Analysis of exercise density and exercise load in different physical classes for second-year junior high school students from Beijing City
-
摘要:
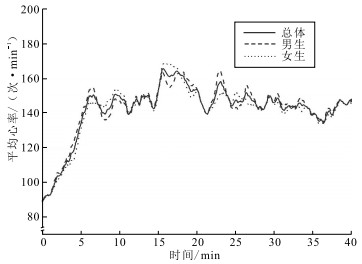
目的 探究北京初二学生不同体能课的运动强度、有效运动负荷情况,为优化体能课的教学内容、合理调控运动负荷、科学开展体育教学提供参考。 方法 于2022年10—11月,选取北京市西城区某中学初二30名学生,通过Polar心率采集设备监测体能课心率,采用心率区间和训练冲量(TRIMP)量化运动强度和运动负荷,采用独立样本t检验对不同维度心率差异进行统计分析。 结果 初二学生体能课平均心率为(140.62±9.41)次/min,有效运动负荷(心率≥120次/min)时间占比为77.2%,中高强度(MVPA)的心率负荷时间占比为51.9%。速度练习、速度耐力练习、耐力练习体能课的平均心率为(137.89±8.82)(137.67±11.27)(145.35±8.98)次/min。体育课男女生的平均心率为(144.22±24.95)(136.31±28.78)次/min,差异无统计学意义(t=4.04,P>0.05),男、女生有效运动负荷累计时长分别为(34.08±7.52)(28.43±5.39)min。体能课平均TRIMP值为(100.46±16.56),练习密度为72.06%。 结论 北京初二学生体能课运动强度适宜,以中高强度为主,MVPA累计时间充足;学生平均心率、练习密度达到要求。应根据学生体质的个体差异科学设置体能课运动负荷,提升中学生体质健康水平。 Abstract:Objective To explore the exercise intensity and effective exercise load of different physical fitness classes for second-year junior high school students in Beijing, so as to provide a reference for optimizing the teaching content of physical fitness classes, reasonably regulating exercise load and the scientific development of physical fitness. Methods From October to November 2022, 30 second-year junior high school students from a middle school in Xicheng District, Beijing were selected to have their heart rate monitored during physical fitness classes using Polar heart rate monitors. Heart rate intervals and training impulse (TRIMP) were used to quantify exercise intensity and load. Independent sample t-test was used to statistically analyze differences in heart rate across different dimensions. Results The average heart rate of students in physical fitness classes was (140.62±9.41) counts/min, with effective exercise load (heart rates ≥120 counts/min) time accounting for 77.2%, and heart rate load of moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) time accounting for 51.9%. The average heart rates for speed, speed endurance, and endurance physical fitness classes were (137.89±8.82) (137.67±11.27) and (145.35±8.98) counts/min, respectively. The average heart rates of male and female students in physical education class were (144.22±24.95) and (136.31±28.78) counts/min, and the difference was not statistically significant (t=4.04, P>0.05). The cumulative durations of effective exercise load among male and female students were (34.08±7.52) and (28.43±5.39) min, respectively. The average TRIMP value for physical fitness classes were (100.46±16.56), with a exercise density of 72.06%. Conclusions The exercise intensity of physical fitness classes for second-year junior high school students in Beijing is appropriate, mainly with moderate to vigorous intensity, and the accumulated time of MVPA is sufficient. The average heart rate and exercise density of students meet the requirements. Scientific setting of physical fitness class exercise load should be based on individual differences in students' physical fitness, in order to improve the physical health level of middle school students. -
Key words:
- Exercise movement techniques /
- Curriculum /
- Motor activity /
- Body burden /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 不同性别学生体能课平均心率(x±s, 次/min)
Table 1. Average heart rate in physical education for students of different genders (x±s, counts/min)
性别 人数 速度练习 速度耐力练习 耐力练习 总计 女 15 135.65±8.74 132.03±9.67 140.69±9.37 136.31±28.78 男 15 140.15±8.59 142.55±10.46 150.35±5.22 144.22±24.95 合计 30 137.89±8.82 137.67±11.27 145.35±8.98 140.62±9.41 表 2 不同教学内容体能课不同运动强度心率负荷累计时间占比/%
Table 2. The proportion of the cumulative time of different exercise intensity load in different teaching contents/%
体能课 不同运动强度心率负荷累计时间占比 有效运动负荷占比 很小强度 小强度 中等强度 高强度 极限强度 速度练习 21.9 25.7 30.8 18.1 3.5 78.1 速度耐力 25.2 27.3 24.4 15.6 7.5 74.8 耐力练习 20.3 24.4 25.2 18.4 11.7 78.6 表 3 不同教学内容体能课TRIMP(x±s)
Table 3. TRIMP Comparison among different physical education courses (x±s)
体能课 很小强度 小强度 中等强度 高强度 极限强度 TRIMP 速度练习 4.76±1.19 20.56±9.84 37.02±12.75 28.64±10.08 6.90±2.79 97.88±11.45 速度耐力 6.20±2.31 21.88±7.14 29.06±10.66 23.12±6.40 15.00±4.26 95.26±9.16 耐力练习 5.60±1.03 19.64±6.32 30.18±9.79 29.36±7.28 23.30±5.13 108.80±14.54 -
[1] 商燕桦, 徐雷, 王泽凤, 等. 初中体育课运动负荷强度特征及其与体质的相关性[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2020, 41(4): 563-565, 572. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.04.022SHANG Y H, XU L, WANG Z F, et al. Sports load intensity in junior middle school physical education class and its correlation with physical constitution[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2020, 41(4): 563-565, 572. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.04.022 [2] 中华人民共和国教育部体育卫生与艺术教育司. 第八次全国学生体质与健康调研结果发布[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2021, 42(9): 1281-1282. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.09.001Department of Physical Health and Arts Education, Ministry of Education of the PRC. Release report of the Eighth National Survey on Student Physical Fitness and Health[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2021, 42(9): 1281-1282. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.09.001 [3] 孟文砚. 聚焦核心素养提升体育课堂教学质量[J]. 中国学校体育, 2023, 42(1): 2-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXT202301001.htmMENG W Y. Focusing on core literacy to improve the quality of physical education classroom teaching[J]. Chin Sch Phys Educ, 2023, 42(1): 2-3. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXT202301001.htm [4] 季浏. 我国《义务教育体育与健康课程标准(2022年版)》解读[J]. 体育科学, 2022, 42(5): 3-17, 67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX202205001.htmJI L. Interpretation of National Physical Education and Health Curriculum Standards for Compulsory Education (2022 Edition) in China[J]. Sports Sci, 2022, 42(5): 3-17, 67. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX202205001.htm [5] 何玉敏, 刘军, 席宇豪, 等. 心率区间和训练冲量对小学生体育课运动负荷评价的实验研究[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2022, 43(3): 378-381. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.03.014HE Y M, LIU J, XI Y H, et al. An experimental study on the evaluation of heart rate interval and training impulse on the exercise load of primary school students in physical education[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2022, 43(3): 378-381. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.03.014 [6] 胡展红. 调控初中体育教学的运动负荷, 全面提高学生健康水平[J]. 冰雪体育创新研究, 2022(6): 126-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYT202206043.htmHU Z H. Regulating the exercise load in junior high school physical education teaching and comprehensively improving students' health Level[J]. Innovat Res Ice Snow Sports, 2022(6): 126-128. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYT202206043.htm [7] 北京市市场监督管理局. 中小学生体育与健康课运动负荷监测与评价: DB11/T 1704—2019[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2019.Beijing Municipal Bureau of Market Supervision and Administration. Monitoring and evaluation of physical education and heaIth class sports load of primary and middle school students: DB11/T 1704-2019[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2019. (in Chinese) [8] 王正珍. ACSM运动测试与运动处方指南[M]. 北京: 北京体育大学出版社, 2019.WANG Z Z. ACSM's Guidelines for exercise testing and prescription[M]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University Press, 2019. (in Chinese) [9] 毛振明. 要科学地加强体育课的密度与负荷: 评"中国健康体育课程模式"的密度和强度理论[J]. 教育家, 2019(42): 40-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYJA201942018.htmMAO Z M. To scientifically strengthen the density and load of physical education courses: a review of the density and intensity theory of the "Chinese Health Physical Education Curriculum Model"[J]. Educator, 2019(42): 40-42. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYJA201942018.htm [10] 季浏. 坚持"三个导向"的义务教育体育与健康课程标准(2022年版)解析[J]. 体育学刊, 2022, 29(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYXK202203001.htmJI L. Analysis of the curriculum standards for physical education and health in compulsory education adhering to the "Three Directions" (2022 Edition)[J]. J Phys Educ, 2022, 29(3): 1-7. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYXK202203001.htm [11] 周誉, 冯强. 北京市西城区高中生体育课生理负荷现状[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40(1): 96-99. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.01.026ZHOU Y, FENG Q. Physiological load of physical education class of high schools in Xicheng District of Beijing[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2019, 40(1): 96-99. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.01.026 [12] 吴衍忠. 论运动负荷价值阈在体育教学中的运用[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 1999, 22(4): 87-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD199904024.htmWU Y Z. On the application of the value threshold of exercise load in physical education teaching[J]. J Beijing Sport Univ, 1999, 22(4): 87-89. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD199904024.htm [13] 王德涛, 吕和武, 李畑存. 《5岁以下儿童体力活动、久坐行为和睡眠指南》特征及启示[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2023, 44(5): 645-648. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.05.002WANG D T, LYU H W, LI T C. Characteristics and enlightenment of Guidelines on Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior and Sleep for Children under 5 Years of Age[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2023, 44(5): 645-648. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.05.002 [14] 李京诚, 徐曰婷, 郝军. 中小学体育课不同教学内容运动负荷监测结果的分析与比较[J]. 体育教学, 2019, 39(3): 19-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYJX201903008.htmLI J C, XU Y T, HAO J. Analysis and comparison of exercise load monitoring results for different teaching contents of physical education classes in primary and secondary schools[J]. Phys Educ Teaching, 2019, 39(3): 19-21. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYJX201903008.htm -







 下载:
下载: