Relationship between SH2B adaptor protein 1 gene and lifestyles with childhood obesity
-
摘要:
目的 研究中国儿童人群中SH2B接头蛋白1基因(SH2B adaptor protein 1 gene, SH2B1)rs7498665多态性与肥胖及相关表型的关联, 为探讨生活方式对该多态性与肥胖关系的影响提供依据。 方法 选取北京市3 305名7~18岁儿童青少年进行身体测量和生活方式问卷调查。利用基质支持的激光释放/电离飞行时间质谱分析法对rs7498665多态性进行分型。采用多元Logistic回归和线性回归方法分析全部人群及不同饮食、运动水平下该基因多态性与肥胖及相关表型的相关性。 结果 在非健康膳食摄入、不是每天吃早餐、经常摄入含糖饮料、不是每天进行中高强度体育锻炼情况下, rs7498665多态性G等位基因与肥胖存在相关性, 肥胖风险分别升高37%, 101%, 45%和64%(P值均 < 0.05)。对不同生活方式进行综合评价, rs7498665多态性只在非健康生活方式组的人群中与肥胖发生有关(OR=1.63, 95%CI=1.23~2.17, P < 0.01)。分析肥胖相关表型发现相同趋势的结果, 该位点与综合生活方式存在交互作用(P基因×生活方式 < 0.05)。 结论 SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性与肥胖易感的非健康生活方式对儿童肥胖及相关表型存在相互作用。 Abstract:Objective To study the associations of rs7498665 polymorphism located in the SH2B adaptor protein 1 gene with obesity-related phenotypes in Chinese children and adolescents, and to explore the gene-lifestyles interactions. Methods Anthropometric measurements and lifestyles investigation were conducted in 3 305 children and adolescents aged 7-18 years old recruited from Beijing. The matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) was used to genotype rs7498665 polymorphism. Multiple Logistic and linear regressions were performed to analyze the associations of rs7498665 with obesity and obesity related phenotypes by different levels of physical activity and diet behavior. Results The G-allele of rs7498665 polymorphism showed 37%, 101%, 45% and 64% high risk of obesity in population groups with unhealthy dietary intake, not eating breakfast daily, high consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages or not daily moderate to vigorous physical activity (P < 0.05). In the further analysis, the G-allele of rs7498665 polymorphism was associated with obesity in population with unhealthy lifestyle score (OR=1.63, 95%CI=1.23-2.17, P < 0.01). There were similar results with obesity related phenotypes, with the gene-comprehensive lifestyle behaviors interactions were significant (Pgene×lifestyle behaviors < 0.05). Conclusion The present study suggests the interactive effect of rs7498665 polymorphism located in the SH2B1 and unhealth lifestyle on childhood obesity and related phenotypes. -
Key words:
- Genes /
- Behavior /
- Obesity /
- Regression analysis /
- Child
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
SH2B接头蛋白1属于接头蛋白家族,可通过SH2结构域与酪氨酸激酶如瘦素受体等结合参与其介导的一系列信号通路作用[1]。动物研究发现小鼠SH2B1蛋白在脑、肝脏、肌肉和脂肪组织中表达[2-3],敲除sh2b1基因可导致小鼠出现肥胖和代谢综合征,神经元特异性表达SH2B1可以改善sh2b1基因敲除小鼠瘦素抵抗从而使其体重降低[3-4]。外周组织中SH2B1可加强胰岛素敏感性[5];人类SH2B1基因位于16p11.2区域,含13个外显子,rs7498665单核苷酸多态性是位于第5外显子的错义突变。多项研究确认rs7498665或与其有强连锁不平衡关系的多态性在不同种族成年人群中与肥胖存在关联[6-10],但青少年人群和华裔人群中的研究结果并不一致。欧裔[11]和中国[12]儿童青少年人群、华裔成年女性人群[13]中均有研究发现其中部分多态性与肥胖有关,但是另外两项中国儿童青少年和一项中国成年人群研究结果并不一致[14-16];可能与不同人群的生活方式不同有关。欧洲或美洲人群中有研究分析运动方式对这些多态性效应的影响[17-18],中国人群中的情况还不清楚。中国社会和经济的快速变化导致生活方式的多样化特点,为研究基因-环境对肥胖的交互作用提供了便利条件。
本研究旨在分析中国儿童人群中SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性与肥胖及相关表型的关联,以及探讨包括饮食和运动在内的综合生活方式对该多态性与肥胖关系的影响。
1. 对象与方法
1.1 对象
采用病例-对照研究方法或整群随机抽样方法在北京市采集4批样本,共计3 305名中小学生。第一批样本是2004年从北京市东城区9所中学选择的937名14~17岁初中生;第二批样本是2007年从北京市海淀区3所中学和2所小学选择的1 093名7~18岁中小学生;这两批样本均为病例对照研究,其中体重正常组是在入选学校每个年级抽取的2个班中获得,超重组和肥胖组则是以上学校所有超重和肥胖的中小学生。另外两批样本均为以学校为基础的儿童肥胖干预研究,采用整群抽样的方法筛选研究对象,本研究中均使用基线数据。第三批研究样本2009年从海淀区8所小学获得,经过筛选456名6~14岁儿童纳入本研究;第四批研究样本是2012年从北京市昌平区的2所小学和2所中学选择的819名7~15岁中小学生。研究剔除了消瘦人群,根据病史和体检资料,剔除了心、肺、肝、肾等重要脏器疾病,身体发育异常、身体残缺、畸形以及内分泌疾病、药物副作用等引起的肥胖儿童青少年。以上4项研究均获得所有研究对象的知情同意,并通过北京大学医学研究伦理委员会(第一批、第二批和第四批样本研究,批准号:IRB00001052-06082,IRB00001052-06084,IRB000010 52-15039)、中国疾病预防控制中心伦理委员会(第三批样本研究,批准号:20081201)的审核批准。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 一般情况和体格检查
采用自行设计的调查表,由经过统一培训的调查人员进行一般人口学特征的调查,并按照统一的测量标准进行身高、体重、腰围和臀围的测量,儿童青少年超重和肥胖的判定采用“中国学龄儿童青少年体质量指数(BMI)超重、肥胖筛查分类标准”[19]。体脂成分在后三批样本中进行检测,所使用的检测仪器为第二批样本:Jawon Genuis-220,韩国;第三和第四批样本:ImpediMed DF50,澳大利亚。
1.2.2 生活行为问卷调查
采用自行设计的问卷调查学生调查日期前一周的饮食情况(膳食摄入种类、频率和摄入量,早餐摄入情况,含糖饮料饮用频率)和身体活动情况(身体活动强度、时间和视屏时间等)。根据《中国学龄儿童膳食指南(2016)》[20]和《中国儿童青少年身体活动指南》[21]的相关建议并结合本研究问卷调查的特点,采用如下标准对饮食和运动情况进行分层:(1)健康膳食,按照多摄入水果、蔬菜和奶类,控制肉类摄入,计算健康膳食分数。首先按照这4类食物摄入量中位数对人群进行评分,其次计算膳食综合评分,再以综合评分的中位数将人群分为健康膳食组和非健康膳食组。(2)早餐情况,分为每天吃早餐和不是每天吃早餐两组。(3)含糖饮料摄入情况,每周饮用次数≥1次为经常摄入。(4)中高等强度运动情况,分为每天中高等强度运动和不是每天中高等运动两组,每天中高等强度锻炼指每天参加至少20 min活动(如跑步、游泳、快走、慢骑自行车等)。(5)每天身体活动时间≥1 h,指每天至少累计完成1 h的体育锻炼(包括课间操、体育课、课外体育活动)。(6)每天视屏时间<2 h,指每天看电脑、电视和玩电子游戏的时间不超过2 h。(7)生活方式综合评价,综合以上健康膳食分数、吃早餐行为、摄入含糖饮料、中高等强度运动、身体活动时间、视屏时间的取值情况,计算得到健康生活方式分数。按照中位数,将人群分为健康生活方式组和非健康生活方式组。
1.2.3 SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性检测方法
采用常规酚/氯仿法或盐析法从血凝块中提取DNA。用基质支持的激光释放/电离飞行时间质谱分析(MALDI-TOF MS)检测SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性的基因型。首先进行多重PCR扩增反应,使用虾碱性磷酸酶灭活未参与扩增反应的脱氧核糖核苷酸,之后加入探针进行单碱基延伸,所得产物用树脂纯化后进行质谱检测。每次实验均设置两个阴性对照和一对平行样本。3 305个样本中共有3 282个(99.30%)样本分型成功。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 24.0软件进行统计学分析。基因型分析和等位基因频率进行Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验。将研究人群、性别、年龄、年龄平方作为协变量,多元线性回归分析多态性与BMI等连续性指标的相关性,Logistic回归分析多态性与肥胖的相关性。按照不同生活行为方式水平分层,分别分析多态性与肥胖及相关表型的相关性。在回归分析中检验rs7498665多态性与不同生活方式的相乘项分析其对肥胖及相关表型的交互作用。检验水准α=0.05。
2. 结果
2.1 研究人群及位点的基本情况
体重正常组、超重组和肥胖组人数分别为1 262,1 014和1 029人,超重组(32.8%)、肥胖组(35.8%)人群中男生比例高于体重正常组的男生比例(31.4%)(χ2=84.84,P<0.01),超重组和肥胖组的平均年龄(12.20±2.80,11.86±2.83)岁均高于体重正常组儿童(11.29±2.95)岁(F=29.78,P<0.05)。如表 1所示,在不同营养状况分组及总人群中,rs7498665多态性的基因分型均符合Hardy-Weinberg遗传平衡定律(P=0.47)。在全部样本中,G等位基因的突变频率为16.41%。
表 1 rs7498665多态性基因型分布、等位基因频率和Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验Table 1. The genotype distribution, allele frequency and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium test of rs7498665 polymorphism组别 基因型(n) 等位基因/% Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验P值 AA GA GG A G 非肥胖组 1 589 607 63 83.78 16.22 0.58 肥胖组 710 282 31 83.19 16.81 0.64 总人群 2 299 889 94 83.59 16.41 0.47 2.2 SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性与肥胖及相关表型的相关性
在加性模型下,采用多元Logistic回归分析,校正研究人群、性别、年龄、年龄平方后,分析肥胖组与非肥胖组中rs7498665多态性基因型的分布差异,未发现该多态性与儿童肥胖存在相关性(OR=1.02,95%CI=0.89~1.18,P=0.77)。采用线性回归进一步分析BMI、腰围、臀围、腰围身高比和体脂百分比,rs7498665多态性与这些表型均无相关性(P值均>0.05)。
2.3 SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性与生活行为方式对儿童肥胖的交互作用
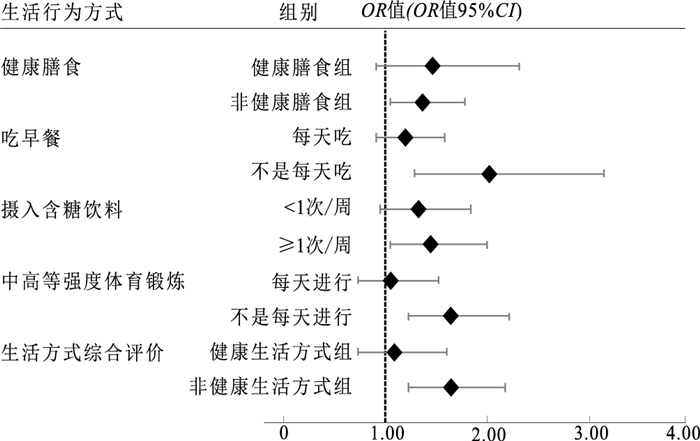
研究不同饮食和运动水平儿童中rs7498665多态性与肥胖的相关性,见图 1。
结果表明,在非健康膳食组中,rs7498665多态性与肥胖存在相关性,每增加1个G等位基因,肥胖发生风险升高37%(OR=1.37,95%CI=1.05~1.77,P=0.02)。同时,在不是每天吃早餐、经常摄入含糖饮料、不是每天进行中高强度体育锻炼情况下,rs7498665多态性G等位基因也与肥胖发生有关,肥胖风险分别升高101%(OR=2.01,95%CI=1.29~3.13),45%(OR=1.45,95%CI=1.05~2.00)和64%(OR=1.64,95%CI=1.22~2.20)(P值均<0.05)。对不同生活方式进行组合,rs7498665多态性G等位基因只在非健康生活方式组的人群中与肥胖发生有关(OR=1.63,95%CI=1.23~2.17,P<0.01),而在健康生活方式组的人群中rs7498665多态性与肥胖无相关性(P=0.67)。检验该位点与生活方式的交互项,发现对肥胖的交互作用无统计学意义。
rs7498665多态性与生活方式综合得分对肥胖相关表型存在交互作用。见表 2。在非健康生活方式组人群中,rs7498665多态性G等位基因与BMI、腰围、臀围、腰围身高比和体脂百分比水平存在相关性(P值均<0.05),在健康生活方式组人群中未发现类似的结果(P值均>0.05)。
表 2 不同生活方式综合得分人群中rs7498665与儿童肥胖相关表型的关联Table 2. Association between rs7498665 and childhood obesity related phenotypes in groups stratified by lifestyle behaviors表型 健康生活方式组(n=963) 非健康生活方式组(n=563) P基因×生活方式值 β值 标准误 P值 β值 标准误 P值 BMI/(kg·m-2) -0.20 0.29 0.50 0.59 0.25 0.02 0.05 腰围/cm -0.71 0.77 0.36 1.49 0.66 0.03 0.03 臀围/cm -0.18 0.63 0.78 1.45 0.52 0.01 0.05 腰围身高比 -0.00 0.01 0.35 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.04 体脂百分比/% -0.53 0.50 0.29 0.87 0.41 0.03 0.03 3. 讨论
本研究发现SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性的效应受生活方式影响,在非健康膳食、不是每天吃早餐、经常摄入含糖饮料、不是每天都进行中高等强度体育锻炼的人群中与肥胖存在相关性。进一步对生活方式进行综合评价后发现,rs7498665多态性仅在非健康生活方式情况下与肥胖存在相关性。
SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性最初在英国成年女性人群中发现与体脂百分比、腰围及血清瘦素水平有关[22],随后多项肥胖全基因组关联分析研究(Genome Wide Association, GWAS)以及一些独立人群研究均证实该多态性或与其存在强连锁不平衡关系的多态性(rs4788099、rs4788102和rs7359397)在成年人群中与肥胖存在相关性[6-10, 13],其中也包括中国人群研究。但是不同儿童人群研究中的结果并不一致,有研究发现德国儿童和中国女童人群中SH2B1基因多态性与肥胖及相关表型存在相关性[12, 23],另外一些研究在欧裔和中国儿童人群中未发现类似的结果[9, 14, 16, 24]。与之一致的是,本研究也没有发现rs7498665多态性与肥胖、中心性肥胖和体脂百分比存在相关性。SH2B1基因参与瘦素信号通路作用,rs7498665多态性是外显子区的错义突变,可能对基因功能有影响。但是Volckmar等[23]在HEK293细胞中进行研究没有发现两个等位基因之间存在明显的瘦素信号转导差异。早期的GWAS研究显示,该位点升高BMI的效应与公认的肥胖基因——FTO基因存在较大差距(0.15,0.39 kg/m2每危险等位基因)[10]。因此效应微效性可能是本研究没有发现rs7498665多态性与肥胖及相关表型存在相关性的原因之一。
前期有多项研究发现肥胖基因的效应大小受不同生活行为方式的影响,环境-基因交互作用可能仅在某些特定的人群中发生,因而一些关联基因可能会逃脱识别[25]。Krishnan等[17]在欧裔儿童中发现rs7498665多态性与中高等强度运动对体脂百分比有交互作用。Richardson等[18]在美国不同种族青少年中没有发现类似的结果。这些研究在欧美人群中进行,中国人群中的情况还没有证据。生活行为方式包括饮食和运动的多个方面,除中高等强度运动以外其它生活行为方式的影响还不清楚。结果显示,尽管rs7498665多态性在全部人群中与肥胖及相关表型无关系,但是当人群处于非健康膳食摄入、不是每天吃早餐、经常摄入含糖饮料、不是每天进行中高等强度体育锻炼的情况下,该多态性危险等位基因可以增加肥胖的发生风险。综合评价这些肥胖易感行为方式,发现非健康生活方式可加强rs7498665多态性对肥胖的贡献,肥胖发生风险增加63%。本研究同时纳入BMI、中心性肥胖表型以及体脂百分比作为敏感性分析,发现与肥胖分析类似的结果。多项行为方式和多个表型的分析为说明rs7498665多态性与生活行为方式的交互作用提供了进一步的证据。
综上所述,本研究在中国人群中发现SH2B1基因rs7498665多态性的效应受生活行为方式的影响,肥胖易感的非健康生活方式可加强该多态性对肥胖的贡献。研究结果提示,应该从遗传和环境角度共同探讨儿童青少年肥胖的病因,进行肥胖干预时特别关注肥胖遗传易感且有非健康生活行为方式的人群,对于强化干预效果具有重要的实际应用价值。
-
表 1 rs7498665多态性基因型分布、等位基因频率和Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验
Table 1. The genotype distribution, allele frequency and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium test of rs7498665 polymorphism
组别 基因型(n) 等位基因/% Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验P值 AA GA GG A G 非肥胖组 1 589 607 63 83.78 16.22 0.58 肥胖组 710 282 31 83.19 16.81 0.64 总人群 2 299 889 94 83.59 16.41 0.47 表 2 不同生活方式综合得分人群中rs7498665与儿童肥胖相关表型的关联
Table 2. Association between rs7498665 and childhood obesity related phenotypes in groups stratified by lifestyle behaviors
表型 健康生活方式组(n=963) 非健康生活方式组(n=563) P基因×生活方式值 β值 标准误 P值 β值 标准误 P值 BMI/(kg·m-2) -0.20 0.29 0.50 0.59 0.25 0.02 0.05 腰围/cm -0.71 0.77 0.36 1.49 0.66 0.03 0.03 臀围/cm -0.18 0.63 0.78 1.45 0.52 0.01 0.05 腰围身高比 -0.00 0.01 0.35 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.04 体脂百分比/% -0.53 0.50 0.29 0.87 0.41 0.03 0.03 -
[1] REN D, LI M, DUAN C, et al. Identification of SH2B as a key regulator of leptin sensitivity, energy balance, and body weight in mice[J]. Cell Metab, 2005, 2(2): 95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.07.004 [2] DUAN C, YANG H, WHITE M F, et al. Disruption of the SH2-B gene causes age-dependent insulin resistance and glucose intolerance[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(17): 7435-7443. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7435-7443.2004 [3] REN D, ZHOU Y, MORRIS D, et al. Neuronal SH2B1 is essential for controlling energy and glucose homeostasis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2007, 117(2): 397-406. doi: 10.1172/JCI29417 [4] RUI L. SH2B1 regulation of energy balance, body weight, and glucose metabolism[J]. World J Diabet, 2014, 5(4): 511-526. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i4.511 [5] MORRIS D L, CHO K W, ZHOU Y, et al. SH2B1 enhances insulin sensitivity by both stimulating the insulin receptor and inhibiting tyrosine dephosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins[J]. Diabetes, 2009, 58(9): 2039-2047. doi: 10.2337/db08-1388 [6] GUO Y, LANKTREE M B, TAYLOR K C, et al. Gene-centric Meta-analyses of 108 912 individuals confirm known body mass index loci and reveal three novel signals[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2013, 22(1): 184-201. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds396 [7] GRAFF M, SCOTT R A, JUSTICE A E, et al. Genome-wide physical activity interactions in adiposity-A Meta-analysis of 200, 452 adults[J]. PLoS Genet, 2017, 13(4): e1006528. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006528 [8] SHUNGIN D, WINKLER T W, CROTEAU-CHONKA D C, et al. New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7538): 187-196. doi: 10.1038/nature14132 [9] WILLER C J, SPELIOTES E K, LOOS R J, et al. Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation[J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41(1): 25-34. doi: 10.1038/ng.287 [10] SPELIOTES E K, WILLER C J, BERNDT S I, et al. Association analyses of 249 796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index[J]. Nat Genet, 2010, 42(11): 937-948. doi: 10.1038/ng.686 [11] PATERNOSTER L, EVANS D M, NOHR E A, et al. Genome-wide population-based association study of extremely overweight young adults: the GOYA study[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(9): e24303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024303 [12] XI B, SHEN Y, REILLY K H, et al. Sex-dependent associations of genetic variants identified by GWAS with indices of adiposity and obesity risk in a Chinese children population[J]. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2013, 79(4): 523-528. doi: 10.1111/cen.12091 [13] SHI J, LONG J, GAO Y T, et al. Evaluation of genetic susceptibility loci for obesity in Chinese women[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2010, 172(3): 244-254. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwq129 [14] HONG J, SHI J, QI L, et al. Genetic susceptibility, birth weight and obesity risk in young Chinese[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2013, 37(5): 673-677. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2012.87 [15] ZHU J, LOOS R J, LU L, et al. Associations of genetic risk score with obesity and related traits and the modifying effect of physical activity in a Chinese Han population[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(3): e91442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091442 [16] 张美仙, 赵小元, 席波, 等. 基因多态性对儿童肥胖和代谢异常的影响[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2014, 48(9): 776-783.ZHANG M X, ZHAO X Y, XI B, et al. Impact of obesity-related gene polymorphism on risk of obesity and metabolic disorder in childhood[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2014, 48(9): 776-783. (in Chinese) [17] KRISHNAN M, SHELLING A N, WALL C R, et al. Gene-by-activity interactions on obesity traits of 6-year-old New Zealand European children: a children of SCOPE Study[J]. Pediatr Exerc Sci, 2018, 30(1): 69-80. doi: 10.1123/pes.2017-0077 [18] RICHARDSON A S, NORTH K E, GRAFF M, et al. Moderate to vigorous physical activity interactions with genetic variants and body mass index in a large US ethnically diverse cohort[J]. Pediatr Obes, 2014, 9(2): e35-e46. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2013.00152.x [19] JI C Y. Report on childhood obesity in China(1): body mass index reference for screening overweight and obesity in Chinese school-age children[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2005, 18(6): 390-400. [20] 中国营养学会. 中国学龄儿童膳食指南(2016)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016.Chinese Nutrition Society. Dietary guidelines for school-age children in China(2016)[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2016. (in Chinese) [21] 张云婷, 马生霞, 陈畅, 等. 中国儿童青少年身体活动指南[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2017, 12(6): 401-409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZEK201706001.htmZHANG Y T, MA S X, CHEN C, et al. Guidelines of physical activity for chinese children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Evidence-Based Pediatr, 2017, 12(6): 401-409. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZEK201706001.htm [22] JAMSHIDI Y, SNIEDER H, GE D, et al. The SH2B gene is associated with serum leptin and body fat in normal female twins[J]. Obesity(Silver Spring), 2007, 15(1): 5-9. [23] VOLCKMAR A L, BOLZE F, JARICK I, et al. Mutation screen in the GWAS derived obesity gene SH2B1 including functional analyses of detected variants[J]. BMC Med Genom, 2012, 5: 65. [24] ZHAO J, BRADFIELD J P, LI M, et al. The role of obesity-associated loci identified in genome-wide association studies in the determination of pediatric BMI[J]. Obesity(Silver Spring), 2009, 17(12): 2254-2257. [25] HEBEBRAND J, VOLCKMAR A L, KNOLL N, et al. Chipping away the "missing heritability": GIANT steps forward in the molecular elucidation of obesity-but still lots to go[J]. Obes Facts, 2010, 3(5): 294-303. -







 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:

