Association of maternal emotional symptoms and childhood adverse experiences with children's emotional and behavioral problems
-
摘要:
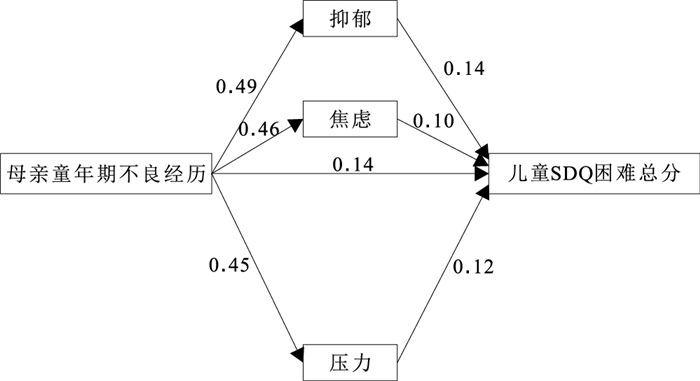
目的 探讨母亲情绪症状在童年期不良经历与儿童情绪行为问题间的中介作用,为情绪行为问题儿童的家庭干预提供科学依据。 方法 2021年6—8月采用多阶段抽样法抽取芜湖市3个区县的12所托幼机构3 012名学龄前儿童。使用问卷星方式调查其家庭及儿童基本情况、儿童情绪行为发展、母亲生活经历、母亲情绪症状等,采用SPSS 23.0软件进行一般描述性分析和Spearman相关分析;并采用GLS法评估母亲情绪症状在母亲不良经历与儿童情绪行为问题间的中介作用。 结果 芜湖市学龄前儿童困难与长处问卷(SDQ)中的困难因子得分为(10.08±4.05)分,困难总分异常检出率为6.6%,亲社会行为异常检出率为16.5%。母亲不良经历总分与SDQ困难总分以及母亲抑郁、焦虑、压力症状得分均呈正相关,儿童SDQ困难总分与母亲抑郁、焦虑、压力情绪得分均呈正相关(r=0.17~0.71,P值均 < 0.01)。中介效应分析结果显示,母亲抑郁、焦虑、压力等情绪在母亲不良经历总分与儿童SDQ困难总分间的中间效应系数均有统计学意义(P值均 < 0.05),中介效应分别占总效应的22.6%,15.2%,17.1%。 结论 母亲童年不良经历与儿童情绪行为问题的关系受到母亲情绪症状的影响。关注母亲早期生活经历和心理健康,有益于儿童情绪行为问题的防控。 Abstract:Objective To explore the mediating effect of maternal emotional symptoms on maternal adverse experiences and children's emotional behavior problems, so as to provide a scientific basis for family intervention of children with emotional behavior problems. Methods A multi-stage sampling method was used to select 12 kindergartens in 3 districts and counties of Wuhu City. The questionnaire star method was used to investigate the love of homosexuality in families and children, children's emotional behavior development questionnaire, mother's life experience questionnaire, mother's emotional symptoms questionnaire, etc. SPSS 23.0 software was used for general descriptive analysis and Spearman correlation analysis. GLS method was used to evaluate the mediating effect of maternal mental health level between maternal adverse experiences and children's emotional and behavioral problems. Results The difficulty factor score in the Strength and Difficulty Questionnaire (SDQ) of preschool children in Wuhu City was (10.08±4.05) points, the abnormal detection rate of the total difficulty score was 6.6%, and the abnormal detection rate of prosocial behavior was 16.5%, the total score of mother's adverse experience was positively correlated with the total score of mother's SDQ difficulties and the scores of mother's depression, anxiety and stress symptoms. The total score of children's SDQ difficulties was positively correlated with the scores of mother's depression, anxiety and stress emotions(r=0.17-0.71, P < 0.01). The results of mediating effect analysis showed that the intermediate effect coefficients of maternal depression, anxiety, stress and other emotions between the total score of maternal adverse experience and the total score of children's SDQ difficulties were statistically significant(P < 0.05), and the mediating effect accounted for 22.6%, 15.2% and 17.1% of the total effect, respectively. Conclusion The relationship between maternal adverse childhood experiences and children's emotional behavior problems was influenced by maternal emotional symptoms. Attention to mothers' early life experience and mental health is beneficial to the prevention and control of children's emotional and behavioral problems. -
Key words:
- Emotions /
- Life change events /
- Mental health /
- Child
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 学龄前儿童母亲ACEs、儿童情绪行为问题和母亲情绪相关性分析(r值,n=3 012)
Table 1. Mothers' adverse childhood experiences, children's emotional behavior problems and mothers' emotional relationship of preschool children(r, n=3 012)
变量 母亲ACEs 母亲抑郁症状 母亲焦虑症状 母亲压力症状 母亲抑郁症状 0.48 母亲焦虑症状 0.44 0.71 母亲压力症状 0.42 0.69 0.63 儿童SDQ困难总分 0.17 0.20 0.21 0.23 注: P值均 < 0.01。 -
[1] 顾莉萍, 陈昂, 邓成, 等. 学龄前儿童心理行为问题与家庭环境关系的调查[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2014, 32(10): 965-969. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3606.2014.10.018GU L P, CHEN A, DENG C, et al. The relationship between behavioral problems and family environment in preschool-age children[J]. J Clin Pediatr, 2014, 32(10): 965-969. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3606.2014.10.018 [2] 王海莲, 冉启美, 雷素姣, 等. 学龄前儿童行为问题与家庭环境的相关研究[J]. 中国妇幼卫生杂志, 2018, 9(4): 20-23, 28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZWS201804005.htmWANG H L, RAN Q M, LEI S J, et al. Study on the behavioral problems, family environment factors and their relationship of preschool children[J]. Chin J Women Children Health, 2018, 9(4): 20-23, 28. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZWS201804005.htm [3] 林瑶, 吴和鸣, 施琪嘉. 创伤的代际传递[J]. 心理科学进展, 2013, 21(9): 1667-1676. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXD201309016.htmLIN Y, WU H M, SHI Q J. The intergenerational transmission of trauma[J]. Adv Psychol Sci, 2013, 21(9): 1667-1676. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXD201309016.htm [4] LOVIBOND P F, LOVIBOND S H. The structure of negative emotional states: comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS) with the beck depression and anxiety inventories[J]. Behav Res Ther, 1995, 33(3): 335-343. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(94)00075-U [5] MCDONALD S W, MADIGAN S, RACINE N, et al. Maternal adverse childhood experiences, mental health, and child behaviour at age 3: the all our families community cohort study[J]. Prev Med, 2019, 118(1): 286-294. [6] ESTEVES K C, JONES C W, WADE M, et al. Adverse childhood experiences: implications for offspring telomere length and psychopathology[J]. Am J Psychiatry, 2020, 177(1): 47-57. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18030335 [7] CHOI K W, SIKKEMA K J, VYTHILINGUM B, et al. Maternal childhood trauma, postpartum depression, and infant outcomes: avoidant affective processing as a potential mechanism[J]. J Affect Disord, 2017, 211(4): 107-115. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165032716315233 [8] GIALLO R, GARTLAND D, SEYMOUR M, et al. Maternal childhood abuse and children's emotional-behavioral difficulties: intergenerational transmission via birth outcomes and psychosocial health[J]. J Fam Psychol, 2020, 34(1): 112-121. doi: 10.1037/fam0000623 [9] 余敏, 王睿, 何海燕. 家庭因素与学龄前儿童心理行为问题的关系研究[J]. 中国妇幼卫生杂志, 2022, 13(3): 6-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZWS202203002.htmYU M, WANG R, HE H Y. Study on association of family factors with psychological and behavioral problems in preschool children[J]. Chin J Women Children Health, 2022, 13(3): 6-11. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZWS202203002.htm [10] CHI T C. Mother-child relationships of children with ADHD: the role of maternal depressive symptoms and depression-related distortions[J]. J Abnorm Child Psychol, 2002, 30(4): 387-400. doi: 10.1023/A:1015770025043 [11] KIDMAN R, SMITH D, PICCOLO L R, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the Adverse Childhood Experience International Questionnaire (ACE-IQ) in Malawian adolescents[J]. Child Abuse Negl, 2019, 92(3): 139-145. [12] GOODMAN A, LAMPING D L, PLOUBIDIS G B. When to use broader internalising and externalising subscales instead of the hypothesised five subscales on the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire(SDQ): data from British parents, teachers and children[J]. J Abnorm Child Psychol, 2010, 38(8): 1179-1191. doi: 10.1007/s10802-010-9434-x [13] 陈秋, 于伟平, 陈瑞美, 等. 学龄前儿童生活方式对情绪与行为问题影响的研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(1): 82-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202101020.htmCHEN Q, YU W P, CHEN R M, et al. The influence of preschool children's lifestyle on emotional and behavioral problems[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(1): 82-85. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202101020.htm [14] 邓淑敏. 父母教养方式对学龄前儿童情绪行为问题的影响: 睡眠状况的中介效应[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2020.DENG S M. Impacts of parenting styles on emotional and behavior problems of preschool children: the mediating effect of sleep status[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2020. (in Chinese) [15] 吴瑞, 陈佳, 颜引妹, 等. 镇江市学龄前儿童情绪行为问题现况调查及其影响因素分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2020, 47(4): 616-619, 661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202004010.htmWU R, CHEN J, YAN Y M, et al. Investigation and influencing factors on emotional behavior problems of preschool children in Zhenjiang[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2020, 47(4): 616-619, 661. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202004010.htm [16] ANDA R F, DONG M, BROWN D W, et al. The relationship of adverse childhood experiences to a history of premature death of family members[J]. BMC Public Health, 2009, 9(1): 106. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-106 [17] PHILOGENE-KHALID H L, CUNNINGHAM E, YU D, et al. Depression and its association with adverse childhood experiences in people with substance use disorders and comorbid medical illness recruited during medical hospitalization[J]. Add Behav, 2020, 110(1): 106489. [18] WANG X Y. The role of maternal adverse childhood experiences on the psychological and behavioral problems of preschool children[M]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2022. (in Chinese) [19] COOKE J E, RACINE N, PLAMONDON A, et al. Maternal adverse childhood experiences, attachment style, and mental health: pathways of transmission to child behavior problems[J]. Child Abuse Negl, 2019, 93: 27-37. [20] MADIGAN S, WADE M, PLAMONDON A, et al. Maternal adverse childhood experience and infant health: biomedical and psychosocial risks as intermediary mechanisms[J]. J Pediatr, 2017, 187(4): 282-289. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022347617305991 [21] KELLERMANN N P. Transmission of holocaust trauma: an integrative view[J]. Psychiatry, 2001, 64(3): 256-267. [22] SHONKOFF J P, BOYCE W T, MCEWEN B S. Neuroscience, molecular biology, and the childhood roots of health disparities: building a new framework for health promotion and disease prevention[J]. JAMA, 2009, 301(21): 2252-2259. [23] 马月, 刘莉, 王欣欣, 等. 焦虑的代际传递: 父母拒绝的中介作用[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2016, 24(1): 23-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLCY201601005.htmMA Y, LIU L, WANG X X, et al. Intergenerational transmission of anxiety: the mediating role of parental rejection[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2016, 24(1): 23-27. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLCY201601005.htm [24] FREED R D, TOMPSON M C. Predictors of parental locus of control in mothers of pre- and early adolescents[J]. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol, 2011, 40(1): 100-110. [25] 马心宇, 陈福美, 玄新, 等. 父亲、母亲抚养压力在母亲抑郁和学龄前儿童内外部问题行为间的链式中介作用[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2019, 35(1): 103-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLFZ201901012.htmMA X Y, CHEN F M, XUAN X, et al. The role of paternal and maternal parenting stress in the relationship between maternal depression and internal and external problem behavior in preschool children[J]. Psychol Dev Educ, 2019, 35(1): 103-111. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLFZ201901012.htm [26] DOIS, FUJIWARA T, ISUMI A. Association between maternal adverse childhood experiences and mental health problems in offspring: an intergenerational study[J]. Dev Psychopathol, 2021, 33(3): 1041-1058. -







 下载:
下载: