Aassociation of school natural environment perception, exercise identification and exercise behavior among junior high school students
-
摘要:
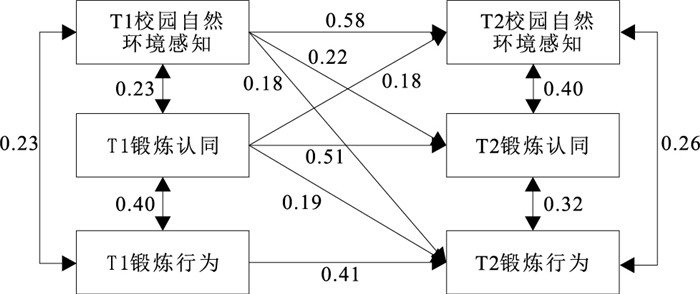
目的 分析初中生校园自然环境感知、锻炼认同与其锻炼行为的关系,为促进和改善初中生锻炼行为提供参考。 方法 于2023年3—6月,采用方便抽样和分层整群随机抽样相结合的方法从江苏、安徽、江西、吉林、河南5个省抽取607名初中生进行为期3个月、两阶段的纵向追踪调查(T1:2023年3月,T2:2023年6月),采用校园自然环境感知量表、锻炼认同量表和体育活动等级量表进行评估。采用相关性分析和构建交叉滞后模型探讨初中生校园自然环境感知和锻炼认同与锻炼行为的关联。 结果 T1和T2时初中生的校园自然环境感知、锻炼认同与锻炼行为之间两两均呈正相关(r=0.04~0.61,P值均<0.01)。交叉滞后分析显示,T1校园自然环境感知可以预测T2锻炼认同(β=0.22)和T2锻炼行为(β=0.18),T1锻炼认同可以预测T2校园自然环境感知(β=0.18)及T2锻炼行为(β=0.19)(P值均<0.01);而T1锻炼行为对T2校园自然环境感知(β=0.03)和T2时锻炼认同(β=0.03)的影响均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。 结论 初中生校园自然环境感知及锻炼认同均是锻炼行为的原因变量,且校园自然环境感知与其锻炼认同具备交互效应。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the relationship of school natural environment perception, exercise identification and exercise behavior, so as to provide references for promoting and improving exercise behavior among junior high school student. Methods A total of 607 junior high school students were selected from Jiangsu, Anhui, Jiangxi, Jilin and Henan provinces by adopting a combination of convenience sampling and stratified cluster random sampling methods, and a longitudinal tracking survey was conducted over a three-month period in two stages (T1: March 2023, T2: June 2023), from March to June 2023. Assessment was carried out by using School Natural Environment Perception Scale, Physical Exercise identification Scale and Physical Activity Rating Scale. The associations of school natural environment perception, exercise identification and exercise behavior were explored using correlation analysis and the cross-lagged model. Results For the junior high school students during T1 and T2 periods, there were positive correlations between the two of school natural environment perception, exercise identification and exercise behavior (r=0.04-0.61, P < 0.01). The cross-lagged analysis revealed that school natural environment perception in T1 period significantly predicted exercise identification (β=0.22, P < 0.01) and exercise behavior (β=0.18, P < 0.01) in T2 period. Moreover, the exercise identification in T1 period significantly predicted school natural environment perception (β=0.18, P < 0.01) and exercise behavior in T2 period (β=0.19, P < 0.01). However, the effects of exercise behavior on the school natural environment perception (β=0.03) and exercise identification (β=0.03) were not statistically significant (P>0.05). Conclusions For the junior high school students, school natural environment perception and exercise identification are the cause variables of the exercise behavior. Moreover, school natural environment perception and exercise identification have an interactive effect. -
Key words:
- Environment /
- Perception /
- Exercise movement techniques /
- Identification(psychology) /
- Behavior /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 初中生校园自然环境感知和锻炼认同与锻炼行为的相关性分析(r值,n=607)
Table 1. Partial correlation analysis of school natural environment perception, exercise identification and exercise behavior among junior high school students(r, n=607)
变量 T1校园自然环境感知 T2校园自然环境感知 T1锻炼认同 T2锻炼认同 T1锻炼行为 T2校园自然环境感知 0.54 T1锻炼认同 0.21 0.21 T2锻炼认同 0.26 0.46 0.61 T1锻炼行为 0.04 0.04 0.40 0.31 T2锻炼行为 0.11 0.21 0.35 0.46 0.49 注:P值均<0.01。 -
[1] 丹豫晋, 刘映海. 家庭体育支持与青少年体质的关系研究[J]. 教育理论与实践, 2015, 35(34): 30-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYLL201534007.htmDAN Y J, LIU Y H. Study on the relationship between family sport support and BMI of teenagers[J]. Theory Pract Educ, 2015, 35(34): 30-33. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYLL201534007.htm [2] 董宝林. 个体、家庭及学校因素对青少年体育锻炼行为的交互影响研究[D]. 上海: 上海体育学院, 2021.DONG B L. Research on the interactive influence of the factors of individual, family and school on adolescents' physical exercise behavior[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Sport, 2021. (in Chinese) [3] DOMINICK G M, SAUNDERS R P, FRIEDMAN D B, et al. Factors associated with provision of instrumental social support for physical activity in a foster parent population[J]. Child Youth Serv Rev, 2015, 52: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2015.02.005 [4] 叶浩生, 苏佳佳. 预测认知模型: 认知科学的新统一范式?[J]. 南京师大学报(社会科学版), 2022(5): 65-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJSS202205007.htmYE H S, SU J J. Predictive cognition model: a new unified paradigm of cognitive science?[J]. J Nanjing Norm Univ (Soc Sci Edit), 2022(5): 65-78. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJSS202205007.htm [5] 徐陆璐, 董宝林. 同伴关系、主观锻炼体验与青少年余暇锻炼习惯的关系: 一项交叉滞后分析[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2020, 35(6): 697-702. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY202006014.htmXU L L, DONG B L. Relationship of peer relationship, subjective exercise experience, and adolescents' leisure physical exercise habits: a cross-lagged analysis[J]. J Tianjin Univ Sport, 2020, 35(6): 697-702. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY202006014.htm [6] 梁德清. 高校学生应激水平及其与体育锻炼的关系[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 1994, 8(1): 5-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXWS401.001.htmLIANG D Q. Stress level of college students and its relationship with physical exercises[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 1994, 8(1): 5-6. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXWS401.001.htm [7] 纪林芹, 潘斌, 王春燕, 等. 青少年早期同伴拒绝、同伴侵害与抑郁的关系: 交叉滞后分析[J]. 心理科学, 2018, 41(3): 579-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLKX201803011.htmJI L Q, PAN B, WANG C Y, et al. A cross-lagged analysis of associations between peer rejection, peer victimization and depression in early adolescence[J]. J Psychol Sci, 2018, 41(3): 579-585. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLKX201803011.htm [8] 许欣, 姚家新, 杨剑, 等. 基于知信行理论的父母—儿童运动参与的关系[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2014, 37(10): 89-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD201410017.htmXU X, YAO J X, YANG J, et al. Relationship among parents and child's sport participation: based on the oretical model of knowledge, attitude and practice[J]. J Beijing Sport Univ, 2014, 37(10): 89-95. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD201410017.htm [9] SALLIS J F, OWEN N, FISHER E B. Ecological models of health behavior[J]. Health Educ Behav, 2008, 4: 465-485. [10] 论宇超, 王辉, 韩增林, 等. 社区和学校邻里建成环境对青少年体质健康的影响: 以大连市初中学生为例[J]. 地理研究, 2023, 42(7): 1842-1855. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ202307008.htmLUN Y C, WANG H, HAN Z L, et al. Effects of community and school neighborhood built environment on adolescents' physical fitness: a case study of junior high school students in Dalian[J]. Geogr Res, 2023, 42(7): 1842-1855. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ202307008.htm [11] ALVARSSON J J, WIENS S, NILSSON M E. Stress recovery during exposure to nature sound and environmental noise[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2010, 7(3): 1036-1046. [12] KIM Y, KOSMA M. Psychosocial and environmental correlates of physical activity among Korean older adults[J]. Res Ag, 2013, 35(6): 750-767. [13] 程韵枫, 董宝林. 锻炼氛围、主观体验对大学生余暇体育锻炼的影响[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2018, 33(2): 177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY201802012.htmCHEN Y F, DONG B L. The influence of exercise atmosphere and subjective experience on leisure sports exercise of college students[J]. J Tianjin Univ Sport, 2018, 33(2): 177-184. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY201802012.htm [14] 董宝林, 毛丽娟. 学校人际支持、锻炼认同与青少年锻炼行为的关系[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2020, 43(9): 86-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD202009010.htmDONG B L, MAO L J. The relationship among interpersonal support of school, exercise identity and adolescents' exercise behavior[J]. J Beijing Sport Univ, 2020, 43(9): 86-98. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD202009010.htm [15] 虞力宏, 汤国杰, 高可清. 高校体育教师职业认同与工作投入的关系研究[J]. 中国体育科技, 2011, 47(6): 136-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY201106024.htmYU L H, TANG G J, GAO K Q. Study on relationship between the professional identity and the work engagement of college sports teachers[J]. China Sport Sci Technol, 2011, 47(6): 136-141. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY201106024.htm [16] 乐国安, 韩振华. 认知心理学[M]. 天津: 南开大学出版社, 2011.YUE G A, HAN Z H. Cognitive psychology[M]. Tianjin: Nankai University Press, 2011. (in Chinese) [17] AMORNSRIWATANAKUL A, LESTER L, BULL F C, et al. Ecological correlates of sport and exercise participation among Thai adolescents: a hierarchical examination of a cross-sectional population survey[J]. J Sport Health Sci, 2023, 12(5): 592-605. [18] LAKOFF G, JOHNSON M. The metaphorical structure of the human conceptual system[J]. Cognit Sci, 1980, 4(2): 195-208. [19] BANDURA A. Social learning theory of aggression[J]. J Commun, 2010, 28(3): 12-29. [20] GIULIANI M V, FELDMAN R. Place attachment in a developmental and cultural context[J]. J Environ Psychol, 1993, 13(3): 267-274. [21] 蔡玉军, 周鹏, 张本家, 等. 城市居民公共体育空间感知与体育活动行为的关系[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2018, 44(4): 48-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SORT201804009.htmCAI Y J, ZHOU P, ZHANG B J, et al. The relationship between urban residents' public sports space perception and physical activity behavior[J]. J Chengdu Sport Univ, 2018, 44(4): 48-53. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SORT201804009.htm [22] BREAKWELL G M. Coping with threatened identity[M]. London: Methuen, 1986. [23] HIDALGO M C, HERNÁNDEZ B. Place attachment: conceptual and empirical questions[J]. J Environ Psychol, 2001, 21: 273-281. [24] HENRY E S. Bodies at home and at school: toward a theory of embodied social class status[J]. Educ Theory, 2013, 63(1): 1-16. -







 下载:
下载: