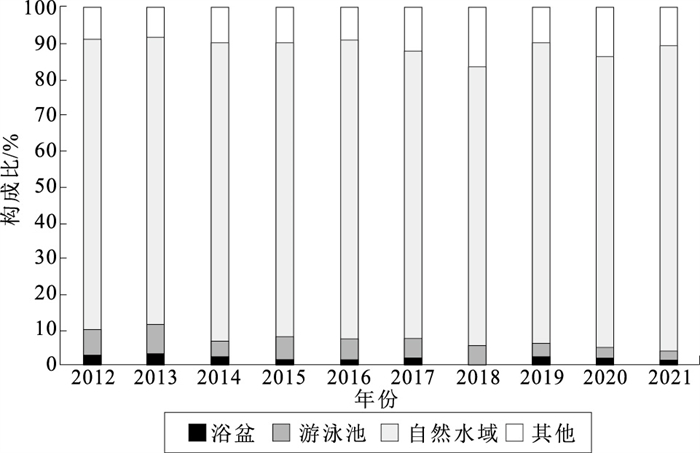
Trend of drowning mortality among children and adolescent in Chongqing, 2012-2021
-
摘要:
目的 了解2012-2021年重庆市儿童青少年溺水死亡率及趋势变化, 为开展溺水干预提供建议。 方法 2012-2021年重庆市儿童青少年溺水死亡(ICD-10:W65.0~W74.9)个案信息来自于重庆市死因监测系统, 对不同性别、地区死亡率比较采用χ2检验, 死亡率的趋势分析采用年度变化百分比(annual percent of change, APC)表示。 结果 重庆市儿童青少年溺水死亡率与标化死亡率由2012年的9.57/10万、9.42/10万下降到2021年的2.80/10万、2.83/10万, APC分别为-13.15%, 13.06%(t值分别为10.93, 10.52, P值均 < 0.01)。2012-2021年男生溺水死亡率高于女生, 农村地区溺水死亡率高于城市(P值均 < 0.05)。0~4、5~9、10~14岁年龄组溺水死亡率分别以年均15.30%, 17.80%与11.40%下降, 变化趋势差异有统计学意义(APC分别为-15.30%, -17.80%, -11.40%, t值分别为11.11, 9.22, 5.62, P值均 < 0.05)。自然水域是发生溺水死亡的主要场所, 约占80%。 结论 重庆市儿童青少年溺水死亡率呈快速下降的趋势, 男性、农村儿童青少年、0~14岁儿童是溺水防控的重点人群, 应继续加强溺水的综合防控。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the trend change of the drowning mortality among children and adolescents in Chongqing, 2012-2021, and to provide suggestion for drowning prevention and control. Methods Drowning death cases (ICD-10:W65.0-W74.9) among children and adolescents in Chongqing from 2012 to 2021 were derived from Chongqing death registration system.The difference of the drowning mortality between male and female, urban and rural area were compared by Chi-square test.The trend change of the drowning mortality between 2012 and 2021 was analyzed by annual percent change (APC). Results The mortality and ASMR of drowning among children and adolescents decreased from 9.57/105, 9.42/105 in 2012 to 2.80/105, 2.83/105 in 2021 significantly (t=10.93, 10.52, P < 0.01).And its APC were-13.15% and 13.06% respectively.The drowning mortality in male was higher than that in female (P < 0.05).The drowning mortality in rural area was higher than that in urban area (P < 0.05).The mortality of drowning among children aged between 0 and 4 years old, 5 and 9 years old, 10 and 14 years old decreased by 15.30%, 17.80% and 11.40%(APC=-15.30%, -17.80%, -11.40%, t=11.11, 9.22, 5.62, P < 0.05).The proportion of drowning in natural water field among children and adolescents accounted for about 80%. Conclusion The mortality of drowning among children and adolescents in Chongqing decreases rapidly.Vulnerable population of drowning includes boys, rural children and adolescents, and children age of 0-14 years old.Comprehensive prevention for drowning should be carried out continuously. -
Key words:
- Drowning /
- Mortality /
- Epidemiologic studies /
- Child /
- Adolescent
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 重庆市儿童青少年2012—2021年溺水死亡率性别间比较/10-5
Table 1. Trend of the mortality of drowning in different sexual among children and adolescents in Chongqing among 2012-2021/10-5
年份 男 女 χ2值 P值 死亡率 标化死亡率 死亡率 标化死亡率 2012 12.12 11.91 6.67 6.57 6.91 0.01 2013 14.08 14.29 5.33 5.15 10.79 < 0.01 2014 10.89 10.63 5.09 4.92 7.85 0.01 2015 9.98 10.18 4.52 4.41 7.76 0.01 2016 9.96 10.21 4.65 4.91 7.54 0.01 2017 7.79 7.99 3.25 3.17 7.61 0.01 2018 5.52 5.68 2.04 2.06 7.13 0.01 2019 5.13 5.21 3.27 3.10 3.65 0.06 2020 5.10 5.03 2.37 2.35 5.58 0.02 2021 3.68 3.78 1.81 1.76 4.45 0.04 注:χ2值为性别间死亡率比较。 表 2 重庆市儿童青少年2012—2021年溺水死亡率城乡间比较/10-5
Table 2. Trend of the mortality of drowning in urban and rural areas among children and adolescents in Chongqing among 2012-2021/10-5
年份 城市 农村 合计 χ2值 P值 死亡率 标化死亡率 死亡率 标化死亡率 死亡率 标化死亡率 2012 4.21 4.25 10.73 10.48 9.57 9.42 6.32 0.01 2013 3.77 4.02 11.24 11.19 9.93 9.97 7.00 0.01 2014 3.49 3.54 9.18 8.86 8.18 7.97 5.88 0.02 2015 2.74 3.00 8.43 8.44 7.43 7.50 6.18 0.01 2016 3.06 3.23 8.49 8.72 7.46 7.71 6.05 0.01 2017 2.33 2.50 6.41 6.43 5.64 5.70 5.36 0.02 2018 1.67 1.92 4.36 4.44 3.86 3.97 4.29 0.04 2019 1.83 1.87 4.79 4.75 4.25 4.22 4.49 0.03 2020 1.24 1.27 4.35 4.28 3.81 3.76 4.85 0.03 2021 0.67 0.75 3.29 3.31 2.80 2.83 4.86 0.03 注:χ2值为性别间死亡率比较。 表 3 重庆市2012—2021年不同年龄段儿童青少年溺水死亡率变化/10-5
Table 3. Trend of drowning mortality of different age group among children and adolescents in Chongqing, 2012-2021/10-5
年份 0~4岁 5~9岁 10~14岁 15~17岁 2012 14.47 11.65 7.73 3.97 2013 12.55 8.97 10.57 7.36 2014 11.25 8.73 7.09 4.98 2015 8.86 8.06 7.90 4.36 2016 7.14 8.35 9.15 4.52 2017 7.18 5.04 6.44 3.52 2018 4.28 3.00 4.84 3.28 2019 5.70 3.33 4.53 3.20 2020 4.31 3.03 3.54 4.64 2021 2.92 1.86 3.12 3.57 -
[1] HAAGSMA J A, GRAETZ N, BOLLIGER I, et al. The global burden of injury: incidence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years and time trends from the Global Burden of Disease study 2013[J]. Inj Prev, 2016, 22(1): 3-18. doi: 10.1136/injuryprev-2015-041616 [2] 王一茸, 蔡伟聪, 雷林. 儿童溺水的流行现况及干预研究进展[J]. 伤害医学(电子版), 2020, 9(1): 61-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYD202001011.htmWANG Y R, CAI W C, LEI L. Epidemiological characteristics and research progress of prevention measures for children drowning[J]. Inj Med(Electronic Version), 2020, 9(1): 61-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYD202001011.htm [3] 戴萌娜, 袭燕, 尹文强, 等. 中国0~14岁儿童1990-2019年溺水死亡现状及趋势分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2022, 43(2): 256-259, 264. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.02.022DAI M N, XI Y, YIN W Q, et al. Incidence, mortality and trends of drowning among children aged 0-14 years old in China, 1990-2019[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2022, 43(2): 256-259, 264. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.02.022 [4] 丁贤彬, 焦艳, 毛德强, 等. 2012—2018年重庆市居民溺水疾病负担变化趋势[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2020, 31(1): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FBYF202001013.htmDING X B, JIAO Y, MAO D Q, et al. Trend of disease burden of drowning in Chongqing residents, 2012-2018[J]. J Public Health Prev Med, 2020, 31(1): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FBYF202001013.htm [5] WANG M, LIU Y, KANG L, et al. Social and environmental risk factors for the accidental drowning of children under five in China[J]. BMC Public Health, 2020, 20(1): 1553. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09650-0 [6] 李蕾, 张志泉, 郑成中, 等. 儿童溺水的防治方案专家共识[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2021, 23(1): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDKZ202101003.htmLI L, ZHANG Z Q, ZHENG C Z, et al. Expert consensus on the prevention and treatment of drowning in children[J]. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2021, 23(1): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDKZ202101003.htm [7] 董景五. 疾病和有关健康问题的国际统计分类(第十次修订)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2021: 849-852.DONG J W. The international statistical classification of diseases and related health problems(10th Revision)[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2021: 849-852. [8] 邓晓, 金叶, 叶鹏鹏, 等. 1990与2013年中国人群溺水死亡疾病负担分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(10): 1308-1314. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.10.003DENG X, JIN Y, YE P P, et al. Disease burden on drowning in the Chinese population, in 1990 and 2013[J]. Chin J Epidem, 2017, 38(10): 1308-1314. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.10.003 [9] 朱银潮, 王永, 李辉, 等. 宁波市20岁以下人群溺水死亡流行特征分析[J]. 预防医学, 2017, 29(8): 766-769. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2017.08.020ZHU Y C, WANG Y, LI H, et al. An analysis on the epidemic characteristics and time trends of drowning induced deaths among the Ningbo residents under 20 years, 2002-2015[J]. Prev Med, 2017, 29(8): 766-769. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2017.08.020 [10] 余伯韬, 王若楠, 李贝, 等. 1990—2019年中国20岁以下人群溺水疾病负担分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(23): 4229-4233, 4285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202123002.htmYU B T, WANG R N, LI B, et al. Disease burden of drowning in population ages under 20 in China, 1990-2019[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(23): 4229-4233, 4285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202123002.htm [11] 何田静, 张岚, 张庆军, 等. 1990与2015年湖北省人群溺水疾病负担分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2018, 34(10): 1390-1394. doi: 10.11847/zgggws1116919HE T J, ZHANG L, ZHANG Q J, et al. Disease burden of drowning among residents in Hubei Province, 1990-2015[J]. Chin J Public Health, 2018, 34(10): 1390-1394. doi: 10.11847/zgggws1116919 [12] FRANKLIN R C, PEDEN A E, HAMILTON E B, et al. The burden of unintentional drowning: global, regional and national estimates of mortality from the Global Burden of Disease 2017 Study[J]. Inj Prev, 2020(Supp 1): i83-i95. [13] 李胜, 刘应焱, 王红英, 等. 2005—2019年中国溺水死亡现状及趋势分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(15): 2705-2709, 2715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202115005.htmLI S, LIU Y Y, WANG H Y, et al. Current situation and trend of drowning death in China, 2005-2019[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(15): 2705-2709, 2715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202115005.htm [14] 吴才娟, 薛金玉, 吴姿谊, 等. 象山半岛学龄前儿童家长预防溺水知识、技能和行为调查[J]. 现代实用医学, 2021, 33(7): 896-897, 914. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2021.07.024WU C J, XUE J Y, WU Z Y, et al. Survey on knowledge, skill and behavior related to drowning among parents of preschool children in Xiangshan Peninsula[J]. Mod Practic Med, 2021, 33(7): 896-897, 914. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2021.07.024 -







 下载:
下载: