2019, 31(4): 375-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BTSF201904017.htm [52] WILLOUGHBY M T, WYLIE A C, CATELLIER D J. Testing the association between physical activity and executive function skills in early childhood. Early Childhood Res Quart, 2018, 44: 82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2018.03.004 [53] NIET A, SMITH J, SCHERDER E, et al. Associations between daily physical activity and executive functioning in primary school-aged children. J Sci Med Sport, 2015, 18(6): 673-677. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2014.09.006 [54] 陈爱国, 殷恒婵, 王君, 等. 短时中等强度有氧运动改善儿童执行功能的磁共振成像研究. 体育科学, 2011, 31(10): 35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-677X.2011.10.004CHEN A G, YIN H C, WANG J, et al. A magnetic resonance imagin study on the improvement of executive function in children during short, moderate intensity aerobic exercise. Chin Sport Sci, 2011, 31(10): 35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-677X.2011.10.004 [55] 杨远都, 李佑发, 王思佳, 等. 有氧运动改善儿童执行功能研究进展. 中国预防医学杂志, 2020, 21(1): 116-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYC202001028.htmYANG Y D, LI Y F, WANG S J, et al. Progress of aerobic exercise on improving executive function of children. Chin J Prev Med, 2020, 21(1) : 116-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYC202001028.htm [56] TOMPOROWSKI P D, LAMBOURNE K, OKUMURA M S. Physical activity interventions and children's mental function: an introduction and overview. Prev Med, 2011, 52(Suppl 1): S3-S9. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Phillip_Tomporowski/publication/50594580_Physical_activity_interventions_and_children's_mental_function_An_introduction_and_overview/links/5576ff6908aeb6d8c01cd992.pdf [57] 江大雷, 曾从周. 8周中等强度足球运动游戏对学龄前儿童执行功能发展的影响. 中国体育科技, 2015, 51(2): 43-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9826.2015.02.005JIANG D L, ZENG C Z. The effect of 8-week soccer exercise with medium intensity on executive function in preschool children. Chin Sport Sci Technol, 2015, 51(2): 43-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9826.2015.02.005 [58] ISHIHARA T, MIZUNO M. Effects of tennis play on executive function in 6-11-year-old children: a 12-month longitudinal study. Eur J Sport Sci, 2018, 18(5): 741-752. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2018.1444792 [59] VAN DER NIET A G, SMITH J, SCHERDER E J, et al. Associations between daily physical activity and executive functioning in primary school-aged children. J Sci Med Sport, 2015, 18(6): 1-5. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036750418110_70ac.html [60] 盖笑松, 许洁, 闫艳, 等. 体感游戏促进儿童的执行功能: 运动强度和认知参与的作用. 心理学报, 2021, 53(5): 505-514. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXB202105006.htmGAI X S, XU J, YAN Y, et al. Exergame can improve children's executive function: the role of physical intensity and cognitive engagement. Acta Psychol Sinica, 2021, 53(5): 505-514. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXB202105006.htm [61] 崔洁, 李琳, 朱春山, 等. 屏前静坐行为与学龄儿童认知灵活性的关系. 体育学刊, 2021, 28(3): 112-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYXK202103017.htmCUI J, LI L, ZHU C S, et al. Relationship between screen-based sedentary behaviour and cognitive flexibility in school-age children. J Phys Educ, 2021, 28(3): 112-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYXK202103017.htm [62] LUDYGA S, GERBER M, MVCKE M, et al. The acute effects of aerobic exercise on cognitive flexibility and task-related heart rate variability in children with ADHD and healthy controls. J Attent Disord, 2018, 44(4): 1-11. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29468917?utm_source=research-news&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=research-news [63] XUAN X, LI N Z, XIAO X D, et al. Aerobic exercise intervention alters executive function and white matter integrity in deaf children: a randomized controlled study. Neur Plastic, 2018, 18(4): 1-8. http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/np/2018/3735208.pdf [64] 朱莉, 余少兵, 王树明, 等. 运动干预对中国儿童执行功能改善效果的Meta分析. 安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(3): 300-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHSZ202003015.htmZHU L, YU S B, WANG S M, et al. Meta-analysis for exercise intervension's effect on Chinese children's excutive function improvement. J Anhui Normal Univ(Natural Sci), 2020, 43(3): 300-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHSZ202003015.htm -







 下载:
下载: