A follow-up study on academic pressure and Internet addiction of college students in Jiangsu
-
摘要:
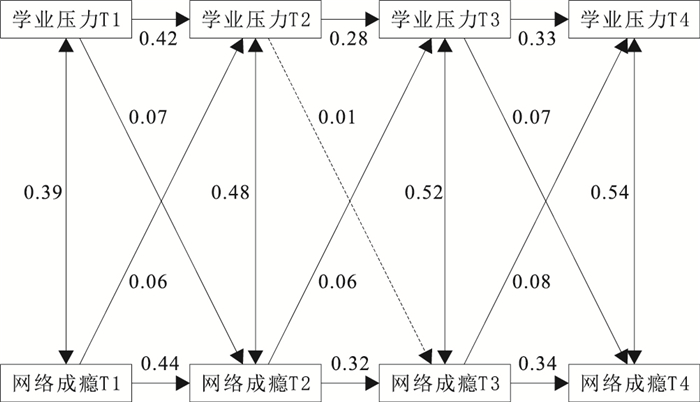
目的 考查大学生学业压力与网络成瘾的纵向关系,为促进大学生心理健康发展提供参考。 方法 于2016年10月开始对整群抽取的江苏某高校5 372名大学生进行4次(T1、T2、T3、T4)纵向追踪研究,每次间隔1年。采用中国大学生心理健康筛查量表(CSMHSS)中的“学业压力”和“网络成瘾”筛查指标进行测查,采用交叉滞后分析探讨大学生学业压力与网络成瘾的关系。 结果 重复测量方差分析显示,大学生学业压力的时间主效应有统计学意义[F(3, 16 113)=767.28,P < 0.01,η2=0.13]。大学生的学业压力随时间呈下降趋势,T1阶段最高,T4阶段最低。大学生网络成瘾的时间主效应有统计学意义[F(3, 16 113)=165.22,P < 0.01,η2=0.03]。大学生的网络成瘾随时间呈“先升后降”的趋势,T2阶段最高,T4阶段最低。交叉滞后分析表明,T1的学业压力可以显著预测T2的网络成瘾,T3的学业压力可以显著预测T4的网络成瘾,路径系数分别为0.07,0.07(P值均 < 0.01)。前测(Tn)的网络成瘾可以显著预测后测[T(n+1)]的学业压力,路径系数分别为0.06,0.06,0.08(P值均 < 0.01)。 结论 大学生学业压力能部分预测网络成瘾,网络成瘾能显著预测学业压力。高校要加强学风建设,降低学生的学业压力,同时要通过多种途径减少大学生网络成瘾,以促进大学生心理健康发展。 Abstract:Objective To examine the longitudinal relationship between academic pressure and Internet addiction of college students and to provide reference for the development of college students' mental health. Methods In October 2016, a longitudinal 4 waves (T1 to T4) of follow-up study was conducted among 5 372 college students from a university in Jiangsu, with an interval of 1 year each time. Academic pressure and Internet addiction were derived from the College Students Mental Health Screening Scale. A cross-lag analysis was used to explore the relationship between college students' academic pressure and Internet addiction. Results Repeated measures analysis of variance showed that the main effect of time for academic pressure was significant[F(3, 16 113)=767.28, P < 0.01, η2=0.13]. The academic pressure of college students showed a downward trend over time, with the highest at T1 stage and the lowest at T4 stage. The main effect of time for college students' Internet addiction was significant[F(3, 16 113)=165.22, P < 0.01, η2=0.03]. The Internet addiction of college students showed a trend of decreasing after increasing over time, with the highest stage T2 and the lowest stage T4. The cross-lag analysis showed that academic pressure of T1 could significantly predict the Internet addiction of T2, and academic pressure of T3 could significantly predict the Internet addiction of T4, and the path coefficients are 0.07 and 0.07(P < 0.01). In addition, the pre-test (Tn) Internet addiction can significantly predict the post-test [T(n+1)] academic pressure, and the path coefficients were 0.06, 0.06, 0.08(P < 0.01). Conclusion Academic pressure can partially predict Internet addiction among college students, while Internet addiction can also significantly predict academic pressure. Colleges and universities should strengthen the construction of learning style, reduce the academic pressure of students, and reduce the Internet addiction of college students through various ways, so as to promote the healthy development of college students. -
Key words:
- Learning /
- Pressure /
- Internet /
- Behavior, addictive /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 大学生学业压力与网络成瘾相关分析(r值,n=5 372)
Table 1. Correlation analysis of college students' academic stress and Internet addiction(r, n=5 372)
变量 学业压力(T1) 学业压力(T2) 学业压力(T3) 学业压力(T4) 网络成瘾(T1) 网络成瘾(T2) 网络成瘾(T3) 学业压力(T2) 0.44 学业压力(T3) 0.29 0.31 学业压力(T4) 0.35 0.42 0.36 网络成瘾(T1) 0.39 0.22 0.16 0.23 网络成瘾(T2) 0.24 0.48 0.20 0.30 0.46 网络成瘾(T3) 0.14 0.17 0.52 0.25 0.29 0.33 网络成瘾(T4) 0.22 0.25 0.24 0.54 0.39 0.45 0.38 注:P值均 < 0.01。 -
[1] 郑晓江. 生命困顿与生命教育[J]. 南昌大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2012, 43(2): 48-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0448.2012.02.009ZHENG X J. Life hardship and life education[J]. J Nanchang Univ(Humman Soc Sci Edit), 2012, 43(2): 48-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0448.2012.02.009 [2] 旦增卓玛, 管芳, 游旭群. 西藏高校大学生心理压力源与压力体验之间的关系: 心理资本的中介与调节作用[J]. 西藏大学学报(社会科学版), 2021, 36(3): 229-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZDX202103031.htmTENZEN D, GUAN F, YOU X Q. The relationship between psychological stressors and stress experience of college students in Tibet: the mediating and regulating effects of psychological capital[J]. J Tibet Univ(Soc Sci Edit), 2021, 36(3): 229-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZDX202103031.htm [3] 杨爱华. 新时代大学生社区育人面临的挑战与优化路径[J]. 思想教育研究, 2021(5): 154-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SIXI202105028.htmYANG A H. Challenges and optimization paths facing college students' community education in the new era[J]. Stud Ideol Educ, 2021(5): 154-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SIXI202105028.htm [4] 魏华, 周宗奎, 张永欣, 等. 压力与网络成瘾的关系: 家庭支持和朋友支持的调节作用[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2018, 16(2): 266-271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2018.02.018WEI H, ZHOU Z K, ZHANG Y X, et al. Relationship between stress and Internet addiction: the moderating effects of family support and friend support[J]. Stud Psychol Behav, 2018, 16(2): 266-271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2018.02.018 [5] 公娜, 黄巧敏, 张孟思, 等. 深圳市初中生网络成瘾3年追踪研究[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2021, 42(12): 1833-1837. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.12.018GONG N, HUANG Q M, ZHANG M S, et al. A three-year longitudinal study on Internet addiction among junior students in Shenzhen City[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2021, 42(12): 1833-1837. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.12.018 [6] O'CONNOR E L, LONGMAN H, WHITE, K M, et al. Sense of community, social identity and social support among players of massively multiplayer online games(MMOGS): a qualitative analysis[J]. J Commun Appl Soc Psychol, 2015, 25(6): 459-473. doi: 10.1002/casp.2224 [7] 张素华, 姚雪, 张丽, 等. 成都市初中生网络成瘾与心理健康的相关性研究[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2021, 29(1): 37-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXB202101009.htmZHANG S H, YAO X, ZHANG L, et al. Study on the correlation between Internet addiction and mental health among junior high school students in Chengdu[J]. Chin J Prev Control Chronic Dis, 2021, 29(1): 37-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXB202101009.htm [8] 徐涛, 周县委, 张天成, 等. 中国中学生抑郁症状危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2022, 49(5): 814-818, 844. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202205010.htmXU T, ZHOU X W, ZHANG T C, et al. Risk factors of depressive symptoms among Chinese middle school students: a Meta-analysis[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2022, 49(5): 814-818, 844. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202205010.htm [9] 董佩宝. 社会工作视角下的大学生网络成瘾问题初探: 以西部某大学为例[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2014.DONG P B. A preliminary study on college students' Internet addiction from the perspective of social work: taking a university in the west as an example[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2014. [10] 隋文馨, 秦燕, 黎红友. 跨界与融合: 短视频时代高校网络文化育人的价值困境与路径探析[J]. 四川师范大学学报(社会科学版), 2021, 48(2): 112-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSF202102014.htmSUI W X, QIN Y, LI H Y. Crossover and integration: the value dilemma and path analysis of college network culture education in the short video era[J]. J Sichuan Normal Univ(Soc Sci Edit), 2021, 48(2): 112-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSF202102014.htm [11] 方晓义, 袁晓娇, 胡伟, 等. 中国大学生心理健康筛查量表的编制[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2018, 16(1): 111-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2018.01.015FANG X Y, YUAN X J, HU W, et al. The development of College Students Mental Health Screening Scale[J]. Stud Psychol Behav, 2018, 16(1): 111-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2018.01.015 [12] 张超, 鲁光启. 思想政治教育中大学生压力管理的对策研究[J]. 思想政治教育研究, 2014, 30(5): 88-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9749.2014.05.023ZHANG C, LU G Q. Research on the countermeasures of college students' stress management in ideological and political education[J]. Ideol Politic Educ Res, 2014, 30(5): 88-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9749.2014.05.023 [13] 周铭, 胡一文, 郑一瑾, 等. 某综合院校大学生网络成瘾现状及其影响因素[J]. 中国健康教育, 2015, 31(4): 416-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJK201504021.htmZHOU M, HU Y W, ZHENG Y J, et al. Current situation on Internet addiction and its influencing factors among undergraduates in a comprehensive university[J]. Chin J Health Educ, 2015, 31(4): 416-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJK201504021.htm [14] LAI C, MAK K, WATANABE H, et al. The mediating role of Internet addiction in depression, social anxiety, and subjective psychosocial well-being among adolescents in six Asian countries: a structural equation modelling approach[J]. Public Health, 2015, 129(9): 1224-1236. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2015.07.031 [15] 宫盛花, 苏骁征, 叶宝娟. 贵州省少数民族大学生心理健康素质培养现状的调查研究: 以苗族、侗族为例[J]. 中国特殊教育, 2011(6): 83-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3728.2011.06.017GONG S H, SU X Z, YE B J. An Investigation into the current mental health training of ethnic minority college students in Guizhou Province[J]. Chin J Spec Educat, 2011(6): 83-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3728.2011.06.017 [16] 吕素香. 大二低潮现象原因与对策[J]. 中国高等教育, 2015(10): 56-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDJ201510021.htmLYU S X. Causes and countermeasures of sophomore low tide phenomenon[J]. China Higher Educ, 2015(10): 56-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDJ201510021.htm [17] 东靓, 丛石, 张楠, 等. 太原市大学生健康危险行为及其影响因素研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(15): 2781-2785, 2796. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202115022.htmDONG L, CONG S, ZHANG N, et al. Health risk behavior and its influencing factors of undergraduates, Taiyuan[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(15): 2781-2785, 2796. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF202115022.htm [18] 高文斌, 陈祉妍. 网络成瘾病理心理机制及综合心理干预研究[J]. 心理科学进展, 2006, 14(4): 596-603. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXD200604018.htmGAO W B, CHEN Z Y. A study on psychopathology and psychotherapy of Internet addiction[J]. Advanc Psychol Sci, 2006, 14(4): 596-603. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXD200604018.htm [19] HOBFOLL S E. Conservation of resources. A new attempt at conceptualizing stress[J]. Am Psychol, 1989, 44(3): 513-524. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.44.3.513 [20] 张金健, 陈红. 大学新生学校适应困难与网络成瘾的交叉滞后分析[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2021, 29(5): 1073-1077. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLCY202105037.htmZHANG J J, CHEN H. A cross-lag analysis between school adaptation difficulties and Internet addiction of college freshmen[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2021, 29(5): 1073-1077. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLCY202105037.htm [21] 雷雳, 王兴超. 网络平台青少年模式缘何形同虚设[J]. 人民论坛, 2020(28): 123-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3381.2020.28.037LEI L, WANG X C. Why is the online platform youth model ineffective[J]. People's Tribun, 2020(28): 123-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3381.2020.28.037 -







 下载:
下载: