Trends of overweight and prevalence among Ningxia Han ethnic students during 2000-2019
-
摘要:
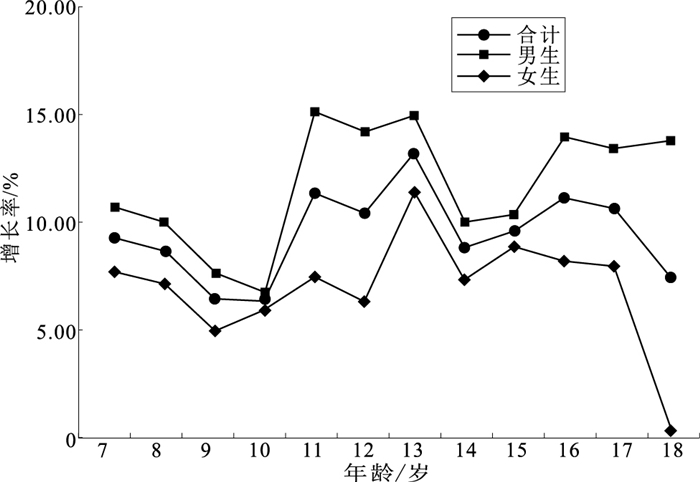
目的 了解2000—2019年宁夏7~18岁汉族中小学生超重肥胖变化趋势,为预防控制儿童青少年超重肥胖提供科学依据。 方法 基于2000—2019年5次“全国学生体质与健康调研”中宁夏地区数据,选取7~18岁汉族中小学生体重、身高等数据进行趋势分析。 结果 2019年宁夏7~18岁儿童青少年超重和肥胖检出率分别为13.34%(1 181/8 855),9.19%(814/8 855),男生2000—2019年超重增长率为11.68%,肥胖增长率为10.07%(χ2=27.60,P<0.01)。女生2000—2019年超重增长率为6.95%,肥胖增长率为5.77%(χ2=33.82,P<0.01)。城市男生的超重和肥胖总体增长率均最高,为11.38%和10.45%。农村男生的超重和肥胖增长率在2010年之后均高于城市男生(χ2值分别为13.90,17.09,P值均<0.05),女生肥胖增长率在2014年之后农村均高于城市(χ2值分别为9.94,33.39,P值均<0.05)。不论是城市还是农村,经济发展片区由好到差时,超重和肥胖检出率由高到低(χ2值分别为35.19,35.35,P值均<0.01)。 结论 2000—2019年宁夏中小学生超重、肥胖检出率及体质量指数趋于持续性增长趋势,且农村超重和肥胖增长率逐渐超过城市。预防儿童青少年超重肥胖的具体措施应尽快制定,降低因儿童青少年超重肥胖所造成的社会经济负担。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the trend of overweight and obesity among Han students aged 7-18 in Ningxia from the year of 2000 to 2019, and to provide scientific basis for obesity prevention and control among children and adolescents. Methods Based on the five waves of "National Student Physical Fitness and Health Survey" in Ningxia region during 2000 to 2019, body weight, height, waist circumference, hip circumference and other data of Han students aged 7-18 years were included was used for trend analysis. Results In 2019, the detection rates of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents aged 7 to 18 in Ningxia were 13.34% (1 181/8 855) and 9.19% (814/8 855), respectively. The increase rate of overweight and obesity in boys from 2000 to 2019 was 11.68% and 10.07% (χ2=27.60, P < 0.01). The rate of overweight and obesity in female students from 2000 to 2019 was 6.95% and 5.77% (χ2=33.82, P < 0.01). Urban boys had the highest rates of overweight and obesity, which were 11.38% and 10.45%. The growth rate of overweight and obesity in rural boys was higher than that in urban boys after 2010 (χ2=13.90, 17.09, P < 0.05), and the growth rate of obesity in rural girls was higher than that in urban girls after 2014 (χ2=9.94, 33.39, P < 0.05). Overweight and obesity prevalence showed positive associations with the economic status in both urban and rural areas (χ2=35.19, 35.35, P < 0.01). Conclusion From 2000 to 2019, the prevalence of overweight and obesity and body mass index among children and adolescents in Ningxia increased consistently, with more rigirous in rural areas. Specific strategies and measures for overweight and obesity prevention in children and adolescents are in urgent need, to reduce potential social and economic burden. -
Key words:
- Overweight /
- Obesity /
- Body mass index /
- Students
-
表 1 宁夏汉族7~18岁不同性别儿童青少年BMI比较(x±s,kg/m2)
Table 1. BMI of Han children and adolescents aged 7 to 18 in Ningxia from 2000 to 2019(x±s, kg/m2)
年龄/岁 男生(n=19 332) 女生(n=18 634) t值 P值 2000年 2005年 2010年 2014年 2019年 2000年 2005年 2010年 2014年 2019年 7 15.03±2.14 15.98±2.57 15.81±2.21 15.39±2.05 16.49±2.43 14.42±1.17 15.12±2.47 15.20±1.83 15.06±2.05 15.56±2.76 385.53 <0.01 8 15.23±1.69 16.22±2.10 16.33±2.50 16.17±2.53 17.31±4.69 14.70±1.28 15.53±1.83 15.50±2.36 15.36±1.91 16.02±3.05 332.63 <0.01 9 15.62±1.81 16.45±2.49 16.46±2.94 16.94±3.01 17.48±3.34 14.96±1.55 15.88±2.09 15.84±2.10 15.95±2.35 16.39±2.71 358.78 <0.01 10 16.21±2.47 17.09±2.89 17.43±3.32 17.44±3.11 17.82±3.24 15.65±2.72 16.21±2.30 16.55±2.62 16.76±2.57 16.84±2.82 337.25 <0.01 11 16.53±2.41 17.58±2.81 17.75±3.26 18.20±3.39 19.01±3.97 16.13±2.26 16.98±2.50 17.22±2.79 17.33±2.90 18.07±3.69 314.83 <0.01 12 16.73±2.00 17.77±2.62 18.09±3.20 19.00±3.31 19.32±3.75 16.92±2.15 17.47±2.47 17.62±2.52 18.59±3.11 18.67±2.79 339.18 <0.01 13 17.36±2.27 18.24±2.73 18.47±2.99 19.17±3.42 20.21±3.92 18.23±2.38 18.35±2.45 18.46±2.77 19.01±2.75 19.90±3.12 335.08 <0.01 14 18.35±2.30 19.33±3.02 18.94±3.23 20.36±3.91 20.69±4.47 19.18±2.49 19.73±2.26 19.17±3.90 20.08±2.91 20.26±3.48 320.82 <0.01 15 18.97±2.14 19.41±2.96 19.62±3.17 20.29±3.44 20.38±3.20 19.80±2.19 19.96±2.48 19.70±2.64 20.18±2.77 21.00±2.96 384.12 <0.01 16 19.28±2.08 20.47±3.19 19.87±2.79 20.80±3.39 21.35±3.81 20.39±2.09 20.56±2.34 20.11±2.62 20.96±2.90 21.38±3.06 384.04 <0.01 17 19.55±1.69 20.61±2.80 20.39±3.08 21.30±3.57 21.55±3.83 20.87±2.19 20.98±2.88 20.26±2.45 20.89±2.77 21.51±3.17 390.68 <0.01 18 20.49±2.19 20.89±3.00 20.75±2.95 21.30±3.44 22.22±3.90 21.19±2.26 21.01±2.18 20.57±2.47 20.70±2.54 21.48±3.80 373.56 <0.01 -
[1] RUIZ L D, ZUELCH M L, DIMITRATOS S M, et al. Adolescent obesity: diet quality, psychosocial health, and cardiometabolic risk factors[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 12(1): 43. doi: 10.3390/nu12010043 [2] 刘洋. 《中国儿童肥胖报告》发布学龄儿童肥胖率30年增加13倍[J]. 求医问药, 2017(6): 4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJQY201706003.htmLIU Y. The obesity rate of school-age children has increased by 13 times in 30 years since the Release of "Report on Childhood Obesity in China"[J]. Seek Med Adv, 2017(6): 4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJQY201706003.htm [3] 马冠生. 儿童肥胖: 达能营养中心2019年论文汇编[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019, 1.MA G S. Childhood obesity: the 2019 paper compilation of the Danone Nutrition Center[M]. Beijing: People's Health Press, 2019: 1. [4] SIMMONDS M, BURCH J, LLEWELLYN A, et al. The use of measures of obesity in childhood for predicting obesity and the development of obesity-related diseases in adulthood: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Health Technol Assess, 2015, 19(43): 1-336. doi: 10.3310/hta19430 [5] DELVECCHIO M, PASTORE C, VALENTE F, et al. Cardiovascular implications in idiopathic and syndromic obesity in childhood: an update[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2020, 11: 330. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00330 [6] 杨贵仁. 2000年全国学生体质健康状况调研结果[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2002, 23(1): 2-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9817.2002.01.002YANG G R. 2000 National students physical health survey results[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2002, 23(1): 2-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9817.2002.01.002 [7] 全国学生体质健康调研组. 2005年全国学生体质与健康调研结果[J]. 中国学校体育, 2006, 10: 6-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXT200610003.htmNational Student Physical Health Research Group of the PRC. 2005 national student physical health research results[J]. Chin Sch Phys Educ, 2006, 10: 6-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXT200610003.htm [8] 全国学生体质健康调研组. 2010年全国学生体质与健康调研结果[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2011, 32(9): 1024, 1026. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIWS201109003.htmNational Student Physical Health Research Group of the PRC. 2010 national student physical fitness and health survey results[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2011, 32(9): 1024, 1206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIWS201109003.htm [9] 国家体育总局. 2014年全国学生体质健康调研结果[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2015, 36(12): 4.General Administration of Sport of the PRC. Study on the physical health of students in China[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2015, 36(12): 4. [10] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2014年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2016.Chinese Students' Physique and Health Research Group. 2014 Chinese students' Physique and health survey Report [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2016. [11] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1987.Chinese Students' Physique and Health Research Group. Research report on Chinese students' physique and health[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1987. [12] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 1995年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1996.Chinese Students' Physique and Health Research Group. 1995 Chinese students' physique and health survey report[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1996. [13] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2000年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002.Chinese Students' Physique and Health Research Group. 2000 Chinese students' physique and health survey report[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2002. [14] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2005年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007.Chinese Students' Physique and Health Research Group. 2005 Chinese students' physique and health survey report[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007. [15] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查标准: WS/T 586—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. Screening criteria for overweight and obesity in school-age children and adolescents: WS/T 586-2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018. [16] 宁夏回族自治区统计局. 宁夏统计年鉴[M]. 宁夏: 中国统计出版社, 2000-2019.Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Statistics Bureau. Ningxia statistical yearbook[M]. Ningxia: China Statistics Press, 2000-2019. [17] 李艳辉, 董彬, 邱爱明, 等. 男生营养状况与青春期启动的关联性[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2020, 41(6): 807-810. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.06.003LI Y H, DONG B, QIU A M, et al. Association between mutritional status and puberty onset in boys[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2020, 41(6): 807-810. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.06.003 [18] WAGNER I V, SABIN M A, PFÄFFLE R W, et al. Effects of obesity on human sexual development[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2012, 8(4): 246-254. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.241 [19] HAJIN J, HANNAH O. Trends and inequalities in overall and abdominal obesity by sociodemographic factors in Korean adults, 1998-2018[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18(8): 4162. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18084162 [20] DEREń K, WYSZYńSKA J, NYANKOVSKYY S, et al. Secular trends of underweight, overweight, and obesity in children and adolescents from Ukraine[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18(6): 3302. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18063302 [21] BARBARA I, STEPHEN W, YANA V, et al. Long-term body mass index changes in overweight and obese adults and the risk of heart failure, cardiovascular disease and mortality: a cohort study of over 260000 adults in the UK[J]. BMC Public Health, 2021, 21(1): 576. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10606-1 [22] SKINNER A C, RAVANBAKHT S N, SKELTON J A, et al. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity in US children, 1999-2016[J]. Pediatircs, 2018, 141(3): e20173459. http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/141/3/e20173459.full-text.pdf [23] SUTHERLAND M E. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among African American children and adolescents: risk factors, health outcomes, and prevention/intervention strategies[J]. J Rac Ethnic Health Disparit, 2021, 8(5): 1281-1292. doi: 10.1007/s40615-020-00890-9 [24] HAYASHI K, TSUJIGUCHI H, HORI D, et al. The association between overweight and prevalence of food allergy in Japanese children: a cross-sectional study[J]. Environ Health Prev Med, 2021, 26(1): 44. doi: 10.1186/s12199-021-00960-2 [25] 马淑婧, 张艳青, 羊柳, 等. 1991—2015年中国9个省份儿童青少年超重和肥胖率的变化趋势分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2020, 2: 133-138. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2020.02.004MA S J, ZHANG Y Q, YANG L, et al. Analysis on the trend of overweight and obesity of children and adolescents in 9 provinces of China from 1991 to 2015[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2020, 2: 133-138. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2020.02.004 [26] ZHU Z, TANG Y, ZHUANG J, et al. Physical activity, screen viewing time, and overweight/obesity among Chinese children and adolescents: an update from the 2017 physical activity and fitness in China-the youth study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2019, 19(1): 197. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6515-9 [27] DONG Y, JAN C, MA Y, et al. Economic development and the nutritional status of Chinese school-aged children and adolescents from 1995 to 2014: an analysis of five successive national surveys[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2019, 7(4): 288-299. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30075-0 [28] UIJTDEWILLIGEN L, WATERS C N, MVLLER-RIEMENSCHNEIDER F, et al. Preventing childhood obesity in Asia: an overview of intervention programmes[J]. Obes Rev, 2016, 17(11): 1103-1115. doi: 10.1111/obr.12435 [29] IP P, HO F K, LOUIE L H, et al. Childhood obesity and physical activity-friendly school environments[J]. J Pediatr, 2017, 191: 110-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.08.017 [30] AU W W, YU I T. Socio-economic influence on weight status through time in schoolchildren[J]. J Paediatr Child Health, 2014, 50(10): E85-E93. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.2012.02475.x [31] CHUNG S T, ONUZURUIKE A U, MAGGE S N. Cardiometabolic risk in obese children[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2018, 1411(1): 166-183. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13602 [32] UMER A, KELLEY G A, COTTRELL L E, et al. Childhood obesity and adult cardiovascular disease risk factors: a systematic review with Meta-analysis[J]. BMC Public Health, 2017, 17(1): 683. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4691-z [33] AYER J, CHARAKIDA M, DEANFIELD J E, et al. Lifetime risk: childhood obesity and cardiovascular risk[J]. Eur Heart J, 2015, 36(22): 1371-1376. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv089 -







 下载:
下载: