Cross-lagged analysis of adolescent social adaptability, physical exercise and mental health
-
摘要:
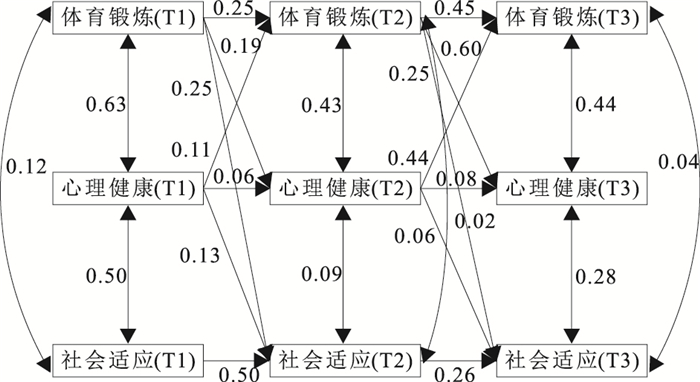
目的 探讨青少年社会适应能力与体育锻炼及心理健康之间的作用机制,为促进青少年社会适应能力提升及身心健康发展提供理论依据。 方法 采用整群随机抽样方法,于2021年9月(T1)、2022年1月(T2)和2022年6月(T3)对山东省济南市1 163名中小学生的社会适应能力、体育锻炼及心理健康水平进行纵向追踪调查数据,通过交叉滞后分析青少年社会适应能力、体育锻炼与心理健康的关系。 结果 青少年体育锻炼和心理健康在T1、T2、T3上的性别差异均有统计学意义(Z值分别为-3.83,-3.43,-4.59;-12.45,-8.93,-8.72,P值均 < 0.01),且男生体育锻炼和心理健康水平均优于女生;而社会适应能力(T1、T2、T3)的性别差异均无统计学意义(Z值分别为-0.79,-1.19,-1.34,P值均>0.05)。青少年在社会适应能力、体育锻炼和心理健康上存在稳定、同步的正相关性(r=0.18~0.67,r=0.12~0.68,P值均 < 0.01);青少年体育锻炼、心理健康均可以跨时间预测社会适应能力(βT1-T2值分别为0.25,0.13;βT2-T3值分别为0.25,0.06,P值均 < 0.05),且心理健康在体育锻炼对社会适应能力的影响路径上存在中介效应(β=0.14,P < 0.05)。 结论 青少年体育锻炼、心理健康与社会适应能力之间存在纵向因果关系。应加强青少年体育锻炼、提高青少年心理健康水平,从而有效提升青少年社会适应水平。 Abstract:Objective To explore the relationships among social adaptation, physical exercise, and mental health of adolescents, so as to provide theoretical basis for social adaptation and mental health improvement. Methods Longitudinal follow-up survey data were collected from 1 163 adolescents in Jinan City, Shandong Province in September 2021 (T1), January 2022 (T2), and June 2022 (T3) by cluster random sampling method. The relationship between social adaptability, physical exercise, and mental health of adolescents was analyzed through cross lagged analysis. Results There were significant sex differences in physical exercise and mental health among adolescents on T1, T2, and T3 (Z=-3.83, -3.43, -4.59; -12.45, -8.93, -8.72, P < 0.01), with male students had more physical exercise [35(28, 42), 36(33, 42), 38(35, 43)] and better mental health [12(12, 17), 17(17, 21), 14(14, 26)] levels than female students [33(27, 40), 35(31, 40), 36(33, 41); 9(9, 12), 12(12, 23), 12(12, 23)]. No similar sex difference in social adaptability (T1, T2, T3) [male: 22 (14, 24), 22 (14, 24), 22 (16, 24); female: 21 (11, 23), 20 (14, 24), 22 (17, 24)] (Z=-0.79, -1.19, -1.34, P>0.05). Temporal and synchronous correlations were found in social adaptability, physical exercise and mental health (r=0.18-0.67, 0.12-0.68, P < 0.01). Teenager physical exercise and mental health could predict social adaptability across time (βT1-T2=0.25, 0.13; βT2-T3=0.25, 0.06, P < 0.05), with a mediating effect on the impact path of physical exercise on social adaptability in psychological health (β=0.14, P < 0.05). Conclusions There is a causal relationship between physical exercise, mental health, and social adaptability among adolescents. Encouraging adolescents to actively participate in physical exercise and promoting mental health can effectively enhance their social adaptability. -
Key words:
- Social adjustment /
- Exercise movement techniques /
- Mental health /
- Adolescent
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 不同性别青少年不同测试时间社会适应能力、体育锻炼及心理健康量表得分比较[M(P25,P75)]
Table 1. Comparison of social adaptability, physical exercise and mental health scale scores among teenagers of different genders at different test times[M(P25, P75)]
性别 人数 社会适应T1 体育锻炼T1 心理健康T1 社会适应T2 体育锻炼T2 心理健康T2 社会适应T3 体育锻炼T3 心理健康T3 男 595 22(14, 24) 35(28, 42) 12(12, 17) 22(14, 24) 36(33, 42) 17(17, 21) 22(16, 24) 38(35, 43) 14(14, 26) 女 568 21(11, 23) 33(27, 40) 9(9, 12) 20(14, 24) 35(31, 40) 12(12, 23) 22(17, 24) 36(33, 41) 12(12, 23) 合计 1 163 22(13, 24) 34(27, 41) 12(9, 14) 22(14, 24) 36(32, 41) 16(12, 22) 22(16, 24) 37(33, 43) 14(13, 24) Z值 -0.79 -3.83 -12.45 -1.19 -3.43 -8.93 -1.34 -4.59 -8.72 P值 0.43 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.24 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.18 < 0.01 < 0.01 表 2 青少年社会适应能力、体育锻炼及心理健康的相关系数(r值,n=1 163)
Table 2. Correlation coefficient between adolescents' social adaptability, physical exercise and mental health(r, n=1 163)
变量 社会适应T1 体育锻炼T1 心理健康T1 社会适应T2 体育锻炼T2 心理健康T2 社会适应T3 体育锻炼T3 体育锻炼T1 0.63 心理健康T1 0.50 0.12 社会适应T2 0.59 0.54 0.15 体育锻炼T2 0.65 0.58 0.19 0.68 心理健康T2 0.39 0.35 0.18 0.19 0.26 社会适应T3 0.67 0.45 0.49 0.43 0.44 0.17 体育锻炼T3 0.64 0.64 0.15 0.54 0.67 0.59 0.40 心理健康T3 0.29 0.31 0.18 0.41 0.60 0.24 0.17 0.46 注:P值均 < 0.01。 -
[1] 逯小龙, 王坤. 课外体能锻炼对大学生心理资本心理健康及社会适应能力的影响[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40(3): 392-395. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.03.021LU X L, WANG K. Influence of extracurricular physical exercise on psychological capital, psychological health and social adaptability of college students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2019, 40(3): 392-395. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.03.021 [2] 孙双明, 刘波, 孙妍, 等. 青少年体育参与和社会适应关系的实证研究: 以清华大学为个案[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2019, 42(2): 76-85, 125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD201902009.htmSUN S M, LIU B, SUN Y, et al. An empirical study on the relationship between youth sports participation and social adjustment: taking Tsinghua University as a case[J]. J Beijing Sport Univ, 2019, 42(2): 76-85, 125. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD201902009.htm [3] 杨颖, 邹泓, 余益兵, 等. 中学生社会问题解决能力的特点及其与社会适应的关系[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2011, 27(1): 44-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLFZ201101006.htmYANG Y, ZOU H, YU Y B, et al. The characteristics of adolescents' social problem solving ability and its relationship with social adaption[J]. Psychol Dev Educ, 2011, 27(1): 44-51. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLFZ201101006.htm [4] 杨剑, 王韶君, 季浏, 等. 中学生运动友谊质量、体育锻炼行为与心理健康关系模型构建[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报, 2013, 32(4): 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYTB201304004.htmYANG J, WANG S J, JI L, et al. Constructing model of relationship among middle school students' sport friendship quality, physical exercise behavior and mental health[J]. J Shenyang Sport Univ, 2013, 32(4): 9-13. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYTB201304004.htm [5] 周翔, 陈强, 吴静, 等. 拓展训练改善中学生心理健康水平和社会适应能力的研究[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2015, 36(2): 245-247, 251. http://www.cjsh.org.cn/article/id/zgxxws201502024ZHOU X, CHEN Q, WU J, et al. Impact of outward training on psychological health and social adaptability of junior middle school students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2015, 36(2): 245-247, 251. (in Chinese) http://www.cjsh.org.cn/article/id/zgxxws201502024 [6] 辛勇, 刘传军, 陈幼平. 四川省流动儿童社会适应能力时间管理倾向与心理健康的关系[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2016, 37(1): 63-66. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2016.01.019XIN Y, LIU C J, CHEN Y P. Relationships among social adaption, time management and mental health among floating children in Sichuan[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2016, 37(1): 63-66. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2016.01.019 [7] 郑日昌. 大学生心理诊断[M]. 济南: 山东教育出版社, 1999: 440-443.ZHENG R C. Psychological diagnosis of college students[M]. Jinan: Shandong Education Press, 1999: 440-443. (in Chinese) [8] 梁德清. 高校学生应激水平及其与体育锻炼的关系[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 1994, 8(1): 5-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXWS401.001.htmLIANG D Q. The stress level of college students and its relationship with physical exercise[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 1994, 8(1): 5-6. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXWS401.001.htm [9] 李艺敏, 李永鑫. 12题项一般健康问卷(GHQ-12)结构的多样本分析[J]. 心理学探新, 2015, 35(4): 355-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXT201504012.htmLI Y M, LI Y X. The factor structure of the 12-item General Health questionnaire: the multi-group analyses[J]. Psychol Explor, 2015, 35(4): 355-359. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXT201504012.htm [10] 王聪帅, 闫建华. 大学生新冠肺炎疫情风险感知与体育锻炼及心理健康的关系[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2022, 43(11): 1664-1667, 1672. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.11.016WANG C S, YAN J H. Association of COVID-19 epidemic risk perception, physical exercise and mental health in college students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2022, 43(11): 1664-1667, 1672. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.11.016 [11] 林晓桂, 徐建清. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情下体育锻炼对大学生心理健康的影响[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2020, 41(11): 1682-1687. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.11.023LIN X G, XU J Q. Influence of physical exercise on mental health of college students during the epidemic of COVID-19[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2020, 41(11): 1682-1687. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.11.023 [12] 秦国阳, 贾巍, 秦勇. 济南市中小学生2019—2022年体质健康水平变化[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2023, 44(9): 1373-1381. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.09.021QIN G Y, JIA W, QIN Y. Changes in physical health among primary and secondary school students in Jinan City during 2019 to 2022[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2023, 44(9): 1373-1381. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.09.021 [13] 张文娟, 邹泓, 梁钰苓. 青少年父母支持的特点及其对社会适应的影响: 情绪智力的中介作用[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2012, 28(2): 160-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLFZ201202010.htmZHANG W J, ZOU H, LIANG Y L. The characteristics of adolescents' parental support and their effects on their social adjustment: the mediating role of emotional intelligence[J]. Psychol Dev Educ, 2012, 28(2): 160-166. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLFZ201202010.htm [14] 董宝林, 张欢. 性别角色、主观锻炼体验、运动承诺与锻炼行为: 链式中介模型[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2016, 31(5): 414-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY201605008.htmDONG B L, ZHANG H. Gender-roles, subjective exercise experience, sport commitment and exercise behavior of undergraduates: a model of chain mediating effect[J]. J Tianjin Univ Sport, 2016, 31(5): 414-421. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY201605008.htm [15] 朱从庆, 舒盛芳. 体育锻炼与青少年社会适应能力的因果关系探骊: 交叉滞后分析[J]. 中国体育科技, 2022, 58(7): 42-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY202207004.htmZHU C Q, SHU S F. Causal relationship between physical exercise and children and adolescents' social adaptation: cross-lagged analysis[J]. Chin Sport Sci Technol, 2022, 58(7): 42-47. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY202207004.htm [16] BRISTOL L M. Social adaptation: a study in the development of the doctrine of adaptation as a theory of social progress[M]. New York: Harvard University Press, 1915: 52-61. [17] 秦国阳, 秦勇. 青少年体育锻炼对学校适应能力的影响: 同伴关系与体育学习兴趣的链式中介作用[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2023, 31(8): 1223-1228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JKXL202308023.htmQIN G Y, QIN Y. Influence of teenagers' physical training on school adaptability: the chain mediated roles of peer relationship and sports learning interest[J]. Chin Health Psychol, 2023, 31(8): 1223-1228. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JKXL202308023.htm [18] 马超, 石振国, 王先亮, 等. 体育活动与幸福感的互促互进: 基于大学生同伴关系与自我认知的中介效应[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2022, 30(6): 893-899. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JKXL202206021.htmMA C, SHI Z G, WANG X L, et al. Influence of physical activity on college students' subjective well-being: the mediating effect of peer relationship self-cognition[J]. Chin J Health Psychol, 2022, 30(6): 893-899. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JKXL202206021.htm -







 下载:
下载: