Relationship between weight-adjusted-waist index and cardiopulmonary endurance in Chinese middle school students
-
摘要:
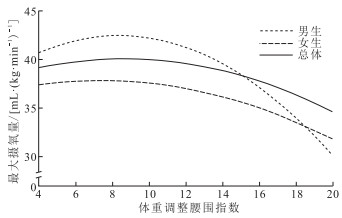
目的 了解中学生体重调整腰围指数(WWI)与心肺耐力之间的关联,为青少年心肺耐力水平的提高提供参考和借鉴。 方法 2015年6月—2018年12月采用立意抽样的方法,分别在中国东北、华北、华东、中南、西南、西北地区对44 870名13~18岁中学生进行身高、体重、腰围、20 m往返跑的测试,计算WWI和间接计算最大摄氧量(VO2max)。采用t检验、单因素方差分析的方法进行单因素分析,采用曲线回归分析的方法进行WWI与VO2max关系的分析。 结果 中国13~18岁中学生WWI为(9.35±1.02),20 m往返跑次数为(38.89±18.14)次,VO2max为(39.96±5.88)mL/(kg·min-1)。13~18岁各年龄段男生WWI四分位数组间VO2max比较,差异均有统计学意义(F值分别为15.19,9.00,14.97,20.48,28.13,10.13,P值均<0.01);女生有相同趋势(F值分别为23.36,16.61,33.45,32.96,18.23,19.36,P值均<0.01)。WWI与心肺耐力呈倒U型曲线关系,当WWI为8.5时,VO2max水平达到最高,为40.07 mL/(kg·min-1)。与女生相比,男生WWI对心肺耐力的影响更为显著。 结论 有效控制中学生WWI适宜水平可能更好地促进心肺耐力的提高。 Abstract:Objective To understand the association between weight-adjusted-waist index (WWI) and cardiopulmonary endurance among middle school students, so as to provide references for the improvement of cardiopulmonary endurance levels in adolescents. Methods From June 2015 to December 2018 by using the method of purposive sampling, height, weight, waist circumference, and 20 m shuttle-run tests were measured among 44 870 adolescents aged 13-18 from Northeast, North, East, South, Southwest and Northwest of China. The WWI of the adolescents and the maximum oxygen uptake (VO2max) were calculated indirectly. The t-test and one-way analysis of variance were used for comparison, and the curve regression analysis method was adopted to analyze the relationship between WWI and VO2max. Results For Chinese middle school students aged 13-18, the WWI was (9.35±1.02), the number of 20 m shuttle-run was (38.89±18.14) times, and VO2max was (39.96±5.88) mL/(kg ·min-1). The differences of VO2max between WWI quartile arrays of boys aged 13-18 were statistically significant (F=15.19, 9.00, 14.97, 20.48, 28.13, 10.13, P < 0.01), girls had the same trend (F=23.36, 16.61, 33.45, 32.96, 18.23, 19.36, P < 0.01). There was an inverted U-shaped curve relationship between WWI and cardiopulmonary endurance. When WWI was 8.5, the VO2max level reached the highest, which was 40.07 mL/(kg ·min-1). Compared with girls, WWI in boys had a more significant impact on cardiopulmonary endurance. Conclusion Maintaining optimal WWI levels may enhance adolescents' cardiopulmonary endurance. -
Key words:
- Weight-adjusted waist index /
- Heart /
- Lung /
- Regression analysis /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 不同性别中学生基本指标比较(x ±s)
Table 1. Comparison of the basic indicators for middle school students in different gender(x ±s)
性别 人数 年龄/岁 身高/cm 体重/kg 腰围/cm WWI 20 m往返跑次数/laps 20 m往返跑等级 20 m往返跑最高跑速/(km·h-1) VO2max/[mL·(kg·min-1)-1] 男 22 338 15.45±1.67 170.95±8.44 60.64±12.89 72.63±10.56 9.39±1.06 46.31±19.66 5.87±2.02 10.94±1.01 42.25±5.90 女 22 532 15.60±1.67 161.55±6.11 52.09±8.70 66.80±7.96 9.30±0.97 31.54±12.77 4.35±1.41 10.18±0.70 37.69±4.89 合计 44 870 15.52±1.67 166.23±8.74 56.35±11.79 69.70±9.79 9.35±1.02 38.89±18.14 5.11±1.90 10.56±0.95 39.96±5.88 t值 -9.05 135.19 82.40 66.11 9.49 94.48 92.75 92.75 89.03 P值 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 表 2 不同WWI四分位数、不同性别中学生VO2max比较(x ±s)
Table 2. Comparison of VO2max in the quartiles of WWI and gender among middle school students(x ±s)
WWI 男生 女生 13岁 14岁 15岁 16岁 17岁 18岁 13岁 14岁 15岁 16岁 17岁 18岁 Q1 44.40±4.62 44.01±5.24 43.45±5.83 42.01±6.06 40.40±6.11 38.93±5.89 42.33±3.62 40.54±3.91 38.18±3.82 37.15±3.83 35.57±3.86 33.17±4.43 Q2 45.18±4.96 44.38±5.20 44.10±5.60 42.64±5.98 41.88±6.01 39.38±6.46 42.39±3.75 40.82±3.95 39.29±3.78 37.47±3.66 35.87±4.03 34.13±4.87 Q3 44.56±4.80 44.30±5.08 43.20±5.49 42.21±5.61 41.15±5.81 39.16±6.29 42.30±3.79 40.81±3.79 39.21±3.96 37.10±3.70 35.92±4.03 33.75±4.68 Q4 43.72±4.78 43.29±5.07 42.44±5.23 40.76±5.37 39.36±5.75 37.85±6.00 41.08±4.31 39.64±4.00 37.88±3.59 35.87±3.50 34.64±3.66 32.69±3.75 F值 15.19 9.00 14.97 20.48 28.13 10.13 23.36 16.61 33.45 32.96 18.23 19.36 P值 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 表 3 不同性别中学生WWI与VO2max的曲线回归分析
Table 3. Curve regression analysis of WWI and VO2max in middle school students of different genders
性别 自变量 β值 标准误 t值 P值 男 WWI 0.27 0.27 5.65 <0.01 (n=22 338) WWI2 -0.31 0.01 -6.47 <0.01 常数 1.29 27.91 <0.01 女 WWI 0.11 0.28 2.00 0.05 (n=22 532) WWI2 -0.14 0.02 -2.53 0.01 常数 1.32 27.10 <0.01 合计 WWI 0.13 0.21 3.45 <0.01 (n=44 870) WWI2 -0.14 0.01 -3.85 <0.01 常数 1.00 37.08 <0.01 -
[1] 毕存箭, 尹小俭, 施利娟, 等. 中高强度课堂体育锻炼对藏族初一年级学生心肺耐力和执行功能的干预效果[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(3): 322-325.BI C J, YIN X J, SHI L J, et al. Intervention effects of moderate and high intensities of classroom physical activity on cardiorespiratory fitness and executive function among junior grade one students in Tibetan[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(3): 322-325. (in Chinese) [2] 封秀林. 自编有氧拉丁操对女大学生心肺耐力及体育学习兴趣的影响研究[D]. 广州: 广州体育学院, 2024.FENG X L. Study on the impact of self made aerobic Latin exercises on cardio-respiratory fitness and sports learning interests of female university students[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Sport University, 2024. (in Chinese) [3] 李辉, 王乐. 24 h活动行为对中心性肥胖中学生身体形态与心肺耐力影响的替代效益[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2025, 46(5): 662-666.LI H, WANG L. Alternative benefits of 24-hour activity behavior on the physical shape and cardiorespiratory endurance of middle school students with central obesity[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2025, 46(5): 662-666. (in Chinese) [4] 马奇, 陈曼曼, 马莹, 等. 儿童青少年生活方式与不同部位脂肪质量指数的关联[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2024, 45(7): 1021-1025.MA Q, CHEN M M, MA Y, et al. Association between lifestyle and fat mass index in different positions of children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2024, 45(7): 1021-1025. (in Chinese) [5] 张帅, 李成跃, 李卫民. 1985—2019年8次中国儿童青少年体质健康监测的爆发力素质研究及长期发展预测[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2025, 33(5): 565-570.ZHANG S, LI C Y, LI W M. Quality of power for monitoring the physical fitness of Chinese children and adolescents based on 8 studies from 1985 to 2019 and long-term development forecasts[J]. Chin J Child Health Care, 2025, 33(5): 565-570. (in Chinese) [6] 陈泽恺, 朱琳, 李展权, 等. 中高强度身体活动量与肥胖儿童青少年心肺适能改善的剂量-效应关系研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2022, 41(9): 687-693.CHEN Z K, ZHU L, LI Z Q, et al. Dose-response relationship between moderate to vigorous physical activities of and cardiorespiratory fitness of obese children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Sports Med, 2022, 41(9): 687-693. (in Chinese) [7] 李明, 尹小俭, 李玉强, 等. 中国汉族儿童青少年体质量指数与20 m往返跑的相关性[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2017, 38(12): 1773-1776.LI M, YIN X J, LI Y Q, et al. Correlation between BMI and 20 m shuttle run of children and adolescents of Han nationality in China[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2017, 38(12): 1773-1776. (in Chinese) [8] 土小红, 谢坚明, 黄智萍, 等. 中学生20 m往返跑成绩与生活行为方式的关联[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2022, 43(12): 1804-1808. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.12.011TU X H, XIE J M, HUANG Z P, et al. Relationship between 20 m shuttle run test performance and lifestyle behaviors of junior high school students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2022, 43(12): 1804-1808. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.12.011 [9] 李瑞林, 于照祥, 赵斌, 等. 体重调整腰围指数与儿童青少年骨密度的最佳平衡状态探索[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2025, 31(4): 501-506.LI R L, YU Z X, ZHAO B, et al. Exploration of the optimal balance between weight-adjusted waist circumference index and bone mineral density in children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Osteop, 2025, 31(4): 501-506. (in Chinese) [10] WANG X, YANG S, HE G, et al. The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and total bone mineral density in adolescents: NHANES 2011-2018[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1191501. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1191501 [11] YE J, HU Y, CHEN X, et al. Association between the weight-adjusted waist index and stroke: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2023, 23(1): 1689. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16621-8 [12] 黄凤连, 陈萍萍, 周圆, 等. 基于中国学生体质调研数据的少数民族中小学生视力不良对比分析[J]. 中国校医, 2021, 35(5): 321-324.HUANG F L, CHEN P P, ZHOU Y, et al. Comparative analysis of poor visual acuity of minority primary and secondary school students based on Chinese students' physique and health survey data[J]. Chin J School Doctor, 2021, 35(5): 321-324. (in Chinese) [13] TOMKINSON G R, LANG J J, BLANCHARD J, et al. The 20-m shuttle run: assessment and interpretation of data in relation to youth aerobic fitness and health[J]. Pediatr Exerc Sci, 2019, 31(2): 152-163. doi: 10.1123/pes.2018-0179 [14] 石秀廷, 尹小俭. 20 m往返跑用于青少年心肺耐力评价的研究进展[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2017, 38(12): 1916-1920.SHI X T, YIN X J. Research progress of 20 m round trip running for evaluating cardiopulmonary endurance in adolescents[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2017, 38(12): 1916-1920. (in Chinese) [15] LÉGER L A, MERCIER D, GADOURY C, et al. The multistage 20 metre shuttle run test for aerobic fitness[J]. J Sports Sci, 1988, 6(2): 93. doi: 10.1080/02640418808729800 [16] 刘自慧, 彭莉, 郭耀明, 等. 重庆市儿童身体质量指数与体质健康指标关系研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 38(12): 164-168.LIU Z H, PENG L, GUO Y M, et al. On relationship between body mass index and physical health variables of Chongqing children[J]. J Southwest China Norm Univ (Nat Sci Edit), 2013, 38(12): 164-168. (in Chinese) [17] 王熙, 王娇娇, 张强, 等. 儿童青少年体格发育指标与20 m往返跑成绩的关联[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2023, 44(11): 1708-1712.WANG X, WANG J J, ZHANG Q, et al. Relationship between anthropometric parameters and 20-meter shuttle run test among children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2023, 44(11): 1708-1712. (in Chinese) [18] 李新, 李晓彤, 王正珍, 等. 肥胖少年颈围、腰围与心肺耐力及心血管疾病危险因素的关系[J]. 体育科学, 2017, 37(3): 79-85.LI X, LI X T, WANG Z Z, et al. Relationship of neck circumference, waist circumference and cardiorespiratory fitness with cardiovascular disease risk factors in obese adolescents[J]. Sci Sports, 2017, 37(3): 79-85. (in Chinese) [19] WEELDREYER N R, DE GUZMAN J C, PATERSON C, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness, body mass index and mortality: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2025, 59(5): 339-346. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2024-108748 [20] 赖丽娟, 蔡莉, 曾霞, 等. 广州市小学生体力活动和静态行为与20 m往返跑的关联[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40(12): 1771-1774.LAI L J, CAI L, ZENG X, et al. Association of physical activity and sedentary behavior with 20 in shuttle run test performance among children[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2019, 40(12): 1771-1774. (in Chinese) [21] MINTJENS S, MENTING M D, DAAMS J G, et al. Reply to tarp comment on: "cardiorespiratory fitness in childhood and adolescence affects future cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review of longitudinal studies"[J]. Sports Med, 2019, 49(1): 163-165. doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-01042-0 [22] 梅凤鸣. 同期耐力与力量训练对非体育专业大学生800米成绩影响的实验研究[D]. 长春: 吉林体育学院, 2024.MEI F M. An experimental study on the influence of simultaneous endurance and strength training on 800 meter performance of non-physical education major college students[D]. Changchun: Jilin Institute of Physical Education, 2024. (in Chinese) [23] KOSMAS C E, BOUSVAROU M D, KOSTARA C E, et al. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease[J]. J Int Med Res, 2023, 51(3): 655741820. [24] ASHRAF M J, BAWEJA P. Obesity: the 'huge' problem in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Mo Med, 2013, 110(6): 499-504. [25] SOTAK M, CLARK M, SUUR B E, et al. Inflammation and resolution in obesity[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2025, 21(1): 45-61. doi: 10.1038/s41574-024-01047-y [26] MCHENRY J, CARRIER N, HULL E, et al. Sex differences in anxiety and depression: role of testosterone[J]. Front Neuroendocrinol, 2014, 35(1): 42-57. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2013.09.001 [27] WANG P, LI Q, WU L, et al. Association between the weight-adjusted-waist index and testosterone deficiency in adult males: a cross-sectional study[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 25574. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76574-9 -







 下载:
下载: