Effectiveness of exercise on body composition for overweight and obese children and adolescents: a network Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
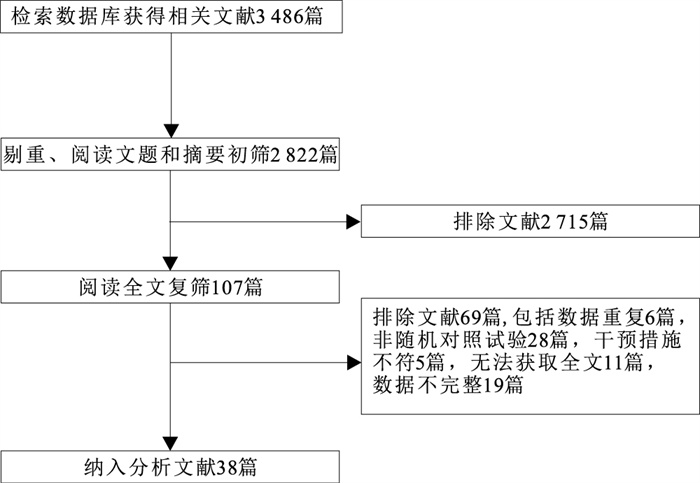
目的 采用网状Meta分析方法比较有氧、抗阻、有氧结合抗阻3种运动方式对超重/肥胖儿童、青少年身体成分的影响,为儿童青少年超重/肥胖干预研究和实践提供更全面有效的证据。 方法 检索中国知网、维普网、万方、PubMed、Web of Science数据库公开发表的与“运动干预对超重/肥胖儿童青少年体成分”相关的随机对照试验,检索时间为建库至2021年10月31日;由2名研究者独立筛选文献、提取数据和评价纳入研究的偏倚风险,采用Stata 15.1和RevMan 5.0进行分析。 结果 共纳入38项研究,网状Meta分析结果显示,与空白对照组比较,有氧结合抗阻干预[MD值(MD值95%CI)=-1.25(-1.76~-0.74),P<0.05]改善超重/肥胖儿童、青少年体质量指数(BMI)最有效,其次是有氧干预[MD值(MD值95%CI)=-0.87(-1.23~-0.52),P<0.05]、抗阻干预[MD值(MD值95%CI)=-0.58(-1.06~-0.10),P<0.05];有氧结合抗阻干预[MD值(MD值95%CI)=-4.02(-5.60~-2.44),P<0.05]对改善超重/肥胖儿童、青少年体脂率(BF%)最有效,其次是抗阻干预[(MD值(MD值95%CI)=-2.89(-4.62~-1.16),P<0.05]、有氧干预[MD值(MD值95%CI)=-1.88(-3.14~-0.62),P<0.05]。 结论 有氧结合抗阻训练是改善超重/肥胖儿童、青少年身体成分的最佳运动方式。在制定运动时,建议将有氧结合抗阻运动作为超重/肥胖儿童青少年的首选运动方案。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the effectiveness of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and aerobic combined resistance exercise on body composition among overweight and obese children and adolescents, to provide more comprehensive and effective evidences for overweight/obesity intervention research and practice in children and adolescents. Methods Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) regarding exercises on body composition among children and adolescents with overweight and obesity published before December 31th, 2020 were searched in databases of CNKI, Wanfang, PubMed, Web of Science. Two reviewers independently screened literature, extracted data and assessed risk of bias of included studies. Stata 15.1 and RevMan 5.0 were used for statistical analysis. Results A total of 38 RCTs were included. The effectiveness of exercise on BMI reduction among overweight/obese children and adolescents were in the following rankings: combined exercise [MD=-1.25(-1.76--0.74), P < 0.05], aerobic exercise [MD=-0.87(-1.23--0.52), P < 0.05], resistance exercise [MD=-0.58(-1.06--0.10), P < 0.05]. The effectiveness of exercise on body fat percentage reduction among overweight/obese children and adolescents were in the following rankings: combined exercise [MD=-4.02(-5.60--2.44), P < 0.05], resistance exercise [MD=-2.89(-4.62--1.16), P < 0.05], aerobic exercise [MD=-1.88(-3.14--0.62), P < 0.05]. Conclusion Aerobic training combined with resistance training is the most effective exercise to improve body composition for children and adolescents with overweight and obesity. When formulating exercise prescription, atrobic combined with resistance exercise can be used as the first choice for overweight and obese children and adolescents. -
Key words:
- Intervention studies /
- Motor activity /
- Overweight /
- Obesity /
- Meta-analysis /
- Child /
- Adolescent
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
表 1 纳入文献基本特征
Table 1. General characteristics of the included studies
第一作者与年份 年龄/岁(T/C) 样本量(T/C) 干预/对照措施 干预周期/月 结局指标 Ackel-D'Elia 2014[5] 15~19 24/24 AT/AT+RT 6 BMI,BF% Alberga 2013[6] 8~12 12/7 RT/C 3 BMI,BF% Elloumi 2015[7] 13.2±0.1/13.2±0.6 7/8 AT/C 2 BMI Farpour-Lambert 2009[8] 8.9±1.5 22/22 AT/C 3 BMI,BF% Giovanni 2017[9] - 15/12 RT/AT 3 BMI,BF% Ghorbanian 2013[10] 17.3±1.1 15/15 AT/C 2 BMI Hagströmer 2009[11] 10~18 16/15 AT/C 3 BMI Karacabey 2009[12] 11.8±0.5/11.2±0.8 20/20 AT/C 3 BMI Kim 2007[13] 17±0.11/16.8±0.13 14/12 AT/C 1.5 BMI,BF% Kim 2008[14] 11 8/9 AT/C 3 BMI,BF% Lee 2012[15] 12~19 15/16/11 AT/RT/C 3 BMI,BF% Meyer 2006[16] 14.7±2.2 33/34 AT/C 6 BMI,BF% Monteiro 2015[17] - 18/14 AT/C 5 BMI,BF% Jong-Hwan 2012[18] 12.2±0.1 15/14 AT+RT/C 3 BMI Saygn 2011[19] 10~12 20/19 AT/C 3 BMI Schranz 2013[20] 13~17 27/26 RT/C 6 BMI,BF% Shaibi 2006[21] 15.1±0.5/15.6±0.5 11/11 RT/C 4 BMI,BF% Goldfield 2018[22] 14~18 69/70/74/69 AT/RT/AT+RT/C 6 BMI,BF% Song 2012[23] 12~13 12/10 AT/C 3 BMI,BF% Vasconcellos 2015[24] 12~17 10/10 AT/C 3 BMI,BF% Hala 2015[25] 14~19 14/9 AT/C 3 BMI,BF% Zehsaz 2016[26] 9~12 16/16 AT+RT/C 4 BMI,BF% 黄开来2013[27] 21.7±1.16/21.11±1.11/21.11±1.12 10/10/10 AT/AR+RT/C 3 BMI,BF% 李旭辉2017[28] - 10/10/10 AT/AR+RT/C 4 BMI,BF% 赵军2019[29] 21.45±1.02/21.68±0.98/21.43±.14 12/12/12 AT/AR+RT/C 3 BMI,BF% Duft 2020[30] 14.6±1.05 18/19 AT+RT/C 3 BMI,BF% Bharath 2018[31] 14.7±1 20/20 AT+RT/C 3 BMI,BF% 荣湘江2007[32] 12~13 54/54 AT/C 3 BMI,BF% 阳桂秋2017[33] 12~16 10/10 RT/C 10 BMI,BF% 白鹏云2020[34] - 8/5 AT/RT 1 BMI,BF% Lee 2013[35] 12~18 14/14/8 AT/RT/C 3 BMI,BF% Jeon 2013[36] - 8/7 AT+RT/C 3 BMI,BF% Lee 2019[37] 12~17 38/40/40 AT/RT/AT+RT 6 BMI,BF% Deldin 2019[38] 12~18 14/14 AT/RT 3 BMI Inoue 2015[39] 15~18 20/13 AT/AT+RT 3 BMI,BF% Kim 2019[40] 14~16 24/24 AT/C 3 BMI,BF% Ghazi 2001[41] 16.6±0.9/16.9±0.1 23/19 AT/C 3 BMI 丁花阳2017[42] 15.45±3.54/14.76±2.80 22/21 AT/AT+RT 1.5 BMI,BF% 注:AT为有氧运动干预,RT为抗阻训练干预,AT+RT为有氧结合抗阻训练干预;T为干预组,C为空白对照组。 -
[1] World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight[EB/OL]. (2018-11-22)[2022-01-18]. http://www.WHO.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. [2] FREEDMAN D S, MEI Z, SRINIVASAN S R, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors and excess adiposity among overweight children and adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study[J]. J Pediatr, 2007, 150(1): 12-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2006.08.042 [3] DANIELS S R, ARNETT D K, ECKEL R H, et al. Overweight in children and adolescents: pathophysiology, consequences, prevention, and treatment[J]. Circulation, 2005, 111: 1999-2012. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000161369.71722.10 [4] SINGH A S, MULDER C, TWISK J W R, et al. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature[J]. Obes Rev, 2008, 9(5): 474-488. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2008.00475.x [5] ACKEL-D'ELIA C, CARNIER J, BUENO C, et al. Effects of different physical exercises on leptin concentration in obese adolescents[J]. Int J Sports Med, 2014, 35(2): 164-171. [6] ALBERGA A S, FARNESI B C, LAFLECHE A, et al. The effects of resistance exercise training on body composition and strength in obese prepubertal children[J]. Phys Sportsmed, 2013, 41(3): 103-109. doi: 10.3810/psm.2013.09.2028 [7] ELLOUMI M, MAKNI E, OUNIS O B, et al. Six-minute walking test and the assessment of cardiorespiratory responses during weight-loss programmes in obese children[J]. Physiother Res Int, 2011, 16(1): 32-42. doi: 10.1002/pri.470 [8] FARPOUR-LAMBERT N J, AGGOUN Y, MARCHAND L, et al. Effects of physical activity on early markers of atherosclerosis in pre-pubertal obese and lean children[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2009, 41(Suppl 1): 103. [9] GIOVANNI F, ENZO I, GIOVANNA A, et al. Different consecutive training protocols to design an intervention program for overweight youth: a controlled study[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2017, 10: 37-45. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S122110 [10] GHORBANIAN B, RAVASSI A, REZA M, et al. The effects of rope training on lymphocyte ABCA1 expression, plasma ApoA-I and HDL-c in boy adolescents[J]. Int J Endocrinol Metab, 2013, 11(2): 76-81. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040846930810_4d86.html [11] HAGSTRÖMER M, ELMBERG K, MÅRILD S, et al. Participation in organized weekly physical exercise in obese adolescents reduced daily physical activity[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2009, 98(2): 352-354. [12] KARACABEY K. The effect of exercise on leptin, insulin, cortisol and lipid profiles in obese children[J]. J Int Med Res, 2009, 37(5): 1472-1478. doi: 10.1177/147323000903700523 [13] KIM E S, IM J A, KIM K C, et al. Improved insulin sensitivity and adiponectin level after exercise training in obese Korean youth[J]. Obesity, 2007, 15(12): 3023-3030. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.360 [14] KIM H J, LEE S, KIM T W, et al. Effects of exercise-induced weight loss on acylated and unacylated ghrelin in overweight children[J]. Clin Endocrinol, 2008, 68(3): 416-422. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.03058.x [15] LEE S, BACHA F, HANNON T, et al. Effects of aerobic versus resistance exercise without caloric restriction on abdominal fat, intrahepatic lipid, and insulin sensitivity in obese adolescent boys: a randomized, controlled trial[J]. Diabetes, 2012, 61(11): 2787-2795. doi: 10.2337/db12-0214 [16] MEYER A A, KUNDT G, LENSCHOW U, et al. Improvement of early vascular changes and cardiovascular risk factors in obese children after a six-month exercise program[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2006, 48(9): 1865-1870. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.035 [17] MONTEIRO P A, KONG Y C, LIRA F S, et al. Concurrent and aerobic exercise training promote similar benefits in body composition and metabolic profiles in obese adolescents[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2015, 14(1): 153. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0152-9 [18] JONG-HWAN P, MASASHI M, YOO-CHAN K, et al. A 12-week after-school physical activity programme improves endothelial cell function in overweight and obese children: a randomised controlled study[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2012, 12(1): 111-119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-111 [19] SAYGN Ö, ÖZTVRK M A. The effect of twelve week aerobic exercise programme on health related physical fitness components and blood lipids in obese girls[J]. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol, 2011, 5(12): 1441-1445. doi: 10.5897/AJPP11.114 [20] SCHRANZ N, TOMKINSON G, PARLETTA N, et al. Can resistance training change the strength, body composition and self-concept of overweight and obese adolescent males? A randomised controlled trial[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2014, 48(20): 1482-1488. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-092209 [21] SHAIBI G Q, CRUZ M L, BALL G D, et al. Effects of resistance training on insulin sensitivity in overweight Latino adolescent males[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2006, 38(7): 1208-2015. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000227304.88406.0f [22] GOLDFIELD G S, KENNY G P, PRUD'HOMME D, et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adolescents with obesity: the hearty randomized controlled trial[J]. Physiol Behav, 2018, 191: 138-145. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.04.026 [23] SONG J K, STEBBINS C L, KIM T K, et al. Effects of 12 weeks of aerobic exercise on body composition and vascular compliance in obese boys[J]. Sports Med Phys Fit, 2012, 52(5): 522-529. [24] VASCONCELLOS F, SEABRA A, CUNHA F, et al. Health markers in obese adolescents improved by a 12-week recreational soccer program: a randomised controlled trial[J]. Sports Sci, 2016, 34(6): 564-575. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2015.1064150 [25] YOUSSEF H, GROUSSARD C, LEMOINE-MOREL S, et al. Aerobic training suppresses exercise-induced lipid peroxidation and inflammation in overweight/obese adolescent girls[J]. Pediatr Exerc Sci, 2015, 27(1): 67-76. doi: 10.1123/pes.2014-0008 [26] ZEHSAZ F, FARHANGI N. Exercise training lowers serum chemerin concentration in obese children[J]. Sports Sci, 2017, 32(1): 39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.scispo.2016.07.007 [27] 黄开来. 有氧运动结合低抗阻训练对肥胖女大学生减肥效果的研究[J]. 武术研究, 2013(5): 122-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSKX201305046.htmHUANG K L. Aerobic exercise combined with low resistance training study of obese female college students result reducing weight[J]. Wushu Stud, 2013(5): 122-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSKX201305046.htm [28] 李旭辉, 范晓梅, 郎胜利. 有氧运动结合抗阻训练对肥胖大学生血清visfatin水平的影响[J]. 疾病监测与控制杂志, 2017, 11(9): 721-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBJK201709021.htmLI X H, FAN X M, LANG S L. The effects of aerobic exercise combined with resistance training on the visfatin level in obese college students[J]. J Dis Monit Control, 2017, 11(9): 721-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBJK201709021.htm [29] 赵军, 梁晋裕. 有氧运动结合抗阻训练对肥胖男性大学生身体成分、心血管功能及血清C反应蛋白水平的改善作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(5): 1134-1140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BQEB201905027.htmZHAO J, LIANG J Y. Improvement effects of aerobic exercise combined with resistance training on body composition, cardiovascular function and serum C-reactive protein level in male obese college students[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Ed), 2019, 45(5): 1134-1140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BQEB201905027.htm [30] DUFT R G, CASTRO A, BONFANTE I L P, et al. Altered metabolomic profiling of overweight and obese adolescents after combined training is associated with reduced insulin resistance[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 16880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73943-y [31] BHARATH L P, CHOI W W, CHO J M, et al. Combined resistance and aerobic exercise training reduces insulin resistance and central adiposity in adolescent girls who are obese: randomized clinical trial[J]. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2018, 118(8): 1653-1660. doi: 10.1007/s00421-018-3898-8 [32] 荣湘江, 朱稼霈, 张世伟, 等. 运动干预青少年单纯性肥胖效果的研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2007, 22(8): 702-705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2007.08.007RONG X J, ZHU J P, ZHANG S W, et al. A study on effects of exercise for simple obesity in young students[J]. Chin J Rehabil Med, 2007, 22(8): 702-770. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2007.08.007 [33] 阳桂秋. 长期抗阻训练对肥胖青少年体重与脂肪含量影响的实验研究[J]. 体育科技, 2017, 38(6): 31-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKJ201706012.htmYANG G Q. Effects of long term resistance training on body weight and fat content in obese adolescents[J]. Sport Sci Technol, 2017, 38(6): 31-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKJ201706012.htm [34] 白鹏云, 房冬梅. 不同干预方式运动对超重/肥胖大学生体成分的影响[J]. 贵州体育科技, 2020, 6(2): 54-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZSZ202101020.htmBAI P Y, FANG D M. The effects of different types of exercise on body composition of overweight and obese college students[J]. Guizhou Sports Sci Technol, 2020, 6(2): 54-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZSZ202101020.htm [35] LEE S, DELDIN A R, WHITE D, et al. Aerobic exercise but not resistance exercise reduces intrahepatic lipid content and visceral fat and improves insulin sensitivity in obese adolescent girls: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2013, 305(10): E1222-E1229. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00285.2013 [36] JEON J Y, HAN J, KIM H J, et al. The combined effects of physical exercise training and detraining on adiponectin in overweight and obese children[J]. Integr Med Res, 2013, 2(4): 145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2013.10.001 [37] LEE S, LIBMAN I, HUGHAN K, et al. Effects of exercise modality on insulin resistance and ectopic fat in adolescents with overweight and obesity: a randomized clinical trial[J]. J Pediatr, 2019, 206(suppl 1): 91-98. [38] DELDIN A, KUK J L, LEE S. Influence of sex on the changes in regional fat and skeletal muscle mass in response to exercise training in adolescents with obesity[J]. Child Obes, 2019, 15(3): 216-222. doi: 10.1089/chi.2018.0329 [39] INOUE D S, MELLO M D, FOSCHINI D, et al. Linear and undulating periodized strength plus aerobic training promote similar benefits and lead to improvement of insulin resistance on obese adolescents[J]. J Diabet Complic, 2015, 29(2): 258-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2014.11.002 [40] KIM J, SON W M, HEADID Ⅲ R J, et al. The effects of a 12-week jump rope exercise program on body composition, insulin sensitivity, and academic self-efficacy in obese adolescent girls[J]. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 33(1): 129-137. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2019-0327 [41] GHAZI R, JEREMY C, WASSIM E, et al. Greater effects of high-compared with moderate-intensity interval training on cardio-metabolic variables, blood leptin concentration and ratings of perceived exertion in obese adolescent females[J]. Biol Sport, 2016, 33(2): 145-152. doi: 10.5604/20831862.1198633 [42] 丁花阳, 汪君民. 有氧及复合运动对单纯性肥胖青少年身体形态和生化指标影响[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2017, 38(12): 1859-1862. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIWS201712032.htmDING H Y, WANG J M. Comparison of the effectiveness of two types of exercise intervention on body fat and biochemical indices among obese adolescents[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2017, 38(12): 1859-1862. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIWS201712032.htm [43] LUMLEY T. Network Meta-analysis for indirect treatment comparisons[J]. Stat Med, 2002, 21(16): 2313-2324. doi: 10.1002/sim.1201 [44] 四川大学华西医院中国Cochrane中心. Cochrane干预措施系统评价手册中文翻译版[EB/OL]. (2014-12-01)[2022-01-18]. http//training.cochrane.org/sites/training.cochrane.org/les/public/uploads/resources/CochraneHandbookChineseDec2014.pdf.China Cochrane Center of West China Hospital of Sichuan University. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions[EB/OL]. (2014-12-01)[2022-01-18]. http://training.cochrane.org/sites/training.cochrane.org/files/public/uploads/resour-ces/cochranehandbookchinesedec2014.pdf. [45] JADAD A R, MOORE R A, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?[J]. Control Clin Trials, 1996, 17(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(95)00134-4 [46] 易跃雄, 张蔚, 刘小媛, 等. 网状Meta分析图形结果解读[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2015, 15(1): 103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXZ201501019.htmYI Y X, ZHANG W, LIU X Y, et al. Result interpretation of network Meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Evid-Based Med, 2015, 15(1): 103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXZ201501019.htm [47] 徐兴凯. 有氧运动和力量训练相结合对减肥效果影响的研究[J]. 体育科技文献通报, 2015, 23(7): 79-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPOR201507039.htmXU X K. Affect research of combining aerobic exercise with strength training in weight-losing[J]. Bull Sport Sci Technol, 2015, 23(7): 79-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPOR201507039.htm [48] 朱稼霈, 王晓强, 荣湘江. 儿童青少年单纯性肥胖运动减肥机制及运动处方的研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2007, 22(6): 566-569.ZHU J P, WANG X Q, RONG X J. The mechanism of exercise for losing weight and exercise prescription for children and adolescents of simple obesity[J]. Chin J Rehabil Med, 2007, 22(6): 566-569. [49] PATTYN N, CORNELISSEN V A, ESHGHI S R, et al. The effect of exercise on the cardiovascular risk factors constituting the metabolic syndrome: a Meta-analysis of controlled trials[J]. Sports Med, 2013, 43(2): 121-133. [50] DRENOWATZ C, SUI X, FRITZ S, et al. The association between resistance exercise and cardiovascular disease risk in women[J]. J Sci Med Sport, 2015, 18(6): 632-636. [51] 代毅, 许传明, 王金泉, 等. 有氧运动、抗阻力训练与饮食干预对年轻肥胖女性减肥效果的影响[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2007, 33(6): 105-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SORT200706029.htmDAI Y, XU C M, WANG J Q, et al. Effects of aerobics, anti-resistance training and diet interference on weight-losing result od obese women[J]. J Chengdu Sport Univ, 2007, 33(6): 105-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SORT200706029.htm [52] 黄利军. 有氧运动减肥的生物学机制及运动处方探析[J]. 榆林学院学报, 2009, 19(2): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLGD200902011.htmHUANG L J. On the biological mechanisms of aerobic exercise to lose weight and exercise prescription[J]. J Yulin Univ, 2009, 19(2): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLGD200902011.htm [53] 路剑. 力量练习结合有氧运动对肥胖男大学生减肥效果的研究[D]. 开封: 河南大学, 2016.LU J. A study about the improvements of weight loss of strength training and aerobic exercise on the obese male undergraduate[D]. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2016. -







 下载:
下载: