Dose-response relationship between elevated blood pressure and body mass index in primary and secondary school students in Shibei District, Qingdao
-
摘要:
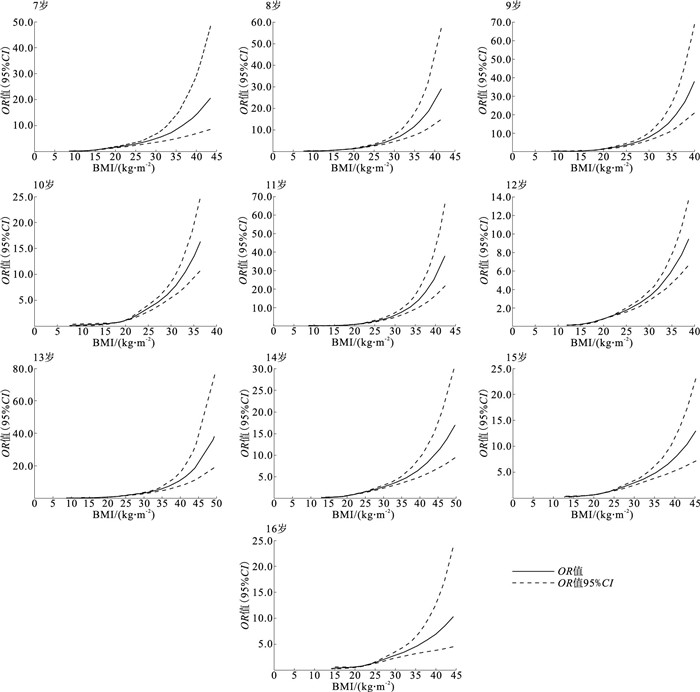
目的 探讨青岛市市北区中小学生血压偏高患病风险与体质量指数(BMI)的剂量反应关系,为采取精准干预措施提供参考依据。 方法 对青岛市市北区2022年92 091名中小学生健康体检数据进行统计分析,应用《学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查》标准对超重与肥胖进行评估;应用《7~18岁儿童青少年血压偏高筛查界值》对血压等级进行评定。运用方差分析、χ2检验、多因素Logistic回归以及结合限制性立方样条分析BMI与血压偏高的关系。 结果 根据不同年龄性别下的标准化评分,将BMI分为5类,与BMI-Z分0~ < 1组相比,随着BMI-Z分的减少,血压偏高风险逐渐降低(OR值分别为0.55,0.53);随着BMI-Z分增加,血压偏高风险不断增大(OR值分别为1.90,3.71)(P值均 < 0.05)。分层分析表明,BMI在不同性别(男、女)、年龄(7~8,9~11,12~14,15~16岁)、腰臀比(≤0.83,>0.83)下与血压偏高患病风险均呈正相关(OR值分别为1.18,1.19,1.15,1.22,1.19,1.18,1.19,1.18,P值均 < 0.01)。BMI和性别、BMI和年龄、BMI和腰臀比之间均存在相乘交互作用(OR值分别为1.53,1.08,2.31,P值均 < 0.01)。限制性立方样条分析表明,随着BMI水平的上升,7,10~16岁人群发生血压偏高的风险均呈非线性增高趋势(χ2值分别为27.56,10.69,6.10,27.26,18.32,25.71,10.53,6.14,P值均 < 0.05)。 结论 随着BMI增高,中小学生血压偏高的风险随之增大,基本呈非线性剂量-反应关系。应及时开展监测,采取综合有效防控措施预防儿童青少年血压偏高。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the dose-response relationship between the risk of elevated blood pressure and body mass index (BMI) in primary and secondary school students in Shibei District, Qingdao, so as to provide a reference for precise interventions of elevated blood pressure. Methods Statistical analysis was conducted on the health examination data of 92 091 primary and secondary school students in Shibei District, Qingdao, in 2022. Overweight and obesity were assessed using the standards from the Screening for Overweight and Obesity among School-aged Children and Adolescents, and blood pressure levels were evaluated using the Reference of Screening for Elevated Blood Pressure among Children and Adolescents Aged 7-18 Years. The relationship between BMI and elevated blood pressure was examined using analysis of variance, Chi-square test, multifactorial Logistic regression, and a combination of restricted cubic spline after data cleaning. Results Based on the standardized scores under different age and gender, BMI was classified into 5 categories. Compared with the group of BMI-Z scores 0- < 1, the risk of developing high blood pressure gradually decreased with BMI-Z scores (OR=0.55, 0.53, P < 0.05). Conversely, the risk of developing high blood pressure increased with increasing BMI-Z scores (OR=1.90, 3.71, P < 0.05). Stratified analyses showed that BMI was positively associated with elevated blood pressure by gender (male, female), age (aged 7-8, 9-11, 12-14, 15-16), and waist-to-hip ratio (≤0.83, >0.83) (OR=1.18, 1.19, 1.15, 1.22, 1.19, 1.18, 1.19, 1.18, P < 0.01). There were multiplicative interactions between BMI and gender, between BMI and age, between BMI and waist-to-hip ratio (OR=1.53, 1.08, 2.31, P < 0.01). Restricted cubic spline analysis showed that as BMI levels increased, the risk of developing elevated blood pressure showed a non-linear increasing trend in both the 7-year-old and the 10 to 16-year-old (χ2=27.56, 10.69, 6.10, 27.26, 18.32, 25.71, 10.53, 6.14, P < 0.05). Conclusions The risk of elevated blood pressure in primary and secondary school students increases with BMI, showing a non-linear dose-response relationship. The blood pressure should be monitored regularly, and comprehensive and effective measures should be implemented to control elevated blood pressure in children and adolescents. -
Key words:
- Blood pressure /
- Body mass index /
- Regression analysis /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 不同BMI分组中小学生基本指标比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of basic indicators of primary and secondary school students among different BMI subgroups(x±s)
BMI分组 人数 年龄/岁 身高/cm 体重/kg 腰围/cm 臀围/cm 舒张压/mmHg 收缩压/mmHg 腰臀比 T1 1 833 10.09±2.62 144.49±15.64 28.69±8.33 58.06±6.59 70.77±8.31 65.38±9.14 100.84±12.09 0.82±0.08 T2 2 192 10.79±2.49 148.62±16.02 33.09±9.33 59.85±6.66 73.74±8.61 66.06±8.78 104.22±12.75 0.82±0.07 T3 52 702 10.24±2.64 146.93±16.64 38.57±12.48 63.67±7.74 77.85±10.35 66.75±8.86 106.75±13.38 0.82±0.07 T4 15 693 10.48±2.62 150.73±16.51 50.08±15.75 72.04±9.13 85.89±11.24 68.45±9.04 112.61±14.20 0.84±0.07 T5 19 671 10.15±2.51 151.56±15.86 61.08±20.55 81.71±11.85 92.81±12.57 70.44±9.51 116.93±15.42 0.88±0.07 F值 63.87 76.08 9 412.79 6 348.41 7 974.64 151.84 712.92 22.86 P值 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 注: 1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。 表 2 BMI-Z分与中小学生血压偏高的相关性[OR值(95%CI)]
Table 2. Correlation of BMI-Z scores and elevated blood pressure among primary and secondary school students[OR(95%CI)]
BMI分组 男生(n=48 343) 女生(n=43 748) 总体(n=92 091) T1 0.44(0.29~0.67)* 0.68(0.49~0.95)* 0.55(0.43~0.71)* T2 0.47(0.33~0.66)* 0.69(0.51~0.93)* 0.53(0.42~0.66)* T3 1.00 1.00 1.00 T4 1.75(1.61~1.90)* 2.06(1.90~2.23)* 1.90(1.80~2.01)* T5 3.56(3.32~3.83)* 3.64(3.38~3.92)* 3.71(3.52~3.90)* χ趋势2 4 723.75 3 956.50 8 310.22 P值 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 注: *P < 0.05。 表 3 不同性别、年龄、腰臀比分层下中小学生BMI和血压偏高的Logistic回归分析
Table 3. Logistic regression analysis of BMI and elevated blood pressure among primary and secondary school students by sex, age and waist-to-hip ratio
自变量 选项 血压偏高数 β值 标准误 Wald χ2值 OR值(95%CI) P值 性别 男 48 343 0.18 0.00 49.68 1.18(1.17~1.19) < 0.01 女 43 748 0.18 0.00 45.69 1.19(1.18~1.20) < 0.01 年龄/岁 7~8 28 445 0.14 0.01 26.38 1.15(1.14~1.17) < 0.01 9~11 31 893 0.20 0.01 40.84 1.22(1.21~1.24) < 0.01 12~14 26 511 0.18 0.00 45.24 1.19(1.18~2.00) < 0.01 15~16 5 242 0.16 0.01 20.34 1.18(1.16~1.19) < 0.01 腰臀比 ≤0.83 53 213 0.18 0.00 49.79 1.19(1.19~1.20) < 0.01 >0.83 38 878 0.17 0.00 47.68 1.18(1.17~1.19) < 0.01 注:年龄根据四分位数分组,腰臀比根据中位数分组;调整变量为性别、年龄、腰臀比,分层组不调整自身;BMI为自变量,按照连续变量处理。 -
[1] ARBE G, PASTOR I, FRANCO J. Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to the hypert ensive crisis[J]. Med Clin (Barc), 2018, 150(8): 317-322. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2017.09.027 [2] 黄婕, 曾淳子, 马婕, 等. 2016—2019年广州市农村9~12岁儿童青少年血压偏高与体质指数的关联分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2023, 50(19): 3519-3524. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202319011.htmHUANG J, ZENG C Z, MA J, et al. Relationship between high blood pressure and body mass index in children and adolescents aged 9 to 12 years in rural areas of Guangzhou from 2016 to 2019[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2023, 50(19): 3519-3524. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202319011.htm [3] COHEN J L, NEES S N, VALENCIA G A, et al. Sildenafil use in children with pulmonary hypertension[J]. J Pediatr, 2019, 205: 29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.09.067 [4] YALI L, BENMAI L, JUAN X, et al. Prevalence of hypertension and prehypertension and its association with anthropometrics among children: a cross-sectional survey in Tianjin, China[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2018, 32(11): 789-798. doi: 10.1038/s41371-018-0088-4 [5] 张奕, 蒋家诺, 陈力, 等. 厦门市儿童肥胖和高血压共病现状及其多维度影响因素[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2023, 44(10): 1464-1467. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.10.006ZHANG Y, JIANG J N, CHEN L, et al. Current status and multidimensional influences on the comorbidity of obesity and high blood pressure among children in Xiamen City[J]. Chin J Sch Heath, 2023, 44(10): 1464-1467. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.10.006 [6] 白鹤, 周佳丽, 程思清, 等. 儿童高血压研究热点与前沿分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2023, 44(4): 606-611. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.04.030BAI H, ZHOU J L, CHENG S Q, et al. Research hotspots and frontiers of childhood hypertension[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2023, 44(4): 606-611. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.04.030 [7] ABMAJID N L, OMAR M A, KHOO Y Y, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in the Malaysian population: findings from the national health and morbidity survey 2006-2015[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2018, 32(8/9): 617-624. [8] RASHIDI H, ERFANIFAR A, LATIFI S M, et al. Incidence of obesity, overweight and hypertension in children and adolescents in Ahvaz southwest of Iran: five years study[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2019, 13(1): 201-205. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.05.021 [9] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 学生健康体检技术规范: GB/T 26343—2010[S]. 2011-05-01.Ministry of Health of the PRC. Technical specifications for student health examination: GB/T 26343-2010[S]. 2011-05-01. (in Chinese) [10] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查: WS/T 586—2018[S]. 2018-08-01.National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC. Screening for overweight and obesity among school-age children and adolescents: WS/T 586-2018[S]. 2018-08-01. (in Chinese) [11] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 7~18岁儿童青少年血压偏高筛查界值: WS/T 610—2018[S]. 2018-12-01.National Health Commission of the PRC. Reference of screening for elevated blood pressure among children and adolescents aged 7-18 years: WS/T 610-2018[S]. 2018-12-01. (in Chinese) [12] DEONIS M, ONYANGO A W, BORGHI E, et al. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents[J]. Bull World Health Organ, 2007, 85(9): 660-667. doi: 10.2471/BLT.07.043497 [13] DONG Y, MA J, SONG Y, et al. Secular trends in blood pressure and overweight and obesity in Chinese boys and girls aged 7 to 17 years from 1995 to 2014[J]. Hypertension, 2018, 72(2): 298-305. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11291 [14] FREEDMAN D S, WOO J G, OGDEN C L, et al. Distance and percentage distance from median BMI as alternatives to BMI score[J]. Br J Nutr, 2020, 124: 493-500. doi: 10.1017/S0007114519002046 [15] 葛文鑫, 谭伟良, 滕皓玥, 等. 苏州市儿童BMI-Z变化轨迹与青春晚期血压偏高的关联研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(10): 1809-1816.GE W X, TAN W L, TENG H Y, et al. Trajectories of body mass index Z-score and risk of high blood pressure in late adolescence in Suzhou children[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2021, 42(10): 1809-1816. (in Chinese) [16] LLEWELLYN A, SIMMONDS M, OWEN C G, et al. Childhood obesity as a predictor of morbidity in adulthood: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Obes Rev, 2016, 17(1): 56-67. [17] WANG X, DONG B, HUANG S, et al. Body mass index trajectory and incident hypertension: results from a longitudinal cohort of Chinese children and adolescents, 2006-2016[J]. Am J Public Health, 2020, 110(11): 1689-1695. [18] 陈春伟, 孙赞, 戚尧, 等. 徐州地区12~17岁青少年体质量指数和高血压患病风险的关系[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2023, 31(5): 465-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ202305012.htmCHEN C W, SUN Z, QI Y, et al. Body mass index of 12-17 year old adolescents in Xuzhou Area and risk of hypertension[J]. Chin J Hypertens, 2023, 31(5): 465-468. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGZ202305012.htm [19] 古力曼·木黑亚提, 梅玉洁, 陶宁. 基于限制性立方样条模型分析新疆石油工人血脂水平与高血压的关系[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2023, 27(4): 392-398. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ202304004.htmMUHEIYATI G, MEI Y J, TAO N. Relationship between blood lipid level and hypertension in Xinjiang oil workers based on restricted cubic spline model[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2023, 27(4): 392-398. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ202304004.htm [20] 陈咏梅, 范明明. 开封市中学生超重肥胖与血压偏高的关联[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2022, 43(2): 300-303. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.02.032CHEN Y M, FAN M M. Relationship between overweight, obesity and high blood pressure among middle school students in Kaifeng City[J]. Chin J Sch Heath, 2022, 43(2): 300-303. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.02.032 [21] LARKINSN G, TEIXEIRA P A, KIM S, et al. The population-based prevalence of hypertension and correlates of blood pressure among Australian children[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2019, 34(6): 1107-1115. [22] GRASSI G, BIFFI A, SERAVALLE G, et al. Sympathetic neural overdrive in the obese and overweight state: Meta-analysis of published studies[J]. Hypertension, 2019, 74(2): 349-358. -







 下载:
下载: