Peripheral blood biological markers for early screening in children with autism spectrum disorder
-
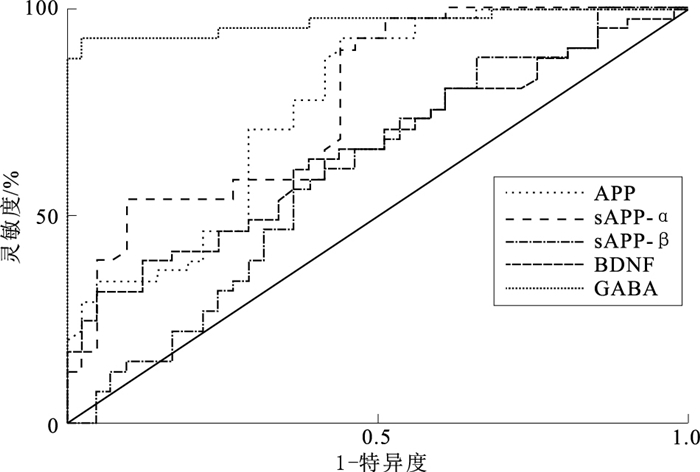
摘要:
目的 研究淀粉样前体蛋白(APP)家族(总sAPP、sAPP-α、sAPP-β)、脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)及γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)在自闭症谱系障碍与正常儿童外周血水平差异,探讨自闭症早期筛查的生物学标记及其与自闭症严重程度的相关性。 方法 选取2019年1—12月在江苏大学附属医院被诊断为自闭症的41名儿童为自闭症组,以同期在该院体检生长发育正常的41名健康儿童为对照组。采用酶联免疫吸附试验检测两组儿童血清总sAPP、sAPP-α、sAPP-β、BDNF及GABA水平。 结果 自闭症组儿童血清总sAPP,sAPP-α水平(2 132.98±333.28 ng/mL, 335.11±33.87 pg/mL)高于对照组(1 734.76±357.97 ng/mL,274.84±32.12 pg/mL),GABA水平(4.17±0.95 μmol/L)低于对照组(6.35±0.84 μmol/L),差异均有统计学意义(t值分别为3.92,4.25,-7.27,P值均 < 0.05);且GABA在重度自闭症患儿外周血水平(3.48±0.77 μmol/L)低于轻-中度患儿(4.94±0.98 μmol/L),差异有统计学意义(t=-3.31,P < 0.05);ROC曲线显示,总sAPP(AUC为0.77, 95%CI=0.66~0.87)、sAPP-α(AUC为0.77, 95%CI=0.67~0.87)及GABA(AUC为0.95, 95%CI=0.90~0.93)具有一定的诊断效能(P值均 < 0.05),其中GABA曲线下面积最大(0.95),其检测灵敏度(85.65%)及特异性(80.76%)最高。二元Logistic回归分析显示,sAPP-α(OR=1.04, 95%CI=1.00~1.07)及GABA(OR=0.02, 95%CI=0.00~0.32)表达水平异常是自闭症发生的相关因素(P值均 < 0.05)。 结论 外周血总sAPP、sAPP-α及GABA表达水平在自闭症儿童具有特异性,可以作为疾病筛查的生物学指标,其中GABA敏感度及特异度最高。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the specifity of amyloid precursor protein(APP), brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)and gamma aminobutyric acid(GABA) in peripheral blood in children with autism spectrum disorder, so as to explore the biomarkers for early screening of ASD and its relationship with the severity of ASD. Methods A total of 41 children diagnosed with autism from January to December 2019 were enrolled in the ASD group. Meanwhile, 41 healthy children with normal growth and development who were examined in the same period were selected as control group. And the sera total sAPP, sAPP-α, sAPP-β, BDNF and GABA of all participants were tested by sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method, and were compared between the two groups. Results The serum sAPP level in ASD group(2 132.98±333.28 ng/mL) was higher than control group(1 734.76±357.97 ng/mL), the serum sAPP-α level(335.11±33.87 pg/mL) was higher than control group(274.84±32.12 pg/mL) and the serum GABA level(4.17±0.95 μmol/L)was lower than control group(6.35±0.84 μmol/L). GABA level (4.17±0.95 μmol/L) was lower than that of control group (6.35±0.84 μmol/L), the differences were statistically significant (t=3.92, 4.25, -7.27, P < 0.05). In addition, the serum GABA level in children with severe ASD (3.48±0.77 μmol/L)was lower than children with mild to moderate (4.94±0.98 μmol/L).The difference was significant (t=-3.31, P < 0.05). ROC curve showed that total sAPP(AUC=0.77, 95%CI=0.66-0.87), sAPP-α(AUC=0.77, 95%CI=0.67-0.87), and GABA (AUC=0.95, 95%CI=0.90-0.93)had diagnostic efficacy for ASD(P < 0.05), among which the AUC of GABA was the largest (0.95)and its sensitivity(85.65%) and specificity(80.76%) were the highest. The results of binary Logistic regression showed that the abnormal expression of sAPP-α (OR=1.04, 95%CI=1.00-1.07) and GABA(OR=0.02, 95%CI=0.00-0.32) were associated with risk for ASD(P < 0.05). Conclusion Considering the specific change of total sAPP, sAPP-α andGABA in peripheral blood in ASD children, total sAPP, sAPP-α and GABA can be considered as promising biomarkers in the early diagnosis of ASD, among which GABA has the highest sensitivity and specificity. -
Key words:
- Autistic disorder /
- Early diagnosis /
- Biological markers /
- Regression analysis /
- Child
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 自闭症及对照组儿童外周血sAPP蛋白家族、GABA及BDNF水平比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparision of expression levels of sAPP, BDNF and GABA in peripheral blood of control group and ASD group (x±s)
组别 人数 总sAPP/(ng·mL-1) sAPP-α/(pg·mL-1) sAPP-β/(pg·mL-1) BDNF/(ng·mL-1) GABA/(μmol·L-1) 自闭症组 41 2 132.98±333.28 335.11±33.87 135.46±19.22 33.20±9.60 4.17±0.95 对照组 41 1 734.76±357.97 274.84±32.12 128.27±25.99 31.06±7.80 6.35±0.84 t值 3.92 4.25 1.55 1.79 -7.27 P值 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.12 0.07 < 0.01 表 2 轻-中度与重度自闭症儿童外周血sAPP家族、BDNF及GABA水平比较(x±s)
Table 2. Comparision of expression levels of sAPP, BDNF and GABA in peripheral blood of mild-moderate and severe ASD children(x±s)
组别 人数 总sAPP/(ng·mL-1) sAPP-α/(pg·mL-1) sAPP-β/(pg·mL-1) BDNF/(ng·mL-1) GABA/(μmol·L-1) 重度 22 2 252.53±386.15 346.71±35.33 144.35±34.80 35.37±9.45 3.48±0.77 轻-中度 19 2 079.84±381.35 326.56±32.68 130.47±32.04 30.74±8.38 4.94±0.98 t值 1.54 0.71 0.67 1.25 -3.31 P值 0.13 0.48 0.52 0.22 < 0.01 表 3 各血清指标诊断自闭症的ROC曲线参数(n=82)
Table 3. ROC curve parameters of each serum index in the diagnosis of autism(n=82)
血清指标 AUC(95%CI) P值 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 总sAPP 0.76(0.66~0.86) < 0.01 72.50 56.10 sAPP-α 0.77(0.67~0.87) < 0.01 70.24 53.66 sAPP-β 0.59(0.47~0.72) 0.12 67.80 34.15 BDNF 0.65(0.53~0.77) 0.06 31.71 45.12 GABA 0.95(0.89~0.92) < 0.01 85.65 80.76 表 4 儿童自闭症发生相关因素的Logistic回归分析(n=82)
Table 4. Logistic regression analysis of related factors of ASD among children(n=82)
血清指标 β值 标准误 Waldχ2值 P值 OR值(OR值95%CI) 总sAPP 0.01 0.00 2.83 0.09 1.01(0.99~1.01) sAPP-α 0.04 0.02 4.34 0.04 1.04(1.00~1.07) sAPP-β 0.02 0.03 0.40 0.53 1.02(0.95~1.09) BDNF 0.41 0.26 2.57 0.11 1.52(0.91~2.53) GABA -4.19 1.55 7.24 0.01 0.02(0.00~0.32) -
[1] 吴梅荣, 徐海青. 孤独症早期诊断生物学标记研究进展[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2015, 23(9): 944-946.WU M R, XU H Q, Research progress on biomarkers for early diagnosis of autism[J]. Chin J Child Health Care, 2015, 23(9): 944-946. [2] BAILEY A R, GIUNTA B N, OBREGON D, et al. Peripheral biomarkers in Autism: secreted amyloid precursor protein-alpha as a probable key player in early diagnosis[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2008, 1(4): 338-344. [3] GOLDANI A A, DOWNS S R, WIDJAJA F, et al. Biomarkers in autism[J]. Front Psychiatry, 2014, 5: 100. [4] ALABDALI A, AL-AYADHI L, EL-ANSARY A. Association of social and cognitive impairment and biomarkers in autism spectrum disorders[J]. J Neuroinflamm, 2014, 11(4): 1-14. [5] TAURINES R, SEGURA M, SCHECKLMANN M, et al. Altered peripheral BDNF mRNA expression and BDNF protein concentrations in blood of children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder[J]. J Neural Transm (Vienna), 2014, 121(9): 1117-1128. [6] American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders[M]. Arlington: American Psychiatric Association, 2013. [7] 李雪荣. 现代儿童精神医学[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 1994: 180.LI X R. Modern child psychiatry[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science & Technology Press, 1994: 180. [8] KAETHER C, HAASS C. A lipid boundary separates APP and secretases and limits amyloid beta-peptide generation[J]. J Cell Biol, 2004, 167(5): 809-812. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200410090 [9] ROSSIGNOL D A, FRYE R E. The use of medications approved for Alzheimer's disease in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review[J]. Front Pediatr, 2014, 2: 87. [10] 郑清文, 陈凯云, 邓红珠, 等. 大头围与低年龄孤独症谱系障碍的相关研究[J]. 新医学, 2015, 46(9): 584-588. doi: 10.3969/g.issn.0253-9802.2015.09.004ZHENG Q W, CHEN K Y, DENG H Z, et al. Study on the relationship between large head circumference and ASD in low-age autistic child[J]. New Med, 2015, 46(9): 584-588. doi: 10.3969/g.issn.0253-9802.2015.09.004 [11] 谭迎花, 郗春艳, 汪永娟, 等. 孤独症患儿头围测量分析[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2011, 26(10): 760-762.TAN Y H, XI C Y, WANG Y J, et al. Analysis of head circumference of autistic child[J]. Chin J Practic Pediatr, 2011, 26(10): 760-762. [12] PHILIPPE A, GUILLOUD-BATAILLE M, MARTINEZ M, et al. Analysis of ten candidate genes in autism by association and linkage[J]. Am J Med Genet, 2002, 114(2): 125-128. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.10041 [13] 李家鑫, 韦斌垣. BDNF基因功能性多态rs6265与孤独症儿童的相关性研究[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2014, 24(16): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2014.16.007LI J X, WEI B H. Study on the relationship between BDNF gene functional polymorphism rs6265 and autistic child[J]. Chin Mordern Med, 2014, 24(16): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2014.16.007 [14] CHEN Q, DEISTER C A, GAO X, et al. Dysfunction of cortical GABA ergic neurons leads to sensory hyper-reactivity in a Shank3 mouse model of ASD[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2020, 23(4): 520-532. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0598-6 [15] CHO K K, HOCH R, LEE A T, et al. Gamma rhythms link prefrontal interneuron dysfunction with cognitive inflexibility in Dlx5/6(+/-) mice[J]. Neuron, 2015, 85(6): 1332-1343. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.02.019 -







 下载:
下载: