Adiposity peak and rebound in early life among primary school students with different body mass index patterns
-
摘要:
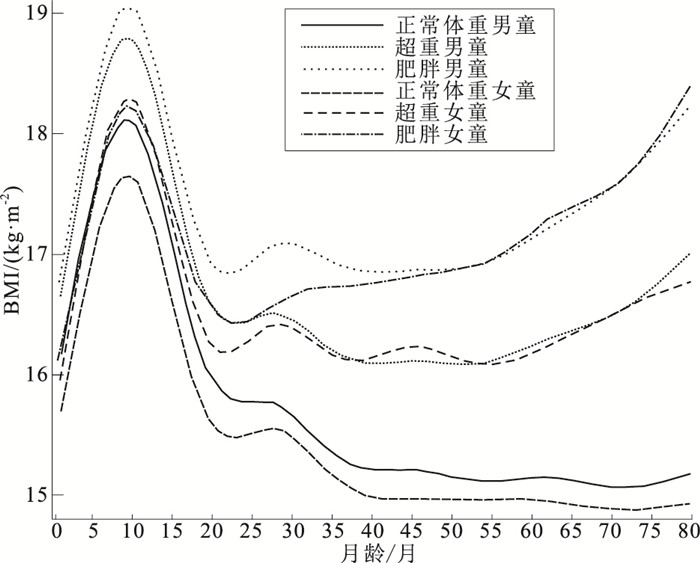
目的 研究不同营养状况小学一年级学生生命早期脂肪高峰和脂肪重积聚特征,为寻求干预工作的重点时机提供参考。 方法 于2019年9—12月选取接受学校常规体检的上海市闵行区2 330名小学一年级学生,根据体质量指数(BMI)分为正常、超重、肥胖3类体重状态。回顾性获取研究对象1~80个月的身高和体重检查记录,使用广义相加混合模型分性别拟合该3类人群BMI生长曲线,计算脂肪高峰和脂肪重积聚时间及对应的BMI值。 结果 一年级小学生超重检出率为16.31%(380名),肥胖检出率为16.09%(375名)。小学一年级时体重状态为肥胖的儿童,生命最初80个月内BMI拟合值持续高于小学一年级时体重状态为超重或正常的儿童。不同体重状态小学一年级学生的脂肪高峰发生时间均为9月龄,但超重与肥胖的小学生在脂肪高峰时的BMI值高于同性别的正常体重小学生。小学一年级正常体重儿童的脂肪重积聚发生时的月龄为72个月,超重男童为52个月,女童为55个月;肥胖男童为22个月,女童为23个月。小学一年级时正常体重的儿童,其脂肪重积聚时的BMI拟合值也小于小学一年级时超重或肥胖的儿童。 结论 不同体重状态的小学一年级学生脂肪高峰月龄趋于一致,但脂肪重积聚月龄却存在差异。肥胖小学生的脂肪重积聚时间明显提前,脂肪重积聚时的BMI值也高于其他体重状态小学生。 Abstract:Objective To explore the characteristics of the adiposity peak and rebound in early life among first-year primary school students with different body-weight measures, so as to provide scientific evidence for the development of prevention interventions to manage childhood overweight and obesity. Methods A total of 2 330 first-year primary school students who received routine physical examinations from September to December in 2019 were selected. According to body mass index (BMI) status, participants were divided into three categories: healthy weight, overweight, and obese. The BMI growth trajectories of the three groups were fitted by gender using the generalized additive mixed model from 1 to 80 months, retrospectively. Each subject's age at the adiposity peak and rebound, and associated BMI values, were calculated. Results The prevalence of overweight and obesity was 16.31% (380/2 330) and 16.09% (375/2 330), respectively. For first-year students with obesity, the BMI value continued to be higher than their overweight or healthy weight counterparts during the first 80 months of life. The age at the adiposity peak for these students, whose BMI status varied, was about nine months. However, the BMI of children with overweight or obesity was much higher than that of healthy weight subjects. Age at adiposity rebound was 72 months for healthy weight children, 52 to 55 months in children defined as overweight, and 22 to 23 months in children with obesity. For healthy-weight children, the fitted value of BMI at the adiposity rebound was less than that of overweight and obese children. Conclusion Age at the adiposity peak was largely similar among first-year students with different BMI patterns; however, age at adiposity rebound was different. Age at adiposity rebound among children with obesity was much earlier than that of other subjects, and their BMI values were much higher. -
Key words:
- Nutritional status /
- Life cycle stager /
- Adipose tissue /
- Body mass index /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 不同性别小学生各营养状况生命早期脂肪高峰和脂肪重积聚的月龄及BMI拟合值/(kg·m-2)
Table 1. Characteristics of BMI growth curve in early life of first-grade primary school students with different weight status/(kg·m-2)
性别 营养状况 人数 脂肪高峰 脂肪重积聚 月龄 BMI值(BMI值95%CI) 月龄 BMI值(BMI值95%CI) 男 正常 768 9 18.12(18.10~18.14) 72 15.07(15.03~15.11) 超重 211 9 18.80(18.76~18.84) 52 16.09(16.05~16.17) 肥胖 229 9 19.05(19.01~19.09) 22 16.84(16.81~16.91) 女 正常 807 9 17.65(17.63~17.67) 72 14.88(14.84~14.92) 超重 169 10 18.29(18.25~18.33) 55 16.09(16.04~16.18) 肥胖 146 10 18.23(18.18~18.28) 23 16.44(16.38~16.50) -
[1] NCD Risk Factor Collaboration(NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390(10113): 2627-2642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3 [2] WEIHRAUCH-BLUHER S, WIEGAND S. Risk factors and implications of childhood obesity[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2018, 7(4): 254-259. doi: 10.1007/s13679-018-0320-0 [3] BRANNSETHER B, EIDE G E, ROELANTS M, et al. BMI and BMI SDS in childhood: annual increments and conditional change[J]. Ann Hum Biol, 2017, 44(1): 28-33. doi: 10.3109/03014460.2016.1151933 [4] WEN X, KLEINMAN K, GILLMAN M W, et al. Childhood body mass index trajectories: modeling, characterizing, pairwise correlations and socio-demographic predictors of trajectory characteristics[J]. BMC Med Res Methodol, 2012, 12: 38. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-38 [5] ROLLAND-CACHERA M F, DEHEEGER M, BELLISLE F, et al. Adiposity rebound in children: a simple indicator for predicting obesity[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 1984, 39(1): 129-135. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/39.1.129 [6] ROLLAND-CACHERA M F, SEMPE M, GUILLOUD-BATAILLE M, et al. Adiposity indices in children[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 1982, 36(1): 178-184. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/36.1.178 [7] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查: WS/T 586—2018[S]. 2018-08-01.National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC. Screening for overweight and obesity among school-age children and adolescents: WS/T 586-2018[S]. 2018-08-01. [8] WOOD S N. Generalized additive models: an introduction with R[M]. Boca Raton: Chapman Hall/CRC, 2006. [9] ROCHE J, QUINART S, THIVEL D, et al. Comparison between type A and type B early adiposity rebound in predicting overweight and obesity in children: a longitudinal study[J]. Br J Nutr, 2020, 124(5): 501-512. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520000987 [10] SKINNER J D, BOUNDS W, CARRUTH B R, et al. Predictors of children's body mass index: a longitudinal study of diet and growth in children aged 2-8 y[J]. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord, 2004, 28(4): 476-482. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802405 [11] FLEXEDER C, THIERING E, KRATZSCH J, et al. Is a child's growth pattern early in life related to serum adipokines at the age of 10 years?[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2014, 68(1): 25-31. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2013.213 [12] GIUSSANI M, ANTOLINI L, BRAMBILLA P, et al. Cardiovascular risk assessment in children: role of physical activity, family history and parental smoking on BMI and blood pressure[J]. J Hypertens, 2013, 31(5): 983-992. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835f17c7 [13] MO-SUWAN L, MCNEIL E, SANGSUPAWANICH P, et al. Adiposity rebound from three to six years of age was associated with a higher insulin resistance risk at eight-and-a-half years in a birth cohort study[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2017, 106(1): 128-134. doi: 10.1111/apa.13639 [14] PERNG W, RAHMAN M L, ARIS I M, et al. Metabolite profiles of the relationship between body mass index (BMI) milestones and metabolic risk during early adolescence[J]. Metabolites, 2020, 10(8): 316. doi: 10.3390/metabo10080316 [15] ARIS I M, RIFAS-SHIMAN S L, LI L J, et al. Patterns of body mass index milestones in early life and cardiometabolic risk in early adolescence[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2019, 48(1): 157-167. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyy286 [16] DI GRAVIO C, KRISHNAVENI G V, SOMASHEKARA R, et al. Comparing BMI with skinfolds to estimate age at adiposity rebound and its associations with cardio-metabolic risk markers in adolescence[J]. Int J Obes(Lond), 2019, 43(4): 683-690. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0144-8 -







 下载:
下载: