Association between maternal pre-pregnancy and pre-delivery overweight with overweight and obesity of middle school students: a case-control study
-
摘要:
目的 探讨广州市母亲孕前及分娩前超重肥胖对子代中学时期超重肥胖的影响, 为预防中学生肥胖提供科学依据。 方法 依托广州市中学生常规体检, 抽取3所高中、3所初中共3 384名学生, 将体检中超重肥胖的中学生纳入超重肥胖组(642名), 其余学生纳入对照组(2 742名), 对学生及家长进行问卷调查。使用倾向性评分匹配(propensity score matching, PSM)前后的数据进行χ2检验和Logistic回归分析, 对比匹配前后结果的变化。 结果 单因素分析显示, 进行PSM前, 超重肥胖组和对照组在性别、学段、是否挑食、肥胖家族史、家庭人均月收入、母亲分娩方式、是否为巨大儿和孕期增重情况差异均有统计学意义(χ2值分别为42.38, 10.64, 14.47, 26.85, 10.58, 13.59, 15.53, 20.64, P值均 < 0.05)。PSM后, 孕前及分娩前超重肥胖组和对照组在学段、分娩方式上组间差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。Logistic回归分析显示, 进行PSM前, 母亲孕前超重肥胖的中学生超重肥胖风险是母亲孕前非超重肥胖的1.54倍(95%CI=1.01~2.36), 而母亲在分娩前超重肥胖同样增加了中学生超重肥胖的风险(OR=2.35, 95%CI=1.67~3.31)。在进行PSM后, 母亲孕前(OR=2.17, 95%CI=1.41~3.34)及分娩前超重肥胖(OR=2.99, 95%CI=2.08~4.31)均明显增加中学生超重肥胖风险。 结论 母亲孕前和分娩前超重肥胖与中学生的超重肥胖风险增高有关联。 Abstract:Objective To explore the association between maternal pre-pregnancy and pre-delivery overweight with overweight and obesity among offspring during adolescence in Guangzhou, and to provide evidence for child obesity prevention. Methods Based on the routine physical examination of primary and secondary school students in Guangzhou, random sampling was used to 6 middle schools and questionnaire survey was conducted among 3 384 students and their parents. Students with overweight and obesity were included in the case group, and the other students were included in the control group. Propensity Score Matching (PSM) was adopted to reduce selection bias. Logistic regression model and χ2 test were used to analyze the data before and after PSM. Results The result of univariate analysis showed that there were statistically significant differences between overweight/obese group and the control group by gender, schooling stage (middle and high schools), picky eater, family history of obesity, family monthly income, delivery mode, high birthweight, and gestational weight gain before PSM(χ2=42.38, 10.64, 14.47, 26.85, 10.58, 13.59, 15.53, 20.64, P < 0.05). After PSM, results showed that there were no statistically significant differences between overweight/obese group and the control group in middle and high schools, and mother delivery mode(P>0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that the risk of overweight and obesity of maternal pre-pregnancy on adolescent offspring was 1.54 times higher than control group (95%CI=1.01-2.36) before PSM, and the overweight and obesity of maternal pre-delivery also increased the risk of overweight and obesity of adolescent offspring(OR=2.35, 95%CI=1.67-3.31). After PSM, maternal overweight and obesity pre-pregnancy (OR=2.17, 95%CI=1.41-3.34) and maternal overweight and obesity pre-delivery(OR=2.99, 95%CI=2.08-4.31) significantly increased the risk of overweight and obesity in adolescent offspring. Conclusion Maternal overweight and obesity pre-pregnancy and pre-delivery are associated with increased risk of overweight and obesity in adolescent offspring. -
Key words:
- Mothers /
- Overweight /
- Obesity /
- Case-control studies /
- Regression analysis /
- Students
1) 利益冲突声明 所有作者声明无利益冲突。 -
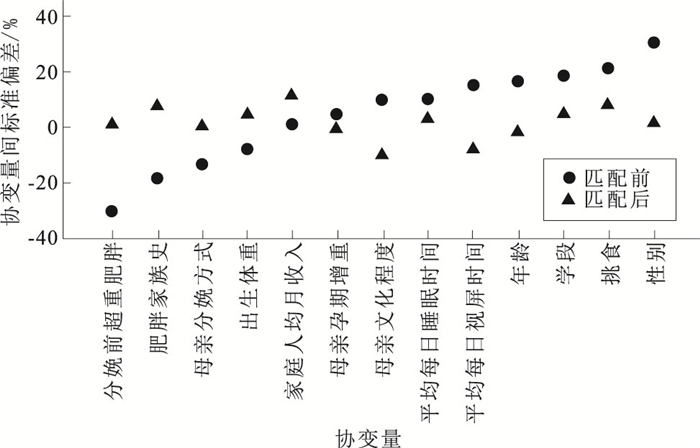
表 1 PSM前超重肥胖组与对照组中学生不同人口学特征分布比较
Table 1. Comparison of basic information between overweight and obesity group and control group before PSM
组别 人数 学段 性别 挑食 肥胖家族史 初中 高中 女 男 是 否 是 否 肥胖超重组 642 438(68.22) 204(31.78) 211(32.87) 431(67.13) 117(18.22) 525(81.78) 135(21.03) 507(78.97) 对照组 2 742 1 681(61.31) 1 061(38.69) 1 290(47.05) 1 452(52.95) 695(25.35) 2 047(74.65) 357(13.02) 2 385(86.98) χ2值 10.64 42.38 14.47 26.85 P值 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 组别 人数 家庭人均月收入/元* 母亲分娩方式 巨大儿 母亲孕期增重 ≤5 000 5 001~9 999 ≥10 000 自然分娩 剖宫产 是 否 不足 合理 过度 肥胖超重组 642 81(13.66) 278(46.88) 234(39.46) 261(40.65) 381(59.35) 62(9.66) 580(90.34) 281(43.77) 151(23.52) 210(32.71) 对照组 2 742 484(19.31) 1 126(44.91) 897(35.78) 1 336(48.72) 1 406(51.28) 150(5.47) 2 592(94.53) 1 181(43.07) 860(31.36) 701(25.57) χ2值 10.58 13.59 15.53 20.64 P值 0.01 0.02 0.01 < 0.01 注: ()内数字为构成比/%; *表示该项目有缺失数据。 表 2 PSM后母亲孕前及分娩前超重肥胖组与对照组中学生不同人口学特征分布比较
Table 2. Comparison of basic information between overweight and obesity group and control group after PSM
母亲孕前及分娩前 组别 人数 统计值 学段 性别 挑食 肥胖家族史 初中 高中 女 男 是 否 是 否 孕前 肥胖超重组 593 192(32.38) 401(67.62) 192(32.38) 401(67.62) 107(18.04) 486(81.96) 126(21.25) 467(78.75) 对照组 1 052 352(33.46) 700(66.54) 389(36.98) 663(63.02) 125(11.88) 927(88.12) 99(9.41) 953(90.59) χ2值 0.20 3.51 11.89 45.01 P值 0.65 0.06 < 0.01 < 0.01 分娩前 肥胖超重组 593 192(32.38) 401(67.62) 192(32.38) 401(67.62) 107(18.04) 486(81.96) 126(21.25) 467(78.75) 对照组 1 057 352(33.30) 705(66.70) 397(37.56) 660(62.44) 122(11.54) 935(88.46) 103(9.74) 954(90.26) χ2值 0.15 4.44 13.44 42.06 P值 0.70 0.04 < 0.01 < 0.01 母亲孕前及分娩前 组别 人数 统计值 家庭人均月收入/元 母亲分娩方式 巨大儿 母亲孕期增重 ≤5 000 5 001~9 999 ≥10 000 自然分娩 剖宫产 是 否 不足 合理 过度 孕前 肥胖超重组 593 81(13.66) 278(46.88) 234(39.46) 360(60.71) 233(39.29) 59(9.95) 534(90.05) 259(43.68) 134(22.60) 200(33.73) 对照组 1 052 71(6.75) 530(50.38) 451(42.87) 414(39.35) 638(60.65) 46(4.37) 1 006(95.63) 510(48.48) 300(28.52) 242(23.00) χ2值 21.60 0.00 19.74 23.14 P值 < 0.01 0.98 < 0.01 < 0.01 分娩前 肥胖超重组 593 81(13.66) 278(46.88) 234(39.46) 360(60.71) 233(39.29) 59(9.95) 534(90.05) 259(43.68) 134(22.60) 200(33.73) 对照组 1 057 74(7.00) 546(51.66) 437(41.34) 408(38.60) 649(61.40) 47(4.45) 1 010(95.55) 491(46.45) 284(26.87) 282(26.68) χ2值 19.99 0.08 19.14 9.84 P值 < 0.01 0.78 < 0.01 0.01 注: ()内数字为构成比/%。 表 3 匹配后母亲孕前及分娩前共同倾向评分情况
Table 3. The number of different common propensity score groups before pregnancy and delivery after PSM
母亲孕前及分娩前 组别 人数 < 0.1 0.1~ < 0.2 0.2~ < 0.3 0.3~ < 0.4 0.4~ < 0.5 0.5~ < 0.6 0.6~0.7 孕前 对照组 1 052 46 512 384 62 35 7 6 超重肥胖组 593 22 235 207 73 39 11 6 分娩前 对照组 1 057 44 524 385 77 20 6 1 超重肥胖组 593 24 232 218 83 29 6 1 -
[1] KELLY T, YANG W, CHEN C S, et al. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030[J]. Int J Obes, 2008, 32(9): 1431-1437. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.102 [2] OZUMUT S H, ERGUVEN M, BESLI E. Obesogenic environment in childhood: implications of high socioeconomic level in a developing country[J]. Medeni Med J, 2020, 35(3): 236-241. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/346101063_Obesogenic_Environment_in_Childhood_Implications_of_High_Socioeconomic_Level_in_a_Developing_Country [3] MEKONNEN T, TARIKU A, ABEBE S M. Overweight/obesity among school aged children in Bahir Dar City: cross sectional study[J]. Ital J Pediatr, 2018, 44(1): 17. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0452-6 [4] DUAN R, KOU C, JIE J, et al. Prevalence and correlates of overweight and obesity among adolescents in northeastern China: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMJ Open, 2020, 10(7): e036820. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-036820 [5] LIU H K, WU C Y, YANG Y N, et al. Association between maternal pre-delivery body mass index and offspring overweight/obesity at 1 and 2 years of age among residents of a suburb in Taiwan[J]. Peer J, 2019, 7: e6473. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6473 [6] GROTH S W, HOLLAND M L, SMITH J A, et al. Effect of gestational weight gain and prepregnancy body mass index in adolescent mothers on weight and body mass index of adolescent offspring[J]. J Adolesc Health, 2017, 61(5): 626-633. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2017.05.005 [7] SPANN M N, SCHEINOST D, FENG T, et al. Association of maternal prepregnancy body mass index with fetal growth and neonatal thalamic brain connectivity among adolescent and young women[J]. JAMA Network Open, 2020, 3(11): e2024661. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.24661 [8] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查: WS/T 586—2018[S]. 2018-08-01.National Health and Family Planning Commission of PRC. Screening for overweight and obesity in school-age children and adolescents: WS/T 586-2018[S]. 2018-08-01. [9] 楚舟, 陶芳标, 郝加虎, 等. 孕前体质指数与4种不良妊娠结局关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2012, 28(6): 763-766. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGW201206015.htmCHU Z, TAO F B, HAO J H, et al. Relationship between pre-pregnancy BMI and adverse birth outcomes[J]. Chin J Public Health, 2012, 28(6): 763-766. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGW201206015.htm [10] PITKIN R M. Nutritional support in obstetrics and gynecology[J]. Clin Obstet Gynecol, 1976, 19(3): 489-513. doi: 10.1097/00003081-197609000-00002 [11] VOERMAN E, SANTOS S, INSKIP H, et al. Association of gestational weight gain with adverse maternal and infant outcomes[J]. JAMA, 2019, 321(17): 1702-1715. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.3820 [12] Institute of Medicine, National Research Council Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines. Weight Gain During Pregnancy: reexamining the Guidelines[M]. Washington(DC): National Academies Press(US), 2009. [13] BROWN C L, VAN DER SCHAAF E B, COHEN G M, et al. Association of picky eating and food neophobia with weight: a systematic review[J]. Child Obes, 2016, 12(4): 247-262. doi: 10.1089/chi.2015.0189 [14] GENTILE D A, REIMER R A, NATHANSON A I, et al. Protective effects of parental monitoring of children's media use: a prospective study[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2014, 168(5): 479-484. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.146 [15] 沈晓明, 王卫平. 儿科学[M]. 9版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018: 86.SHEN X M, WANG W P. Pediatrics[M]. 9 ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2018: 86. [16] 王永吉, 蔡宏伟, 夏结来, 等. 倾向指数第二讲倾向指数常用研究方法[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2010, 31(5): 584-585. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2010.05.026WANG Y J, CAI H W, XIA J L, et al. Propensity score (Ⅱ) Three commonly used methods on propensity score[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2010, 31(5): 584-585. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2010.05.026 [17] 张寿锋, 王慧. 2019年沂源县高中生超重肥胖现状及特征分析[J]. 职业卫生与病伤, 2021, 36(2): 85-88, 93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYWB202102005.htmZHANG S F, WANG H. Current status and features for overweight/obesity among high school students in Yiyuan County in 2019[J]. J Occup Health Damag, 2021, 36(2): 85-88, 93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYWB202102005.htm [18] 杨岳峰. 吉林省733例高中生超重肥胖现况调查及影响因素研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020.YANG Y F. The study of overweight and obesity status and influence factors among 733 high school students in Jilin Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020. [19] 贺玉川, 胡金妹, 张凤云. 江苏省2017年中学生体重控制行为分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40(12): 1815-1819. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.12.014HE Y C, HU J M, ZHANG F Y. Analysis of prevalence of body weight control behavior among middle school students in Jiangsu, 2017[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2019, 40(12): 1815-1819. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.12.014 [20] 何丽, 周黎黎, 赵迎春. 克拉玛依市区儿童青少年肥胖与父母社会经济状况的关系[J]. 海南医学, 2012, 23(1): 126-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2012.01.055HE L, ZHOU L L, ZHAO Y C. Relationship between obesity of children and adolescents and the socioeconomic status of parents in Karamay City[J]. Hainan Med J, 2012, 23(1): 126-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2012.01.055 [21] 刘伟, 林蓉, 熊莉华, 等. 广州市城区小学低年级学生父母对子女体形认知的研究[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2017, 25(11): 1113-1116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO201711009.htmLIU W, LIN R, XIONG L H, et al. Study of parents' cognition on the body shape of low grade students' from primary school in urban Guangzhou[J]. Chin J Child Heal Care, 2017, 25(11): 1113-1116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO201711009.htm [22] YU Z, HAN S, ZHU J, et al. Pre-pregnancy body mass index in relation to infant birth weight and offspring overweight/obesity: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(4): e61627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061627 [23] FLORES G, LIN H. Factors predicting overweight in US kindergartners[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2013, 97(6): 1178-1187. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.052019 [24] BEKKERS M B, BRUNEKREEF B, SMIT H A, et al. Early-life determinants of total and HDL cholesterol concentrations in 8-year-old children, the PIAMA birth cohort study[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(9): e25533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025533 [25] FUIANO N, RAPA A, MONZANI A, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for overweight and obesity in a population of Italian schoolchildren: a longitudinal study[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2008, 31(11): 979-984. doi: 10.1007/BF03345635 [26] FRASER A, TILLING K, MACDONALD-WALLIS C, et al. Association of maternal weight gain in pregnancy with offspring obesity and metabolic and vascular traits in childhood[J]. Circulation, 2010, 121(23): 2557-2564. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.906081 [27] MARGERISON ZILKO C E, REHKOPF D, ABRAMS B. Association of maternal gestational weight gain with short-and long-term maternal and child health outcomes[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2010, 202(6): 574. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20103209133.html [28] SCHACK-NIELSEN L, MICHAELSEN K F, GAMBORG M, et al. Gestational weight gain in relation to offspring body mass index and obesity from infancy through adulthood[J]. Int J Obes(Lond), 2010, 34(1): 67-74. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2009.206 [29] OKEN E, RIFAS-SHIMAN S L, FIELD A E, et al. Maternal gestational weight gain and offspring weight in adolescence[J]. Obstet Gynecol, 2008, 112(5): 999-1006. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31818a5d50 [30] STUEBE A M, FORMAN M R, MICHELS K B. Maternal-recalled gestational weight gain, pre-pregnancy body mass index, and obesity in the daughter[J]. Int J Obes(2005), 2009, 33(7): 743-752. http://www.nature.com/ijo/journal/v33/n7/pdf/ijo2009101a.pdf [31] ROONEY B L, MATHIASON M A, SCHAUBERGER C W. Predictors of obesity in childhood, adolescence, and adulthood in a birth cohort[J]. Matern Child Health J, 2011, 15(8): 1166-1175. doi: 10.1007/s10995-010-0689-1 [32] MAMUN A A, O'CALLAGHAN M, CALLAWAY L, et al. Associations of gestational weight gain with offspring body mass index and blood pressure at 21 years of age: evidence from a birth cohort study[J]. Circulation, 2009, 119(13): 1720-1727. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.813436 [33] LAWLOR D A, LICHTENSTEIN P, FRASER A, et al. Does maternal weight gain in pregnancy have long-term effects on offspring adiposity?a sibling study in a prospective cohort of 146, 894 men from 136, 050 families[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2011, 94(1): 142-148. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.009324 [34] TIE H T, XIA Y Y, ZENG Y S, et al. Risk of childhood overweight or obesity associated with excessive weight gain during pregnancy: a meta-analysis[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2014, 289(2): 247-257. doi: 10.1007/s00404-013-3053-z [35] REBECCA M R. Excess maternal weight gain during pregnancy is associated with overweight/obesity in offspring at age 16 years, but maternal pre-pregnancy obesity has a greater effect[J]. Evid Based Nurs, 2013, 16(2): 43-44. doi: 10.1136/eb-2012-100888 [36] LEE C F, HWANG F M, LIOU Y M, et al. A preliminary study on the pattern of weight change from pregnancy to 6 months postpartum: a latent growth model approach[J]. Int J Obes(Lond), 2011, 35(8): 1079-1086. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2010.225 [37] VILLAMOR E, CNATTINGIUS S. Interpregnancy weight change and risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes: a population-based study[J]. Lancet, 2006, 368(9542): 1164-1170. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69473-7 [38] 王生兰, 李洁, 海妤婷, 等. 妇女孕前超重、肥胖与胎儿出生缺陷关系探讨[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志, 2021, 29(4): 730-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSY202104022.htmWANG S L, LI J, HAI Y T, et al. Study on the relationship between pre-pregnancy overweight or obesity and the fetal birth defects[J]. Chin J Fam Plann, 2021, 29(4): 730-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSY202104022.htm [39] 刘书方. 基于DOHaD理论探讨孕前和孕期肥胖对子代呼吸系统疾病的影响及其机制[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2020.LIU S F. Study on the effect of pregnancy and pregnancy obesity on offspring respiratory diseases and its mechanism based on Dohad theory[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2020. [40] 陈品贤. 孕期肥胖对子代心功能异常程序化的影响及其机制研究[D]. 广州: 广州医科大学, 2014.CHEN P X. The effect of maternal obesity on fetal programming of cardiac dysfunction in offspring and underlying mechanisms[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Medical University, 2014. [41] 房志琴, 彭伟. 孕期高脂饮食易化子代大鼠心血管异常研究进展[J]. 河北北方学院学报(自然科学版), 2016, 32(10): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1492.2016.10.021FANG Z Q, PENG W. Maternal high-fat diet predisposing cardiovascular anomalies of offspring[J]. J Hebei North Univ(Nat Sci Edi), 2016, 32(10): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1492.2016.10.021 [42] PARK S, SAPPENFIELD W M, BISH C, et al. Assessment of the Institute of medicine recommendations for weight gain during pregnancy: florida, 2004-2007[J]. Matern Child Health J, 2011, 15(3): 289-301. doi: 10.1007/s10995-010-0596-5 -







 下载:
下载: