Longitudinal trajectory analysis of orthokeratology lens wearing adherence in myopic children and adolescents
-
摘要:
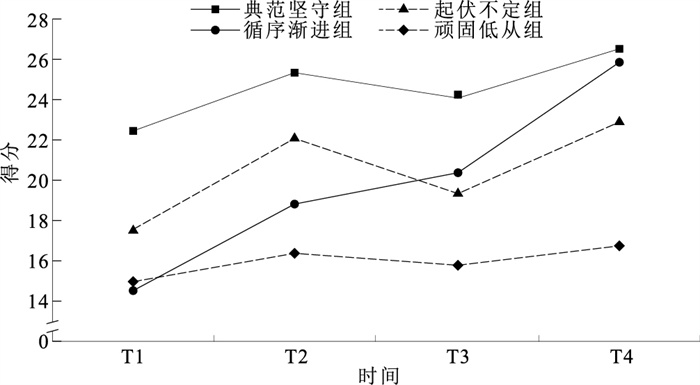
目的 分析近视儿童青少年角膜塑形镜(OK镜)配戴依从性轨迹的潜在类别及影响因素,为近视儿童青少年OK镜配戴依从性的动态精准干预提供依据。 方法 2024年1—6月,采用方便抽样方法选取沧州市中心医院眼科医学中心配戴OK镜的310名近视儿童青少年为研究对象。采用一般资料调查表、OK镜配戴者依从性调查问卷、执行功能行为评定量表自评版(BRIEF-SR)、家庭支持量表以及自制近视控制态度问卷于患者配镜时(T0),戴镜后2周(T1)、1个月(T2)、3个月(T3)及6个月(T4)进行资料收集。采用增长混合模型识别近视儿童青少年OK镜配戴依从性轨迹类别,采用多元Logistic回归分析其影响因素。 结果 近视儿童青少年OK镜配戴依从性大致可以分为4种类别发展轨迹:C1典范坚守型(58例,18.71%)、C2循序渐进型(130例,41.94%)、C3起伏不定型(85例,27.42%)以及C4顽固低从型(37例11.94%)。多元Logistic回归分析结果显示,以C1组为参照,年龄(C3, OR=0.74)、父母受教育程度(C4, OR=0.67)、执行功能(C2, OR=0.69;C4, OR=0.44)、家庭支持(C3, OR=0.75)与近视控制态度(C2, OR=0.39)均是OK镜配戴依从性轨迹类别的影响因素;以C2组为参照,年龄(C3, OR=0.55)、父母受教育程度(C3, OR=0.34;C4, OR=0.64)、执行功能(C3, OR=0.77)、家庭支持(C4, OR=0.58)均是OK镜配戴依从性轨迹类别的影响因素;以C3组为参照,年龄(C4, OR=0.68)、近视控制态度(C4, OR=0.44)均是OK镜配戴依从性轨迹类别的影响因素(P值均 < 0.05)。 结论 近视儿童青少年OK镜配戴依从性可大致分为4种变化轨迹,存在群体异质性。应基于不同轨迹及影响因素,给予动态、精准的配戴依从性干预策略。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the potential categories and influencing factors of the compliance trajectory of orthokeratology lenses (OK lens) in myopic children and adolescents, so as to provide a basis for dynamic and accurate intervention of OK lens compliance in myopic children and adolescents. Methods From January to June 2024, 310 myopic children and adolescents wearing OK lens were selected as research subjects from the Ophthalmology Medical Center of Cangzhou Central Hospital using a convenient sampling method. Data were collected at four time points: when the glasses were first fitted (T0), 2 weeks after fitting (T1), 1 month later (T2), 3 months later (T3), and 6 months later (T4). The data collection methods included general information questionnaires, compliance surveys for OK lens wearers, the Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function-Self-report Version (BRIEF-SR), family support scales, and a self-made questionnaire on myopia control attitudes. A growth mixed model was used to identify the trajectory categories of compliance with OK lens wearing among myopic children and adolescents, and multiple Logistic regression analysis was employed to examine the influencing factors. Results The compliance with OK lens among myopic children and adolescents were roughly divided into four developmental trajectories: C1 exemplary adherent (58 cases, 18.71%), C2 gradual progressor (130 cases, 41.94%), C3 fluctuating (85 cases, 27.42%), and C4 stubborn low follower (37 cases, 11.94%). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that, with C1 group as the reference, age (C3, OR=0.74), parental education level (C4, OR=0.67), executive function (C2, OR=0.69; C4, OR=0.44), family support (C3, OR=0.75) and myopia control attitude (C2, OR=0.39) were all influencing factors for the compliance trajectory of OK lens; with C2 group as the reference, age (C3, OR=0.55), parental education level (C3, OR=0.34; C4, OR=0.64), executive function (C3, OR=0.77), and family support (C4, OR=0.58) were all influencing factors for the compliance trajectory of OK lens; with C3 group as the reference, age (C4, OR=0.68), and myopia control attitude (C4, OR=0.44) were both influencing factors for the compliance trajectory of OK lens (P < 0.05). Conclusions The compliance of wearing OK lens in children and adolescents with myopia can be roughly divided into four trajectories, and there is group heterogeneity. Dynamic and precise compliance intervention strategies should be given based on different trajectories and influencing factors. -
Key words:
- Myopia /
- Orthokeratologic procedures /
- Patient compliance /
- Regression analysis /
- Child /
- Adolescent
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 近视儿童青少年OK镜配戴依从性得分的增长混合模型拟合分析
Table 1. Growth mixed model fitting analysis of OK lens wearing adherence scores for myopic children and adolescents
模型 AIC值 BIC值 aBIC值 Entropy值 PLMR-LRT值 PBLRT值 类别概率 1 4 872.38 4 924.18 4 880.84 - - - 1 2 4 429.12 4 486.30 4 434.28 0.73 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.78/0.22 3 4 189.67 4 218.37 4 196.33 0.87 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.26/0.58/0.16 4 4 073.17 4 136.77 4 109.75 0.93 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.19/0.42/0.27/0.12 5 4 002.11 4 064.17 4 018.35 0.88 0.07 0.03 0.13/0.37/0.24/0.16/0.10 表 2 近视儿童青少年OK镜配戴依从性轨迹类别的单因素分析
Table 2. Univariate analysis of trajectory categories for OK lens wearing adherence in myopic children and adolescents
类别 人数 性别 年龄/岁 居住地 家庭月收入/万元 父母受教育程度 男 女 7~10 >10~12 >12~18 农村 城镇 < 1 1~2 >2 高中及以下 大专/本科 研究生及以上 C1 58 26(44.83) 32(55.17) 15(25.86) 19(32.76) 24(41.38) 22(37.93) 36(62.07) 15(25.86) 30(51.72) 13(22.41) 11(18.97) 28(48.28) 19(32.76) C2 130 62(47.69) 68(52.31) 41(31.54) 68(52.31) 21(16.15) 66(50.77) 64(49.23) 25(19.23) 79(60.77) 26(20.00) 25(19.23) 88(67.69) 17(13.08) C3 85 43(50.59) 42(49.41) 44(51.76) 17(20.00) 24(28.24) 27(31.76) 58(68.24) 22(25.88) 42(49.41) 21(24.71) 39(45.88) 32(37.64) 14(16.47) C4 37 22(59.46) 15(40.54) 10(27.03) 9(24.32) 18(48.65) 16(43.24) 21(56.76) 9(24.32) 20(54.05) 8(21.62) 22(59.46) 10(27.03) 5(13.51) χ2值 1.38 6.28 1.20 1.12 8.13 P值 0.10 0.02 0.19 0.39 0.01 注:()内数字为构成比/%。 -
[1] 徐李莎, 黄烨, 吴汶灿, 等. 河南省中小学生2019—2020年近视队列研究结果[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2023, 44(12): 1814-1818, 1823. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.12.012XU L S, HUANG Y, WU W C, et al. Analysis of a cohort study on myopia among primary and secondary school students in Henan Province, 2019-2020[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2023, 44(12): 1814-1818, 1823. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.12.012 [2] 张玉娇. 角膜塑形镜控制近视的临床研究进展[J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2024, 24(9): 1453-1456.ZHANG Y J. Advances in clinical research on the control of myopia with orthokeratology[J]. Int Eye Sci, 2024, 24(9): 1453-1456. (in Chinese) [3] LIPSON M J, KOFFLER B H. The history and impact of prescribing orthokeratology for slowing myopia progression[J]. Eye Contact Lens, 2024, 50(12): 517-521. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000001123 [4] JUN J, ZHIWEN B, FEIFU W, et al. Level of compliance in orthokeratology[J]. Eye Contact Lens, 2018, 44(5): 330-334. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000516 [5] KESHANI P, SHAHRAKI H R. Modeling trend changes in percent of under five-year-old children with malnutrition amongst 39 Asian countries from 1987 to 2016 via growth mixture model[J]. BMC Nutr, 2022, 8(1): 38. doi: 10.1186/s40795-022-00530-x [6] DALMAIJER E S, NORD C L, ASTLE D E. Statistical power for cluster analysis[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2022, 23(1): 205. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04675-1 [7] 杨羿. 配戴角膜塑形镜需做好定期复查[J]. 中国眼镜科技杂志, 2024(11): 93-94.YANG Y. Wearing an orthokeratology lens requires a regular review[J]. China Glass Sci Technol Mag, 2024(11): 93-94. (in Chinese) [8] FUSTER M, SANTOS M P, DIMOND E, et al. Examining capabilities, opportunities, and motivations for healthy eating behaviors in Latin American restaurants: a quantitative application of the COM-B model to inform future interventions[J]. BMC Nutr, 2023, 9(1): 57. doi: 10.1186/s40795-023-00712-1 [9] WALKER J, D'AMATO R. Test review: Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function-Self-report Version[J]. J Psychoeduc Assess, 2006, 24(4): 394-398. doi: 10.1177/0734282906288390 [10] PROCIDANO M E, HELLER K. Measures of perceived social support from friends and from family: three validation studies[J]. Am J Community Psychol, 1983, 11(1): 1-24. doi: 10.1007/BF00898416 [11] 郑森国. 角膜塑形镜戴镜者卫生依从性及镜盒污染现况的调查分析[D]. 温州: 温州医科大学, 2018.ZHENG S G. Investigation and analysis of hygiene compliance and current status of lens box contamination[D]. Wenzhou: Wenzhou Medical University, 2018. (in Chinese) [12] STILLITANO I, MAIDANA E, LUI M, et al. Bubble and corneal dimple formation after the first overnight wear of an orthokeratology lens: a case series[J]. Eye Contact Lens, 2007, 33(5): 253-258. doi: 10.1097/01.icl.0000252870.05807.ea [13] CHANG L C, SUN C C, LIAO L L. Compliance with orthokeratology care among parents of young children in Taiwan[J]. Cont Lens Anterior Eye, 2021, 44(5): 101427. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2021.02.013 [14] BIAN Z, XU X, CHEN D, et al. Assessment of patient compliance in orthokeratology and analysis of influencing factors: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Ophthalmol, 2021, 21(1): 396. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02148-2 -







 下载:
下载: