Establishment of an intervention model for adolescent obesity based on component isochronous substitution method
-
摘要:
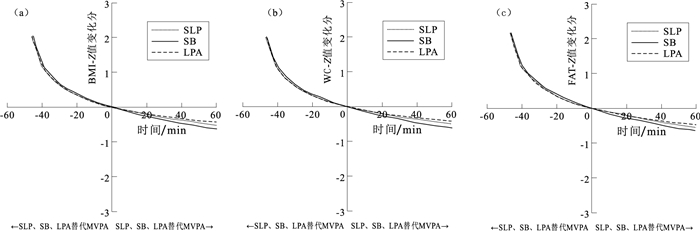
目的 探讨体力活动(PA)、久坐(SB)和睡眠(SLP)之间等时替代与体质量指数(BMI)、腰围(WC)、体脂率(FAT)的关系,为控制青少年肥胖提供有效措施。 方法 2022年5—8月在天津市第三十二中学和滨湖中学招募12~15岁青少年193名,使用常规测试方法测量受试者的身高、体重并计算BMI;采用三维加速度计(ActiGraph GT3X+)测量受试者的PA、SB和SLP。 结果 15 min的等时替代结果发现,增加中高强度身体活动(MVPA)时间并减少其他活动时间时,BMI-Z减少0.17~0.22个单位、WC-Z减少0.16~0.20个单位、FAT-Z减少0.17~0.22个单位;MVPA与SLP、SB、低强度身体活动(LPA)之间的替代具有明显的不对称性;MVPA替代SB产生的效用>MVPA替代SLP产生的效用>MVPA替代LPA产生的效用;MVPA替代其他行为在MVPA时间增加5 min时最大(0.06~0.08个单位)。 结论 MVPA在青少年肥胖的控制中起到不可替代的作用,在减少SB时间的同时应该增加MVPA时间,保证每天不低于55 min的MVPA时间才能有效控制肥胖。 Abstract:Objective To explore the relationship between isochronous substitution and BMI, waist circumference (WC), and body fat rate (FAT) among physical activity (PA), sedentary (SB), and sleep (SLP), so as to provide effective measures for obesity control in adolescents. Methods A total of 193 adolescents aged 12-15 (90 males and 103 females) was randomly selected, and their height, weight, and BMI were measured using routine testing methods from May to August 2022. The PA, SB and SLP of the participants were measured using a 3D accelerometer (ActiGraph GT3X+). Results The arithmetic mean value overestimated SLP (40.8%) and SB (39.6%) to some extent, and underestimated LPA (16.1%) and MVPA (3.5%) to some extent. Based on the ISM at 15 min, MVPA was substituted for other activity, BMI-Z decreased by 0.17-0.22 units, WC-Z decreased by 0.16-0.20 units, and FAT-Z decreased by 0.17-0.22 units. The substitution between MVPA and for other activity exhibited significant asymmetry. The effects of MVPA substitutions for SB was the largest, followed by the effects of MVPA substitutions for SLP, and the effects of MVPA substitutions for LPA was the lowest. As MVPA substitutions for other behaviors, it reached its maximum (0.06-0.08 units) when the MVPA time increased by 5 minutes. Conclusions MVPA plays an irreplaceable role in the control of adolescent obesity. While reducing SB time, MVPA duration should be increased to ensure that the daily MVPA duration is not less than 55 minutes in order to effectively control obesity. -
Key words:
- Isotemporal substitution /
- Obesity /
- Health promotion /
- Sedentary life style /
- Adolescent
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 MVPA、LPA和SLP之间重新分配15 min与青少年BMI-Z、WC-Z、FAT-Z预测值的变化(n=193)
Table 1. Changes of predicted values of BMI-Z, WC-Z and FAT-Z of adolescents after 15 minutes of redistribution among MVPA, LPA and SLP(n=193)
指标 变化 SB↑ LPA↑ MVPA↑ SLP↑ BMI-Z SB↓ — -0.05(-0.09~-0.02)* -0.22(-0.32~-0.13)* -0.04(-0.07~-0.01)* LPA↓ 0.05(0.02~0.09)* — -0.17(-0.29~-0.05)* 0.02(-0.02~0.05)* MVPA↓ 0.30(0.16~0.43)* 0.24(0.09~0.40)* — 0.26(0.12~0.40)* SLP↓ 0.04(0.01~0.07)* -0.02(-0.05~0.02)* -0.19(-0.29~-0.08)* — WC-Z SB↓ — -0.04(-0.08~-0.01)* -0.20(-0.30~-0.10)* -0.03(-0.06~0.01)* LPA↓ 0.04(0.01~0.08)* — -0.16(-0.28~-0.03)* 0.02(-0.02~0.06)* MVPA↓ 0.27(0.13~0.41)* 0.23(0.06~0.39)* — 0.24(0.09~0.40)* SLP↓ 0.02(-0.01~0.06)* -0.02(-0.06~0.02)* -0.18(-0.29~-0.06)* — FAT-Z SB↓ — -0.05(-0.08~-0.01)* -0.22(-0.32~-0.12)* -0.03(-0.06~0.00)* LPA↓ 0.05(0.01~0.08)* — -0.17(-0.30~-0.05)* 0.02(-0.02~0.06)* MVPA↓ 0.29(0.15~0.43)* 0.25(0.09~0.41)* — 0.26(0.12~0.41)* SLP↓ 0.03(0.00~0.06)* -0.02(-0.05~0.02)* -0.19(-0.30~0.08)* — 注: ↓表示该项活动时间减少15 min,↑表示该项活动时间增加15 min;*P < 0.05;()内数字为95%CI。 -
[1] MACIAŁCZYK-PAPROCKA K, STAWIÑSKA-WITOSZYÑSKA B, KOTWICKI T, et al. Prevalence of incorrect body posture in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity[J]. Eur J Pediatr, 2017, 176(5): 563-572. doi: 10.1007/s00431-017-2873-4 [2] KASOVIC M, ŠTEFAN L, PILER P, et al. Longitudinal associations between sport participation and fat mass with body posture in children: a 5-year follow-up from the Czech ELSPAC study[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(4): e0266903. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266903 [3] BENDOR C D, BARDUGO A, PINHAS-HAMIEL O, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity, diabetes and cancer risk among children and adolescents with severe obesity[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2020, 19(1): 79. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01052-1 [4] GENUA I, FRANCH-NADAL J, NAVAS E, et al. Obesity and related comorbidities in a large population-based cohort of subjects with type 1 diabetes in Catalonia[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2022, 13: 1015614. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1015614 [5] 中国儿童中心, 苑立新. 中国儿童发展报告(2021)[M]. 北京: 北京社会科学文献出版社, 2021.China Children's Center, YUAN L X. China Children's Development Report (2021)[M]. Beijing: Beijing Social Science Literature Publishing House, 2021. (in Chinese) [6] CAO Z, XU C, ZHANG P, et al. Associations of sedentary time and physical activity with adverse health conditions: outcome-wide analyses using isotemporal substitution model[J]. E Clin Med, 2022, 48: 101424. [7] DOMINGUES S F, DINIZ DA SILVA C, FARIA F R, et al. Sleep, sedentary behavior, and physical activity in Brazilian adolescents: achievement recommendations and BMI associations through compositional data analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(4): e0266926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266926 [8] MEKARY R A, WILLETT W C, HU F B, et al. Isotemporal substitution paradigm for physical activity epidemiology and weight change[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2009, 170(4): 519-527. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwp163 [9] PROCHASKA J O. Multiple health behavior research represents the future of preventive medicine[J]. Prev Med, 2008, 46(3): 281-285. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2008.01.015 [10] CHASTIN S F, PALAREA-ALBALADEJO J, DONTJE M L, et al. Combined effects of time spent in physical activity, sedentary behaviors and sleep on obesity and cardio-metabolic health markers: a novel compositional data analysis approach[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(10): 1-37. [11] CARSON V, TREMBLAY M S, CHAPUT J P, et al. Associations between sleep duration, sedentary time, physical activity, and health indicators among Canadian children and youth using compositional analyses 1[J]. Appl Physiol Nutr Metabol, 2016, 6(Suppl 3): S294. [12] KIM Y, BURNS R D, LEE D C, et al. Associations of movement behaviors and body mass index: comparison between a report-based and monitor-based method using compositional data analysis[J]. Inter J Obes, 2021, 45(1): 266-275. doi: 10.1038/s41366-020-0638-z [13] NA X N, ZHU Z, CHEN Y Y, et al. Associations of distribution of time spent in physical activity and sedentary behavior with obesity[J]. J Peking Univ Health Sci, 2020, 52(3): 486-491. [14] FARRAHI V, KANGAS M, WALMSLEY R, et al. Compositional associations of sleep and activities within the 24-h cycle with cardiometabolic health markers in adults[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2021, 53(2): 324-332. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002481 [15] DUMUID D, STANFORD T E, PEDIŠIC Ž, et al. Adiposity and the isotemporal substitution of physical activity, sedentary time and sleep among school-aged children: a compositional data analysis approach[J]. BMC Public Health, 2018, 18(1): 311. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5207-1 [16] KNOFCZYNSKI G T. Sample sizes when using multiple linear regression for prediction[J]. Educ Psychol Meas, 2008, 68(3): 431-442. doi: 10.1177/0013164407310131 [17] ZHU Z, CHEN P, ZHUANG J, et al. Intensity classification accuracy of accelerometer-measured physical activities in Chinese children and youth[J]. Res Q Exerc Sport, 2013, 84(Suppl 2): S4-S11. [18] DUMUID D, PEDIŠIC Ž, STANFORD T E, et al. The compositional isotemporal substitution model: a method for estimating changes in a health outcome for reallocation of time between sleep, physical activity and sedentary behaviour[J]. Stat Methods Med Res, 2019, 28(3): 846-857. doi: 10.1177/0962280217737805 [19] CHAPUT J P, SAUNDERS T J, CARSON V, et al. Interactions between sleep, movement and other non-movement behaviours in the pathogenesis of childhood obesity[J]. Obes Rev, 2017, 18(S1): 7-14. doi: 10.1111/obr.12508 [20] CURTIS R G, DUMUID D, OLDS T, et al. The association between time-use behaviors and physical and mental well-being in adults: a compositional isotemporal substitution analysis[J]. J Phys Activ Health, 2020, 18(S1): 7-14. [21] DIEGO J M. Associations of 24-hours activity composition with adiposity and cardiorespiratory fitness: the Pregn Active Project[J]. Scand J Med Sci Sport, 2020, 17(2): 197-203. [22] DUMUID D, WAKE M, CLIFFORD S, et al. The association of the body composition of children with 24-hour activity composition[J]. J Pediatr, 2019, 30(2): 295-302. [23] 张婷, 李红娟, 张曌华, 等. 儿童青少年24 h活动行为与肥胖关联的系统评价[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2023, 44(1): 23-27. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.01.005ZHANG T, LI H J, ZHANG Z H, et al. A systematic review of the association between 24-hour movement behavior and obesity in children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2023, 44(1): 23-27. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2023.01.005 [24] VIDEIRA-SILVA A, SARDINHA L B, FONSECA H. Atherosclerosis prevention in adolescents with obesity: the role of moderate-vigorous physical activity[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 33(9): 811-829. -







 下载:
下载: