Association between dynamic cardiorespiratory fitness and aerobic endurance among university students
-
摘要:
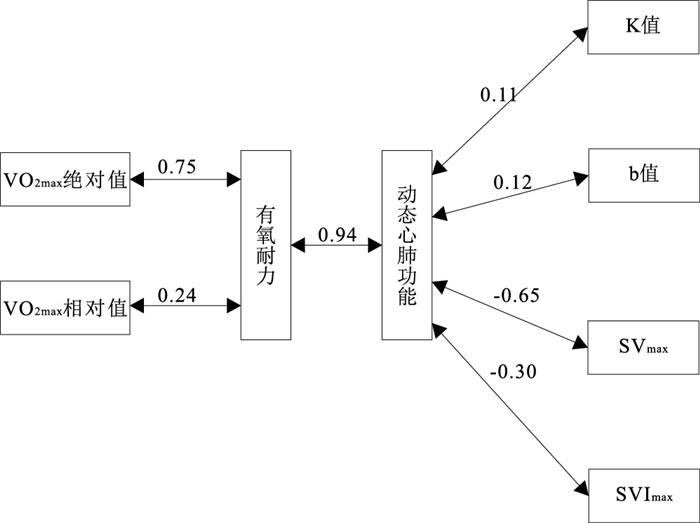
目的 通过递增负荷运动试验,筛选能有效评估有氧耐力的动态心肺功能指标。 方法 于2019年3—11月,从北京市5所高校随机招募能够理解试验并自愿配合整个测试过程的266名志愿者。采用德国Cortex Metalyzer 3B系统和美国Cheetah NICOM系统实时监测气体代谢和心功能,通过线性递增负荷方案测得最大摄氧量。根据研究设计选取有氧耐力和动态心肺功能指标,采用相关和典型性相关分析两者间的关系。 结果 男生最大摄氧量(VO2max)绝对值、VO2max相对值、最大每搏输出量(SVmax)、最大每搏输出量指数(SVImax)均显著高于女生,动态心肺功能指标K值低于女生(t值分别为17.8,10.1,8.5,4.3,-6.3,P值均 < 0.05)。简单相关发现,VO2max绝对值、VO2max相对值与K值、b值呈负相关,VO2max绝对值、VO2max相对值与SVmax、SVImax呈正相关(P值均 < 0.01)。典型相关分析发现,有氧耐力和动态心肺功能2组指标呈正相关(r=0.94,P < 0.01);与动态心肺功能密切相关的有氧耐力指标为VO2max绝对值、VO2max相对值;与有氧耐力密切相关的动态心肺功能指标为K值、b值、SVmax、SVImax。 结论 动态心肺功能的提高有助于有氧耐力的提高,动态心肺功能指标K值、b值、SVmax、SVImax可以作为预测评估有氧运动能力的重要候选指标。 Abstract:Objective To screen dynamic cardiorespiratory fitness indices for effective assessment of aerobic endurance using incremental load exercise tests. Methods From March to November 2019, 266 volunteers who were able to understand the trial and voluntarily cooperated with the entire testing process were randomly recruited from 5 universities in Beijing. Gas metabolism and cardiac function were monitored in real time using the German Cortex Metalyzer 3B system and the US Cheetah NICOM system, and maximum oxygen uptake was measured by a linear incremental loading scheme. Aerobic endurance and dynamic cardiopulmonary function indices were selected according to the study design, and the relationship between the two indicators was analyzed using correlation and typicality correlation. Results The absolute maximum oxygen uptake (VO2max), relative maximum oxygen uptake, maximum stroke volume (SVmax), and maximum stroke volume index (SVImax) were significantly higher in males than in females, and the dynamic cardiopulmonary function index K was significantly lower than in females (t=17.8, 10.1, 8.5, 4.3, -6.3, P < 0.05). Simple correlation revealed that absolute VO2max and relative VO2max were negatively correlated with K and b, and absolute VO2max and relative VO2max were positively correlated with SVmax and SVImax(P < 0.01); Both dynamic cardiopulmonary function indices were significantly correlated with aerobic endurance. Aerobic endurance indexes closely related to dynamic cardiopulmonary function were absolute VO2max, relative VO2max; dynamic cardiopulmonary function indexes closely related to aerobic endurance were K, b, SVmax, SVImax. Conclusion Improvement of dynamic cardiorespiratory fitness contributes to the improvement of aerobic endurance, the dynamic cardiorespiratory fitness indices K, b, SVmax, and SVImax can be used as important candidates to predict the assessment of aerobic exercise capacity. -
Key words:
- Cardio-pulmonary function /
- Oxygen /
- Motor activity /
- Growth and development /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 不同性别大学生有氧耐力和动态心肺功能指标试验结果比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of aerobic endurance and dynamic cardiorespiratory fitness index tests in university students by gender(x±s)
性别 人数 有氧耐力指标 动态心肺功能指标 VO2max绝对值/(L·min-1) VO2max相对值/[kg·(kg·min)-1] K值 b值 SVmax/mL SVImax/(mL·m-2) 男 134 2.7±0.6 37.9±7.0 3.0±0.6 74.2±15.8 108.3±26.7 57.9±12.7 女 132 1.7±0.3 30.6±4.3 3.5±0.6 76.6±15.7 81.1±19.8 51.0±10.9 总体 266 2.2±0.7 34.3±6.8 3.3±0.7 75.4±15.8 94.5±27.1 54.4±12.3 t值 17.8 10.1 -6.3 -1.2 8.5 4.3 P值 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.22 < 0.01 < 0.01 表 2 有氧耐力与动态心肺功能指标的简单相关结果(r值, n=266)
Table 2. Simple correlation results of aerobic endurance and dynamic cardiorespiratory fitness indexes(r, n=266)
有氧耐力指标 K值 b值 SVmax SVImax VO2max绝对值 -0.45 -0.27 0.67 0.47 VO2max相对值 -0.69 -0.23 0.39 0.37 注:P值均 < 0.01。 -
[1] 吴乐. 大学生有氧工作能力的间接测试法的对比研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2016.WU L. A comparative study of indirect testing methods for aerobic work ability of college students[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2016. (in Chinese) [2] 陈依依, 李丹阳, 倪丽丽. 青春期前青少年有氧能力训练: 可训练性, 训练适应机制和实际应用[J]. 体育科学, 2022, 42(7): 51-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX202207005.htmCHEN Y Y, LI D Y, NI L L. Aerobic capacity training in prepubertal adolescents: trainability, training adaptation mechanisms and practical applications[J]. Chin Sport Sci, 2022, 42(7): 51-61. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX202207005.htm [3] 曹国欢, 王润强, 赵彧, 等. 女子拳击运动员有氧和无氧耐力素质与竞技表现的关联性研究[J]. 中国体育科技, 2022, 58(2): 34-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY202202005.htmCAO G H, WANG R Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Study on the correlation between aerobic and anaerobic endurance qualities and competitive performance in female boxers[J]. Chin Sport Sci Technol, 2022, 58(2): 34-40. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY202202005.htm [4] 董亚南, 覃飞, 瞿超艺, 等. 最大摄氧量评定与应用的研究现状与展望[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2017, 36(8): 731-739. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2017.08.013DONG Y N, QIN F, QU C Y, et al. Current status and outlook of research on the assessment and application of maximal oxygen uptake[J]. Chin J Sports Med, 2017, 36(8): 731-739. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2017.08.013 [5] 王彦新, 耿祯, 刘振华. 心肺运动试验对于冠状动脉微血管病变的诊断作用研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2021, 25(10): 1502-1503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2021.10.022WANG Y X, GENG Z, LIU Z H. Study on the diagnostic role of cardiopulmonary exercise test for coronary microangiopathy[J]. Chin J Lab Diag, 2021, 25(10): 1502-1503. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2021.10.022 [6] 苗孟丹, 信栓力, 邵丽莉. 心肺运动试验与冠状动脉狭窄程度的相关性及其诊断冠心病的临床价值[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 19(8): 1321-1324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202108018.htmMIAO M D, XIN S L, SHAO L L. Correlation between cardiopulmonary exercise test and the degree of coronary artery stenosis and its clinical value in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease[J]. Chin J Integr Med Cardio-Cerebrov Dis, 2021, 19(8): 1321-1324. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYY202108018.htm [7] 张超. 基于心肺运动试验评估的运动康复治疗对慢性心力衰竭患者心功能及运动耐力的影响[J]. 反射疗法与康复医学, 2021(15): 172-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXH201711014.htmZHANG C. Effect of exercise rehabilitation therapy based on cardiopulmonary exercise test assessment on cardiac function and exercise tolerance in patients with chronic heart failure[J]. Reflexol Rehabil Med, 2021(15): 172-174. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXH201711014.htm [8] 李四维. 心肺运动试验在心脏康复评估中的应用[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2017, 32(4): 331-333. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2017.04.006LI S W. Application of cardiopulmonary exercise test in cardiac rehabilitation assessment[J]. Chin Circul J, 2017, 32(4): 331-333. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2017.04.006 [9] 孙远东, 薛宁, 王焱, 等. 心肺运动试验在尘肺患者心肺功能评估及康复治疗中的应用[J]. 中国工业医学杂志, 2021, 34(1): 44-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SOLE202101016.htmSUN Y D, XUE N, WANG Y, et al. Application of cardiopulmonary exercise test in the assessment of cardiopulmonary function and rehabilitation of pneumoconiosis patients[J]. Chin J Ind Med, 2021, 34(1): 44-47. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SOLE202101016.htm [10] 敬容, 刘剑, 罗飞, 等. 中年男性静息心率, 最大摄氧量及颈动脉内膜中层厚度与心血管危险因素的相关性[J]. 西部医学, 2020, 32(11): 1690-1693. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2020.11.030JING R, LIU J, LUO F, et al. Correlation of resting heart rate, maximal oxygen uptake and carotid intima-media thickness with cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged men[J]. Med J West Chin, 2020, 32(11): 1690-1693. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2020.11.030 [11] 高理升, 李关东, 叶玉琪, 等. 一种基于摄氧量计算的心肺耐力测量方法及系统, CN112138361A[P]. 2020.GAO L S, LI G D, YE Y Q, et al. A method and system for measuring cardiopulmonary endurance based on oxygen uptake calculation, CN112138361A[P]. 2020. (in Chinese) [12] 陈伟, 顾建仁, 焦启斌, 等. 应用二次负荷跑台法测定最大摄氧量的研究[J]. 辽宁体育科技, 2018, 40(1): 33-35, 39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6204.2018.01.010CHEN W, GU J R, JIAO Q B, et al. Study on the application of secondary load running platform method to determine the maximum oxygen uptake[J]. Liaoning Sports Sci Technol, 2018, 40(1): 33-35, 39. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6204.2018.01.010 [13] 刘海云. 20米折返跑与800/1 000米跑评价中学生心肺耐力的比较研究[D]. 北京: 北京体育大学, 2019.LIU H Y. A comparative study of 20m fold run and 800/1 000 m run to evaluate the cardiorespiratory endurance of secondary school students[D]. Beijing: Beijing Sports University, 2019. (in Chinese) [14] 孙忠伟, 马永平, 马慧敏, 等. 基于BP人工神经网络的大学生最大摄氧量估测模型研究[J]. 中国体育科技, 2021, 52(3): 56-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY201603009.htmSUN Z W, MA Y P, MA H M, et al. Study on maximum oxygen uptake estimation model for university students based on BP artificial neural network[J]. Chin Sport Sci Technol, 2021, 52(3): 56-60. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY201603009.htm [15] 王念辉, 洪平, 苏中军. 基于身高、体重及肺活量的大学一年级男生最大摄氧量推算方法研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2018, 37(3): 202-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2018.03.004WANG N H, HONG P, SU Z J. A study on the derivation of maximum oxygen uptake based on height, weight and lung capacity in first-year college males[J]. Chin J Sports Med, 2018, 37(3): 202-207. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2018.03.004 [16] 杨慧君. 基于心功能、血液、体成分指标预测大学生最大摄氧量的研究[D]. 北京: 国家体育总局体育科学研究所, 2020.YANG H J. Study on predicting maximum oxygen uptake in college students based on cardiac function, blood, and body composition indices[D]. Beijing: China Institute of Sports Science, 2020. (in Chinese) [17] 刘祥茂. 普通大学生身体活动与最大摄氧量关系研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2021.LIU X M. Study on the relationship between physical activity and maximum oxygen uptake in general college students[D]. Xuzhou: China University Mining Technology, 2021. (in Chinese) [18] 贺晓玉, 温英英. 运用verificationphase判定男大学生最大摄氧量的研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2021, 40(2): 92-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX202102002.htmHE X Y, WEN Y Y. Study on the use of verificationphase to determine the maximum oxygen uptake of male college students[J]. Chin J Sports Med, 2021, 40(2): 92-97. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX202102002.htm [19] 郭辉, 刘韵婷, 孔振兴, 等. 基于BP神经网络的最大摄氧量预测方法研究[J]. 实验室科学, 2020, 23(5): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKT202005012.htmGUO H, LIU Y T, KONG Z X, et al. Research on maximum oxygen uptake prediction method based on BP neural network[J]. Lab Sci, 2020, 23(5): 44-48. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKT202005012.htm [20] 陈怡锡, 李小玲, 张新霞, 等. 改良疗程增强型体外反搏对冠心病患者血管功能及心肺功能的疗效研究[J]. 岭南心血管病杂志, 2019, 25(3): 247-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXGB201903002.htmCHEN Y X, LI X L, ZHANG X X, et al. Study on the efficacy of modified course of enhanced external counterpulsation on vascular function and cardiopulmonary function in patients with coronary artery disease[J]. South Chin J Cardiovasc Dis, 2019, 25(3): 247-251. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXGB201903002.htm [21] 石建国, 季华庆, 陈想贵, 等. 高原肺水肿患者血流动力学变化研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(17): 2192-2197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202117022.htmSHI J G, JI H Q, CHEN X G, et al. Study of hemodynamic changes in patients with highland pulmonary edema[J]. Chin Gener Pract, 2021, 24(17): 2192-2197. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202117022.htm [22] 赵美, 秦渤, 范晓英. 心脏运动康复对老年冠心病患者生活质量及心肺功能的影响[J]. 中华保健医学杂志, 2022, 24(1): 7-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFJB202201003.htmZHAO M, QIN B, FAN X Y. Effects of cardiac exercise rehabilitation on quality of life and cardiopulmonary function in elderly patients with coronary artery disease[J]. Chin J Health Care Med, 2022, 24(1): 7-10. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFJB202201003.htm [23] 郭小亚, 吴雪娇, 洪怡, 等. 不同性别、年龄及体力活动心脏康复患者心肺运动试验指标分析[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2021, 29(9): 10-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXL202109005.htmGUO X Y, LIN Q, HONG Y, et al. Analysis of cardiopulmonary exercise test indices in cardiac rehabilitation patients of different genders, ages and physical activities[J]. Pract J Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal Vascu Dis, 2021, 29(9): 10-17. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXL202109005.htm [24] NEVILL A M, DUNCAN M J, SANDERCOCK G. Modeling the dose-response rate/associations between VO2max and self-reported Physical Activity Questionnaire in children and adolescents[J]. J Sport Health Sci, 2020, 9(1): 6. [25] DEGENS H, STASIULIS A, SKURVYDAS A, et al. Physiological comparison between non-athletes, endurance, power and team athletes[J]. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2019, 119(6): 1377-1386. [26] 许金富, 林瑜. 国际体力活动问卷在大学生群体中信效度检验研究[J]. 长春师范大学学报, 2018, 37(10): 106-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCSS201810024.htmXU J F, LIN Y. Study on the credibility of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire in a college student population[J]. J Changchun Norm Univ, 2018, 37(10): 106-108. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCSS201810024.htm [27] 王正珍. ACSM运动测试与运动处方指南[M]. 北京: 北京体育大学出版社, 2015.WANG Z Z. ACSM guide to exercise testing and exercise prescription[M]. Beijing: Beijing Sports University Press, 2015. (in Chinese) [28] 刘自慧, 彭莉. 最大摄氧量判定指标标准的有效性研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 39(10): 111-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNZK201410022.htmLIU Z H, PENG L. Study on the validity of the criteria for determining the index of maximum oxygen uptake[J]. J Southwest Chin Norm Univ(Natur Sci Edit), 2014, 39(10): 111-116. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNZK201410022.htm [29] 王雅薇, 金晶, 冯祎中, 等. 大学生体质健康现状研究: 基于《国家学生体质健康标准(2014年修订)》[J]. 安徽体育科技, 2019, 40(5): 72-77, 90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ATKJ201905017.htmWANG Y W, JIN J, FENG Y Z, et al. Study on the current situation of physical health of college students: based on the National Student Physical Fitness Standards (Revised in 2014)[J]. Anhui Sports Sci Technol, 2019, 40(5): 72-77, 90. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ATKJ201905017.htm [30] 郝璐, 孙兴国, 宋雅, 等. 不同功率递增速率对正常人心肺运动试验整体功能的影响Ⅱ: 亚极限运动相关指标的影响[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志, 2021, 37(2): 120-124, 134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSL202102002.htmHAO L, SUN X G, SONG Y, et al. Effects of different power increment rates on the overall function of cardiopulmonary exercise test in normal subjects Ⅱ: effects of submaximum exercise related indexes[J]. Chin J Appl Physiol, 2021, 37(2): 120-124, 134. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSL202102002.htm [31] 陆耀飞. 运动生理学[M]. 北京: 北京体育大学出版社, 2007.LU Y F. Exercise physiology[M]. Beijing: Beijing Sports University Press, 2007. (in Chinese) [32] Y·休恩费尔德, 邢华城. 根据年龄、体重和安静心率来预测有氧能力[J]. 体育科技, 1983(1): 53-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKJ198301012.htmY·HUENFELD, XING H C. Predicting aerobic capacity based on age, body weight, and quiet heart rate[J]. Sports Technol, 1983(1): 53-55. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKJ198301012.htm [33] 马向阳, 穆建玲, 宋红艳. 青年学生平静时心率与最大摄氧量的关系[J]. 卫生职业教育, 2008, 26(5): 155-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYX200805099.htmMA X Y, MU J L, SONG H Y. Relationship between heart rate and maximum oxygen uptake during calmness in young students[J]. Health Profess Educ, 2008, 26(5): 155-156. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYX200805099.htm [34] ASTRAND P O, CUDDY T E, SALTIN B, et al. Cardiac output during submaximal and maximal work[J]. J Appl Physiol, 1964, 19(2): 268-274. [35] 刘洵, 陈家琦. 通过无损伤动态测定心输出量对最大摄氧量影响因素的探讨[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 1986(1): 25-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY198600004.htmLIU X, CHEN J Q. Exploration of factors influencing maximal oxygen uptake through injury-free dynamic determination of cardiac output[J]. J Tianjin Inst Phys Educ, 1986(1): 25-33. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJTY198600004.htm [36] FOMIN A, SILVA C, AHLSTRAND M, et al. Gender differences in myocardial function and arterio-ventricular coupling in response to maximal exercise in adolescent floor-ball players[J]. Bmc Sports Sci Med Rehabil, 2014, 6(1): 24. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC4084409/pdf/2052-1847-6-24.pdf [37] ANHE F F, ZLITNI S, BARRA N G, et al. Life-long exercise training and inherited aerobic endurance capacity produce converging gut microbiome signatures in rodents[J]. Phys Rep, 2022, 10(5): e15215. -







 下载:
下载: