Research hotspots and frontiers of childhood hypertension
-
摘要:
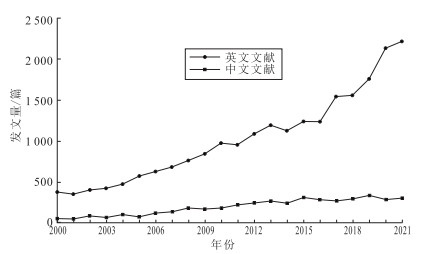
目的 分析中英文文献中儿童高血压研究现状、热点及前沿进展,为儿童高血压的早期预防提供参考。 方法 检索Web of Science(WoS)核心合集数据库和中国知网数据库(CNKI),收集2000—2021年儿童高血压研究相关文献,运用CiteSpace 5.8.R3和VOSviewer 1.6.18可视化工具分析文献发文量、作者、地区、机构合作情况和研究热点与前沿。 结果 共纳入英文文献22 687篇、中文文献4 440篇,儿童高血压主题发文量总体呈上升趋势。英文文献的发文机构以多伦多大学、科罗拉多大学为主,中文文献的发文机构以北京大学第一医院儿科为主。美国和中国在儿童高血压领域所发表的核心期刊数量处于领先地位,美国的发文影响力居于首位。关键词共现分析表明,英文文献高频关键词有“prevalence” “risk” “obesity” “risk factor” “body mass index” “insulin resistance” “overweight” “metabolic syndrome” “cardiovascular disease” “mortality”等,中文文献高频关键词有肥胖、危险因素、肥胖症、影响因素、超重、患病率、糖尿病、治疗、健康教育、体质量指数等。关键词突现分析显示,英文、中文文献各得到25个突现词。 结论 近年来国内外学者对儿童高血压的研究热度持续上升,热点问题在不断更新、涉及的疾病范围也在不断扩大,尤其在肥胖、糖尿病和心血管疾病方面。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the research status, hotspots and frontier progress of hypertension in children in English and Chinese literature, so as to provide reference for the early prevention of hypertension in children. Methods The Web of Science core collection database and CNKI database were searched to collect the literature related to the study of hypertension in children from 2000 to 2021, and the CiteSpace 5.8.R3 and VOSviewer 1.6.18 visualization tools were used to analyze the literature characteristics including publications, authors, regions, institutional cooperation, research hotspots and frontiers. Results A total of 22 687 English studies and 4 440 Chinese studies were finally included. According to the analysis results, the number of articles published on hypertension in children was on the rise. The published English articles were mainly University of Toronto and University of Colorado. The main publishing institution of Chinese articles was the First Affiliated Hospital of Peking University. The United States and China took the lead in the number of core journals published in the field of hypertension in children, the United States ranked first in terms of the influence of publications. Keyword co-occurrence analysis showed that the high-frequency keywords in the English literature included prevalence, risk, obesity, risk factor, body mass index, insulin resistance, overweight, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease and mortality. Chinese high-frequency keywords in the literature include obesity, risk factors, adiposis, influencing factors, overweight, prevalence, diabetes, treatment, health education and body mass index. The analysis of keywords showed that 25 burst terms were obtained separately in English and Chinese literature. Conclusion In recent years, the research interest on hypertension in children continues to grow and keeps updated, with the research scope expanding significantly, regarding obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. -
Key words:
- Hypertension /
- Databases, bibliographic /
- Research /
- Child
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 儿童高血压相关研究核心期刊发文量排名前10位的地区
Table 1. Top 10 countries with the highest number of publications in core journals related to hypertension research in children
地区 发文量 中心性 地区 发文量 中心性 美国 7 261 0.75 德国 957 0.02 中国 1 491 0.00 澳大利亚 855 0.03 英国 1 483 0.05 巴西 787 0.01 加拿大 1 063 0.01 印度 780 0.02 意大利 959 0.03 土耳其 711 0.01 表 2 英文文献发文量排名前10位的机构
Table 2. Top 10 institutions in terms of English literature publication
机构 发文量 中心性 多伦多大学 371 0.04 科罗拉多大学 360 0.02 哈佛大学 287 0.04 匹兹堡大学 267 0.02 费城儿童医院 256 0.02 宾夕法尼亚大学 253 0.01 伦敦大学学院 244 0.02 密歇根大学 234 0.02 约翰霍普金斯大学 232 0.03 哥伦比亚大学 229 0.02 -
[1] 梁亚军. 儿童期高血压预测成年高血压及靶器官损害的前瞻性研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2011.LIANG Y J. Prospective cohort on predictive risk of childhood hypertension to hypertension and subclinical target organ damages in adults[D]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College, 2011. (in Chinese) [2] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace[J]. Exp Opin Biol Ther, 2012, 12(5): 593-608. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507 [3] 许传先, 杜春晓, 吴国荣, 等. 中国儿童青少年高血压患病率及影响因素Meta分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(23): 4276-4280, 4311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202123012.htmXU C X, DU C X, WU G R, et al. Meta analysis of prevalence and influencing factors of hypertension in Chinese children and adolescents[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(23): 4276-4280, 4311. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202123012.htm [4] 宁曼, 何海燕. 浅谈儿童高血压的影响因素及防治[J]. 中国妇幼卫生杂志, 2016, 7(5): 70-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZWS201605021.htmNING M, HE H Y. Introduction of children's hypertension status and prevention[J]. Chin J Women Child Health, 2016, 7(5): 70-74. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZWS201605021.htm [5] KAWABE H, AZEGAMI T, TAKEDA A, et al. Features of and preventive measures against hypertension in the young[J]. Hypertens Res, 2019, 42(7): 935-948. doi: 10.1038/s41440-019-0229-3 [6] KOTANIDOU E P, GIZA S, TSINOPOULOU V R, et al. Diagnosis and management of endocrine hypertension in children and adolescents[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2020, 26(43): 5591-5608. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666201113103614 [7] 张肖笑. 重庆市6~18岁儿童高血压现状及影响因素分析[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2014.ZHANG X X. Current situation and influencing factors of hypertension in children aged 6-18 in Chongqing[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2014. (in Chinese) [8] 朱维维, 姚庆兵, 杨帆, 等. 2020年扬州市儿童青少年血压偏高现状及其与超重和肥胖关系分析[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2022, 38(11): 1850-1853. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYWS202211012.htmZHU W W, YAO Q B, YANG F, et al. Prevalence of high blood pressure and its relationship with overweight and obesity among children and adolescents in Yangzhou City in 2020[J]. J Mod Med Health, 2022, 38(11): 1850-1853. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYWS202211012.htm [9] 赵娜, 李红梅, 田朝霞. 儿童及青少年高血压生活方式的调查分析[J]. 当代护士, 2018, 25(11): 159-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDHS201811073.htmZHAO N, LI H M, TIAN Z X. Investigation and analysis of hypertensive lifestyle in children and adolescents[J]. Mod Nurs, 2018, 25(11): 159-161. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDHS201811073.htm [10] 任宇斌, 顾晓明, 张斌. 学龄期儿童青少年血压与超重肥胖的相关性[J]. 中国卫生工程学, 2019, 18(6): 936-938. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWX201906054.htmREN Y B, GU X M, ZHANG B. Correlation between blood pressure and overweight and obesity in school-age children and adolescents[J]. Chin Health Engineer, 2019, 18(6): 936-938. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWX201906054.htm [11] 张莹, 焦怡琳, 王吉春, 等. 我国儿童青少年原发性高血压影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2015, 23(2): 165-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO201502019.htmZHANG Y, JIAO Y L, WANG J C, et al. A Meta-analysis of influencing factors of essential hypertension in Chinese children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Child Health Care, 2015, 23(2): 165-168. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO201502019.htm [12] LU X, SHI P, LUO C Y, et al. Prevalence of hypertension in overweight and obese children from a large school-based population in Shanghai, China[J]. BMC Public Health, 2013, 13: 24. [13] 李光伟, 李春梅, 孙淑湘, 等. 胰岛素抵抗—遗传和环境因素致高血压的共同途径?[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2003, 42(1): 11-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHNK200301004.htmLI G W, LI C M, SUN S X, et al. Is insulin resistance a common pathway for hereditary and environmental factors-induced hypertension?[J]. Chin J Int Med, 2003, 42(1): 11-15. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHNK200301004.htm [14] TUNE J D, GOODWILL A G, SASSOON D J, et al. Cardiovascular consequences of metabolic syndrome[J]. Transl Res, 2017, 183: 57-70. [15] RABI D M, MCBRIEN K A, SAPIR-PICHHADZE R, et al. Hypertension Canada's 2020 comprehensive guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, risk assessment, and treatment of hypertension in adults and children[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2020, 36(5): 596-624. [16] NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: a pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19.1 million participants[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10064): 37-55. [17] LURBE E, AGABITI-ROSEI E, CRUICKSHANK J K, et al. 2016 European society of hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents[J]. J Hypertens, 2016, 34(10): 1887-1920. [18] 中华医学会儿科学分会内分泌遗传代谢学组, 中华医学会儿科学分会心血管学组, 中华医学会儿科学分会儿童保健学组. 中国儿童青少年代谢综合征定义和防治建议[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2012, 50(6): 420-422.Chinese Medical Association Pediatrics Branch Endocrinology Genetics and Metabolism Group, Chinese Medical Association Pediatrics Branch Cardiovascular Group, Chinese Pediatrics Branch Child Health Group. Definition and prevention of metabolic syndrome in Chinese children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Pediatr, 2012, 50(6): 420-422. (in Chinese) [19] 施仲伟. 回眸过去30年全球和中国的心血管疾病负担及其危险因素: 1990年至2019年全球心血管疾病负担及其危险因素报告解读[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2021, 20(4): 349-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDLS202104005.htmSHI Z W. Looking back at the global and Chinese cardiovascular disease burden and risk factors over the past 30 years: interpretation of the global burden of cardiovascular disease and its risk factors from 1990 to 2019[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2021, 20(4): 349-355. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDLS202104005.htm [20] 石琳, 张静, 姚玮. 儿童高血压的诊断和治疗[J]. 北京医学, 2019, 41(11): 976-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJYX201911006.htmSHI L, ZHANG J, YAO W. Diagnosis and treatment of hypertension in children[J]. Beijing Med J, 2019, 41(11): 976-979. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJYX201911006.htm [21] HARDY S T, URBINA E M. Blood pressure in childhood and adolescence[J]. Am J Hypertens, 2021, 34(3): 242-249. [22] SHARMA D, FARAHBAKHSH N, SHASTRI S, et al. Neonatal hypertension[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2017, 30(5): 540-550. [23] GIRI P, ROTH P. Neonatal hypertension[J]. Pediatr Rev, 2020, 41(6): 307-311. -







 下载:
下载: