Blood lead level of outpatient children in Anqing from 2015 to 2018
-
摘要:
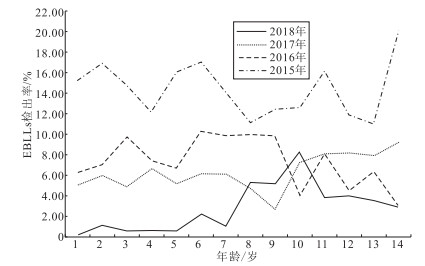
目的 分析安庆市2015—2018年0~14岁门诊儿童血铅水平的特点及影响因素,为防控儿童血铅水平升高提供依据。 方法 采用问卷调查、身体测量、实验室检测等方法,收集安徽医科大学附属安庆医院2015—2018年门诊儿童血铅水平、年龄、身高、体重、个人习惯、环境因素等相关信息,分析儿童血铅水平升高的影响因素。 结果 2015—2018年安徽医科大学附属安庆医院儿科门诊检测血铅水平的儿童人数分别为4 406,4 177,3 833,3 381人,儿童血铅水平升高(elevated blood lead levels, EBLLs)检出者662,326,225,56例,检出率为15.02%,7.80%,5.87%,1.66%,其中男童EBLLs检出率为16.54%,7.31%,6.18%,1.88%,女童检出率为16.04%,8.51%,5.42%,1.33%,性别差异均无统计学意义(χ2值分别为2.47,2.00,0.99,1.53,P值均>0.05)。0~14岁儿童均可能有EBLLs,2015与2017年EBLLs检出率最高的年龄均为14岁。个人行为中,较少进食肉类及奶制品,经常接触土壤或灰尘的儿童更可能患EBLLs;餐前洗手、清洗玩具≥1次/周的儿童患EBLLs的可能性更低,差异均有统计学意义(χ2值分别为13.58,8.91,7.63,9.22,P值均 < 0.05)。环境因素中,住房距离主干道 < 50 m、家庭成员吸烟、父母从事铅相关职业的儿童更可能出现EBLLs,差异均有统计学意义(χ2值分别为4.92,10.63,22.95,P值均 < 0.05)。 结论 安庆市儿童2015—2018年EBLLs检出率逐年降低;餐前洗手、经常清洗玩具可降低EBLLs的风险。 Abstract:Objective To analyze blood lead levels of children aged 0-14 in Anqing City during 2015 to 2018, to provide basic data for child poisoning prevention and control. Methods Using questionnaire surveys, physical examination, and laboratory tests to assess blood lead, age, height, weight, personal habits, environmental factors and other relevant information, to analyze associated factors of elevated blood lead levels. Results From 2015 to 2018, among the 4 406, 4 177, 3 833 and 3 381 children aged 0-14 in the pediatric outpatient, 662, 326, 225, and 56 cases were found with elevated blood lead levels (EBLLs), with the detection rate of 15.02%, 7.80%, 5.87%, and 1.66%, respectively. Detection rate in boys (16.54%, 7.31%, 6.18% and 1.88%) was similar with that of girls (16.04%, 8.51%, 5.42% and 1.33%) (χ2=2.47, 2.00, 0.99, 1.53, P>0.05). Children in any age groups of 0-14 years might have EBLLs, highest in 14-year-old group in the year of 2015 and 2017. Personal behaviors associated with EBLLs included less meat and dairy products consumption, high frequent exposure to soil dust. In contrast, children who wash their hands before meals and wash toys ≥1 time/week were less likely to suffer from EBLLs (χ2=13.58, 8.91, 7.63, 9.22, P < 0.05). Environmental factors associated with EBLLs included were less than 50 m between the main road with residency, family members smoke, and parents engaged in construction, welding, automobile maintenance and other industries are more likely to have EBLLs, and the difference is statistically significant (χ2=4.92, 10.63, 22.95, P < 0.05). Conclusion The detection rate of EBLLs in Anqing City from 2015 to 2018 depressed by year. Washing hands before meals and cleaning toys frequently could reduce the risk of EBLLs. -
Key words:
- Lead /
- Body size /
- Child /
- Prevalence
-
表 1 安庆市0~14岁儿童2015—2018年EBLLs的单因素分析
Table 1. Single factor analysis of EBLLs of aged 0-14 children in Anqing from 2015 to 2018
因素 选项 人数 EBLLs人数 χ2值 P值 居住地 城市 349 31(8.88) 0.63 0.43 农村 162 18(11.11) 年龄段 学龄前 379 36(9.50) 0.17 0.96 小学 103 10(9.71) 中学 29 3(10.34) 消瘦 无 458 42(9.17) 0.89 0.35 有 53 7(13.21) 体重不足 无 452 43(9.51) 0.03 0.87 有 59 6(10.17) 功能性便秘 无 454 43(9.47) 0.07 0.80 有 57 6(10.53) 过敏性疾病 无 446 41(9.19) 0.64 0.43 有 65 8(12.31) 较少进食肉类及奶制品 无 374 25(6.68) 13.58 <0.01 有 137 24(17.52) 餐前洗手 无 280 36(12.86) 7.63 0.01 有 231 13(5.63) 每周清洗玩具 无 292 38(13.01) 9.22 < 0.01 ≥1次 有 219 11(5.02) 经常接触土壤或灰尘 无 382 28(7.33) 8.91 < 0.01 有 129 21(16.28) 住房距离主干道 < 50 m 无 466 40(8.58) 4.92 0.03 有 45 9(20.00) 家庭成员吸烟 无 456 37(8.11) 10.63 < 0.01 有 55 12(21.82) 住在老旧或新 无 487 46(9.45) 0.25 0.62 装修住房 有 24 3(12.50) 父母从事铅相关职业 无 485 39(8.04) 22.95 <0.01 有 26 10(38.46) 注: ()内数字为检出率/%。 -
[1] 张红振, 董璟琦, 吴舜泽, 等. 铅污染损害评估研究[J]. 环境保护, 2016, 44(9): 51-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJBU201609015.htmZHANG H Z, DONG J Q, WU S Z, et al. Study on damage assessment techniques of lead contamination[J]. Environ Protect, 2016, 44(9): 51-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJBU201609015.htm [2] DAPUL H, LARAQUE D. Lead poisoning in children[J]. Adv Pediatr, 2014, 61(1): 313-333. doi: 10.1016/j.yapd.2014.04.004 [3] ZHANG Y F, XU J W, YANG Y, et al. The association between body lead levels and childhood rickets: a meta-analysis based on Chinese cohort[J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(8): e14680. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014680 [4] 黄慧, 李国慧, 李贵霞, 等. 健康儿童血清中钙、镁、铁、锌、铜、铅、镉7种元素检测结果研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2019, 23(3): 503-505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2019.03.050HUANG H, LI G H, LI G X, et al. Study on the detection results of 7 elements of calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, copper, lead and cadmium in the serum of healthy children[J]. Chin J Lab Diagn, 2019, 23(3): 503-505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2019.03.050 [5] 阳海林, 张国旺, 田超逸, 等. 电子废物铅和镉的暴露与小儿听力能力的相关性研究[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2019, 34(15): 3504-3506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFYB201915038.htmYANG H L, ZHANG G W, TIAN C Y, et al. Correlation between exposure of lead and cadmium from electronic waste and hearing ability in children[J]. Matern Child Health Care Chin, 2019, 34(15): 3504-3506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZFYB201915038.htm [6] HAUPTMAN M, STIERMAN B. Children children with autism spectrum disorder and lead poisoning: diagnostic challenges and management complexities[J]. Clinic Pediatr, 2019, 58(6): 605-612. doi: 10.1177/0009922819839237 [7] 赵莎, 钟燕, 赵兰. 儿童孤独症全血微量元素及血铅水平分析[J]. 实用预防医学, 2014, 21(1): 83-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYY201401031.htmZHAO S, ZHONG Y, ZHAO L. Analysis of trace elements and blood lead levels in whole blood of children with autism[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2014, 21(1): 83-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYY201401031.htm [8] REUBEN A, CASPI A, BELSKY D W, et al. Association of childhood blood lead levels with cognitive function and socioeconomic status at age 38 years and with IQ change and socioeconomic mobility between childhood and adulthood[J]. JAMA, 2017, 317(12): 1244-1251. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.1712 [9] KELLER B, FACIANO A, TSEGA A. Epidemiologic characteristics of children with blood lead levels ≥45 μg/dL[J]. J Pediatr, 2017, 180(1): 229-234. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022347616309271 [10] 邓美. 儿童血铅水平测定及其影响因素分析[J]. 实用检验医师杂志, 2018, 10(2): 85-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJCP201802007.htmDENG M. Determination of blood lead level and analysis of its influencing factors in childre[J]. Chin J Lab Pathol, 2018, 10(2): 85-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJCP201802007.htm [11] MOAWAD E M I, BADAWY N M, MANAWILL M. Environmental and occupational lead exposure among children in Cairo, Egypt: a community-based cross-sectional study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2016, 95(9): e2976. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002976 [12] 卫生部. 卫生部关于印发《血铅临床检验技术规范》的通知[J]. 中华人民共和国卫生部公报, 2006(2): 25-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGB200602008.htmMinistry of Health of the People's Republic of China. Notice of the Ministry of Health on Printing and Distributing the "Technical Specifications for Clinical Testing of Blood Lead"[J]. Gazette Ministry Health PRC, 2006(2): 25-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGB200602008.htm [13] 赵露, 李霞, 罗钢. 《儿童高铅血症和铅中毒预防指南》及《儿童高铅血症和铅中毒分级和处理原则(试行)》解读[J]. 中国实用乡村医生杂志, 2007, 14(7): 52-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FACT200707033.htmZHAO L, LI X, LUO G. Interpretation of "Guidelines for the Prevention of Hyperleademia and Lead Poisoning in Children" and "Principles of Classification and Management of Hyperleademia and Lead Poisoning in Children (Trial)"[J]. Chin Pract J Rural Doct, 2007, 14(7): 52-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FACT200707033.htm [14] GELTMAN P L, SMOCK L, COCHRAN J. Trends in elevated blood lead levels using 5 and 10 g/dl levels of concern among refugee children resettled in massachusetts, 1998-2015[J]. Public Health Rep, 2019, 134(6): 608-616. [15] 康宇, 梁小华, 李廷玉, 等. 中国标准和WHO标准检出婴儿生长迟缓, 消瘦, 低体质量和超重率的差异分析[J]. 临床儿科杂志2014, 32(5): 442-445. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCAK201405014.htmKANG Y, LIANG X H, LI T Y, et al. The comparison of wasting, stunting, low weight, and overweight rate in infants by using the World Health Organi-zation Child Growth Standards and China Growth Standards[J]. J Clin Pediatr, 2014, 32(5): 442-445. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCAK201405014.htm [16] 王卫平, 汪翼, 常立文. 儿科学[M]. 9版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018.WANG W P, WANG Y, CHANG L W. Pediatrics-Ninth Edition[M]. 9 ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2018. [17] 王茂贵. 儿童功能性便秘: 罗马Ⅲ诊断标准临床评介[J]. 实用儿科临床杂志, 2007, 22(7): 559-560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQK200707048.htmWANG M G. Childhood functional constipation: clinical evaluation of diagnostic criteria Rome Ⅲ[J]. J Appl Clin Pediatr, 2007, 22(7): 559-560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQK200707048.htm [18] 刘爱华, 李涛, 张帅明, 等. 中国18城市儿童血铅水平及影响因素现况调查[J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2018, 29(5): 539-542. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SANE201805002.htmLIU A H, LI T, ZHANG S M, et al. Study on blood lead level and related risk factors among children in 18 cities of China[J]. Chin J Women Child Health Res, 2018, 29(5): 539-542. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SANE201805002.htm [19] 刘颖, 黄丽红, 林慧. 海口市2015—2018年学龄前儿童血铅水平及影响因素[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40(5): 742-744. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.05.026LIU Y, HUANG L H, LIN H. Blood lead level and associated factors among preschool children in Haikou City from 2015 to 2018[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2019, 40(5): 742-744. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.05.026 [20] 傅苏林, 张黎明, 李辉, 等. 合肥市2005—2011年儿童血铅水平及影响因素分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2013, 34(3): 320-323. http://www.cjsh.org.cn/article/id/zgxxws201303021FU S L, ZHANG L M, LI H, et al. Analysis of blood lead levels and influencing factors of children in Hefei from 2005 to 2011[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2013, 34(3): 320-323. http://www.cjsh.org.cn/article/id/zgxxws201303021 [21] 王珍, 欧洁雯, 肖伟. 湖南省衡阳市17858名儿童血铅水平分析[J]. 中国妇幼卫生杂志, 2018, 9(3): 54-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZWS201803016.htmWANG Z, OU J W, XIAO W. Analysis on blood lead level of 17 858 children in Hengyang City of Hunan Province[J]. Chin J Women Child Health, 2018, 9(3): 54-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZWS201803016.htm [22] 吕玉桦, 石小飞, 刘珊渡, 等. 我国0~6岁儿童血铅水平及流行特征分析[J]. 实用预防医学, 2015, 22(2): 149-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYY201502007.htmLYU Y H, SHI X F, LIU S D, et al. Analysis of blood lead level and its epidemiological characteristics in children aged 0-6 years in China[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2015, 22(2): 149-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYY201502007.htm [23] MAYANS L. Lead poisoning in children[J]. Am Fam Phys, 2019, 100(1): 24-30. [24] 张盟, 郜振彦, 徐健, 等. 上海新华医院铅中毒门诊194例儿童血铅资料的分析[J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2016, 27(2): 165-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SANE201602007.htmZHANG M, GAO Z Y, XU J, et al. Blood lead analysis of 194 outpatient cases of childhood lead poisoning in Shanghai Xinhua Hospital[J]. Chin J Women Child Health Res, 2016, 27(2): 165-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SANE201602007.htm [25] 戴耀华, 樊朝阳. 中国儿童铅中毒的影响因素[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2006, 21(3): 165-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSEK200603002.htmDAI Y H, FAN C Y. Influencing factors of lead poisoning in Chinese children[J]. Chin J Pract Pediatr, 2006, 21(3): 165-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSEK200603002.htm [26] 韩志轩, 闭向阳, 郭祥义, 等. 中国城市儿童血铅含量变化趋势及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(12): 3553-3557. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201712030.htmHAN Z X, BI X Y, GUO X Y, et al. Children blood lead levels in urban and suburban areas of China and its influencing factors[J]. J Ecol, 2017, 36(12): 3553-3557. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201712030.htm [27] LEAL M F, CATARINO R I, PIMENTA A M, et al. Lead migration from toys by anodic stripping voltammetry using a bismuth film electrode[J]. Arch Environ Occupat Health, 2016, 71(5): 300-306. -







 下载:
下载: