Risk perception and behavior status of college students' extracurricular jogging exercise
-
摘要:
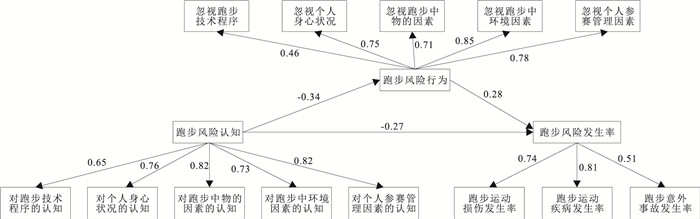
目的 探索跑步风险认知与跑步风险行为及跑步风险发生率之间的关系,为降低大学生课外跑步锻炼风险提供可行路径。 方法 采用方便抽样方法,对北京某大学470名参加课外跑步锻炼的大学生进行追踪调查,运用运动世界校园APP进行跑步锻炼记录和监测,追踪期间,每月统计1次跑步相关信息,共统计6次,同时,分3个阶段发放3份问卷收集相关信息。运用SPSS 26.0进行统计描述。运用AMOS 22.0进行数据相关关系分析。 结果 大学生一学年课外跑步锻炼风险发生率为71.06%,大学生对于跑步风险认知的平均得分为(3.68±0.59)分,对于跑步运动损伤认知的平均得分为(3.25±0.91)分,对于跑步运动疾病认知的平均得分为(3.23±0.96)分;大学生跑步风险认知与跑步风险行为之间呈负相关(r=-0.34),跑步风险认知与跑步伤病发生率呈负相关(r=-0.27),跑步风险行为与跑步伤病发生率呈正相关(r=0.28)(P值均 < 0.01)。体育课是大学生获得跑步风险知识的主要途径(43.40%)。 结论 大学生课外跑步锻炼风险发生率较高,对于跑步风险和跑步运动伤病的认知水平较低。需采取相关措施提高大学生跑步风险认知水平,进而降低跑步风险发生率。 Abstract:Objective To explore the relationship among jogging risk perception, jogging risk behavior and the incidence of jogging risk, so as to provide a feasible way to reduce the risk of college students' extracurricular jogging exercise. Methods The method of convenience sampling was used to conduct a follow-up survey among 470 college students at a university in Beijing participating in extracurricular jogging exercise and the sports world campus app was used to record and monitor jogging exercise. During the tracking period, the jogging related information was counted once a month, a total of 6 times. At the same time, three questionnaires were distributed in three stages to collect relevant information. SPSS 26.0 was used for the descriptive analysis, and AMOS 22.0 was used for correlational analysis. Results The risk rate of extracurricular jogging exercise of college students during the past academic year was 71.06%, score of knowledge on jogging risk was(3.68±0.59), was (3.25±0.91)for jogging injury, and was(3.23±0.96)for jogging-related disease. Significant negative correlation between college students' jogging risk perception and jogging risk behavior (r=-0.34), negative correlation between jogging risk perception and the incidence of jogging injuries (r=-0.27), and positive correlation between jogging risk behavior and the incidence of jogging injuries (r=0.28) were observed(P < 0.01). PE(physical education) class was the main way of obtaining the knowledge about jogging risks among college students(43.40%). Conclusion College students show high vulnerability for extracurricular jogging-related risks, and low level of perception of jogging risks and jogging injuries. Relevant measures need to be taken to improve the cognitive level of running risk among college students, so as to reduce the incidence of running risk. -
Key words:
- Cognition /
- Motor activity /
- Health education /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 大学生一学年课外跑步运动风险发生率(n=470)
Table 1. Incidence of extracurricular jogging risk of college students in one academic year(n=470)
运动损伤类型 发生人数 发生率/% 运动损伤类型 发生人数 发生率/% 皮肤擦伤 54 11.49 膝关节前侧疼痛 110 23.40 脚趾甲损伤 74 15.74 膝关节后侧疼痛 56 11.91 足底水泡 80 17.02 膝关节内侧疼痛 64 13.62 前脚掌疼痛 176 37.45 膝关节外侧疼痛 58 12.34 后脚跟底部疼痛 134 28.51 大腿前侧疼痛 132 28.09 足弓中部疼痛 100 21.28 大腿后侧疼痛 120 25.53 跟腱部位疼痛 74 15.74 大腿前侧疼痛 100 21.28 踝关节疼痛 94 20.00 髋关节疼痛 50 10.64 小腿前侧疼痛 126 26.81 腰背部疼痛 120 25.53 小腿后侧疼痛 164 34.89 -
[1] HULTEEN R M, SMITH J J, MORGAN P J, et al. Global participation in sport and leisure-time physical activities: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Prev Med, 2017, 95(1): 14-25. [2] 杨一卓. 业余跑者跑步损伤危险因素调查及长距离跑后足弓疲劳与纠正效果[D]. 北京: 北京体育大学, 2018.YANG Y Z. A cross-sectional study of risk factors of recreational runners and the arch collapse after long distance running and the correction effects[D]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University, 2018. [3] KEMLER E, BLOKLAND D, BACKX F J, et al. Differences in injury risk and characteristics of injuries between novice and experienced runners over a 4-year period[J]. Phys Sports Med, 2018, 46(4): 485-491. doi: 10.1080/00913847.2018.1507410 [4] 宋广成. 高校体育活动中运动猝死事件的成因与防卫机制的构建[D]. 武汉: 武汉体育学院, 2016.SONG G C. The causes of sudden-death in sports activities of college and construction of defense mechanism[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Sports University, 2016. [5] BAUM P, SHARHAG J, MEYER T, et al. Research on sudden death in sports: based on national data of Germany[J]. Sports Sci, 2016, 37(3): 44-49. [6] 咕咚运动大数据研究院. 2018中国跑者猝死风险报告[R]. 成都: 咕咚运动大数据研究院, 2018-08-14.Codoon Sports BigData Research Institute. The report on the risk of sudden death of Chinese runners in 2018[R]. Chengdu: Codoon Sports BigData Research Institute, 2018-08-14. [7] 国务院办公厅. 关于强化学校体育促进学生身心健康全面发展的意见[A/OL]. (2016-05-06)[2022-01-28]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-05/06/content_5070778.htm.General Office of the State Council of the PRC. Opinions on strengthening school physical education and promoting the all-round development of students' physical and mental health[A/OL]. (2016-05-06)[2022-01-28]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-05/06/content_5070778.htm. [8] HU D G, LIU X L, XIAO H F, et al. Jogging-related risk cognition and the stimulation of risky behavior during jogging[J]. Am J Health Behav, 2021, 45(2): 256-267. doi: 10.5993/AJHB.45.2.6 [9] RUNDMO T, SJOBERG L, MOEN B E. Explaining risk perception: an evaluation of the psychometric paradigm in risk perception research[M]. Trondheim: Rotunde Publikasjoner, 2004: 3-20. [10] 胡德刚, 梁金辉, 张吾龙. 健身跑者跑步风险认知评价模型的构建及实证分析[J]. 首都体育学院学报, 2021, 33(2): 162-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BTSF202102007.htmHU D G, LIANG J H, ZHANG W L. Construction and empirical analysis of risk cognition evaluation model for fitness runners[J]. J Cap Univ Phys Educ Sports, 2021, 33(2): 162-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BTSF202102007.htm [11] 杨一卓, 矫玮, 袁绍婷. 业余马拉松跑者跑步损伤调查及影响因素分析[J]. 山东体育学院学报, 2020, 36(3): 91-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2076.2020.03.013YANG Y Z, JIAO W, YUAN S T. Incidence and risk factors of running-related injuries among amateur marathon runners[J]. J Shandong Inst Phys Educ Sports, 2020, 36(3): 91-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2076.2020.03.013 [12] 浦钧宗. 运动性疾病[M]. 北京: 人民体育出版社, 1993: 1-14.PU J Z. Sports diseases[M]. Beijing: People's Sports Press, 1993: 1-14. [13] 欧秀伶. 马拉松运动意外事故的法律分析[J]. 体育与科学, 2013, 34(3): 66-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4590.2013.03.014OU X L. An analysis of the law cases of accidents and emergencies in marathon races[J]. Sports Sci, 2013, 34(3): 66-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4590.2013.03.014 [14] 李桂娟, 段德平. 大学生对体育锻炼风险认知的分析与研究[J]. 内蒙古教育(职教版), 2015(8): 66-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NEZJ201508044.htmLI G J, DUAN D P. Analysis and research on college students' cognition of physical exercise risk[J]. Inn Mong Educ (Vocat Educ Edit), 2015(8): 66-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NEZJ201508044.htm [15] 闫振龙, 何昌珂, 苏洋. 大学生运动伤害与风险防控研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报(社会科学版), 2019, 39(4): 126-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAJD201904015.htmYAN Z L, HE C K, SU Y. Research on college student sports injuries and risk control[J]. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ (Soc Sci Edit), 2019, 39(4): 126-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAJD201904015.htm [16] VIDEBæK S, BUENO A M, NIELSEN R O, et al. Incidence of running-related injuries per 1000 h of running indifferent types of runners: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Sports Med, 2015, 45(7): 1017-1026. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0333-8 [17] 胡德刚, 于素梅, 张吾龙, 等. 基于"4M理论"构建一体化运动安全教育内容与评价指标体系[J]. 中国健康教育, 2021, 37(12): 1091-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJK202112008.htmHU D G, YU S M, ZHANG W L, et al. Construction of integrated sports safety education content and evaluation index system based on "4M theory"[J]. Chin J Health Educ, 2021, 37(12): 1091-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJK202112008.htm [18] 张东燕, 高书国. 现代家庭教育的功能演进与价值提升: 兼论家庭教育现代化[J]. 中国教育学刊, 2020(1): 66-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYX202001017.htmZHANG D Y, GAO S G. Functional evolution and value promotion of modern family education: also on the modernization of family education[J]. J Chin Soc Educ, 2020(1): 66-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYX202001017.htm [19] 胡德刚, 宗波波, 王宝森, 等. 新冠肺炎疫情期间大学生居家体育锻炼行为与促进研究[J]. 武汉体育学院学报, 2020, 54(6): 80-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTXB202006013.htmHU D G, ZONG B B, WANG B S, et al. Behavior and promotion of college students' home-based physical exercise during COVID-19 pandemic[J]. J Wuhan Inst Phys Educ, 2020, 54(6): 80-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTXB202006013.htm -







 下载:
下载: