Effects of high-intensity interval training on fat loss in overweight and obese female college students: a Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
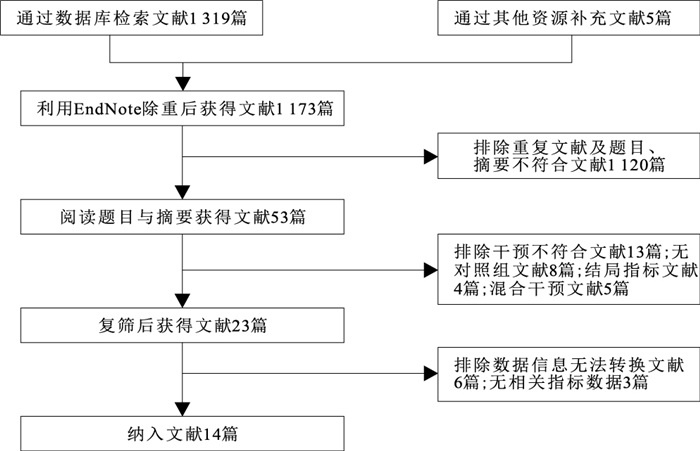
目的 系统评价高强度间歇训练(high-intensity interval training,HIIT)对超重肥胖女大学生体重、身体成分的干预效果,以期为超重肥胖大学生选择HIIT方法提供理论依据。 方法 计算机检索PubMed、the Cochrane Library、Web of Science、Embase、CNKI、CBM、VIP、WanFang Data数据库中有关HIIT对超重肥胖女大学生体重、身体成分的随机对照试验,检索期年限从各数据库收录起始年限至2020年12月14日,根据纳入和排除标准进行文献筛选,并对纳入文献进行方法学质量评价、Meta分析及发表偏倚检验。 结果 共纳入20个随机对照试验,中等质量研究14篇。Meta分析结果显示,HIIT能显著减轻超重肥胖女大学生体重(MD=-4.22,95%CI=-7.20~-1.25,P<0.01);改善体脂率(MD=-5.31,95%CI=-6.88~-3.73,P<0.01)、体质量指数(BMI)(MD=-2.11,95%CI=-2.65~-1.56,P<0.01)、全身脂肪量(MD=-3.66,95%CI=-4.89~-2.43,P<0.01)、腹部脂肪量(MD=-0.31,95%CI=-0.47~-0.15,P<0.01)、躯干脂肪量(MD=-2.15,95%CI=-2.86~-1.44,P<0.01),对瘦体重(MD=0.42,95%CI=-0.94~1.78,P=0.55)影响无统计学意义。 结论 HIIT能显著减轻超重和肥胖女大学生的体重,改善其身体成分,可为超重和肥胖女大学生进行长期的HIIT提供可靠依据。 Abstract:Objective To systematically evaluate the effectiveness of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on body weight and body composition of overweight and obese female college students. In order to provide a theoretical basis for choosing HIIT method. Methods Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published till December 14, 2020 were searched in PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, CNKI, CBM, VIP and WanFang Databases. Literature screening was conducted based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, methodological quality evaluation, Meta-analysis and publication bias test were conducted on the included literature. Results There were 20 RCTs among which 14 studies graded as moderate quality. Meta-analysis showed that HIIT could significantly reduce the weight of overweight and obese female college students (MD=-4.22, 95%CI=-7.20--1.25, P < 0.01). Improved body fat rate (MD=-5.31, 95%CI=-6.88--3.73, P < 0.01), BMI (MD=-2.11, 95%CI=-2.65--1.56, P < 0.01), total body fat (MD=-3.66, 95%CI=-4.89--2.43, P < 0.01), abdominal fat (MD=-0.31, 95%CI=-0.47--0.15, P < 0.01), trunk fat (MD=-2.15, 95%CI=-2.86--1.44, P < 0.01) were observed. There was no significant effect on lean body weight (MD=0.42, 95%CI=-0.94-1.78, P=0.55). Conclusion HIIT can significantly reduce the weight and improve body composition in overweight and obese female college students. It can provide a reliable basis for long-term HIIT in overweight and obese female college students. -
Key words:
- Physical education and training /
- Overweight /
- Obesity /
- Meta-analysis /
- Students /
- Female
-
表 1 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 1. General characteristics of the included studies
第一作者及年份 国籍 样本量(试验组/对照组) 年龄(试验组/对照组)/岁 营养状况 运动形式 运动-间歇-组数 频率/(次·周-1) 周期/周 对照组 结局指标 彭小红2020[14] 中国 17/18 23.41/23.39 超重 跑步 85%~95% HRmax运动4 min,间歇50%~60% HRmax运动3 min,4组 3 12 不做干预 1, 2, 3, 齐玉刚2013[15] 中国 20/20 - 肥胖 跑步 85%VO2max中途跑3 min, 间歇2 min, 4组25 min 5 12 不做干预 1, 2, 3, 韩涵2014[16] 中国 16/13 21.31/21.07 肥胖 功率自行车 90%VO2max, 4 min,间歇休息至RPE下降到13,继续下一组 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7 林坚2016[17] 中国 18/18 20.1/20.3 肥胖 运动平板 90% HRmax运动4 min, 70% HRmax运动3min,4组 2 12 不做干预 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 周广仁2020[18] 中国 24/20 18.5/18.9 肥胖 徒手和器械训练 80%~90% HRmax运动3 min, 50%~60% HRmax 2 min, 1 min间歇, 重复22~30 min 2 17 健康教育 1, 3 曾帅2012[19] 中国 16/13 21.3/21.1 肥胖 功率自行车 90%VO2max运动4 min, 间歇4 min 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 3 曹文玲2016[20] 中国 14/9 20.3/19.7 肥胖 功率自行车 120%VO2max运动1 min, 间歇1.5 min, 当RPE下降到13, 再进行运动4 min 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 3 曹文玲2016[20] 中国 14/9 20.0/19.7 肥胖 功率自行车 90%VO2max运动4 min, 间歇1.5 min, 当RPE下降到13, 再进行运动4 min 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 3 曹文玲2016[20] 中国 14/9 21.2/19.7 肥胖 功率自行车 初始负荷0.5 kg, 逐次递增, 共6次, 全力冲刺6 s间歇9 s为1组,40组 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 3 郑子威2018[21] 中国 12/13 19.7/21.2 肥胖 功率自行车 120%VO2max运动1 min, 间歇1.5 min, 重复直到完成200 kJ机械功 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 6, 7 郑子威2018[21] 中国 12/13 19.7/21.2 肥胖 功率自行车 90%VO2max运动4 min, 间歇休息至RPE下降到13, 重复直到完成200 kJ机械功 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 6, 7 郑子威2018[21] 中国 11/13 20.9/21.2 肥胖 功率自行车 全力冲刺踏车6 s后间歇9 s,初始负荷1 kg, 逐渐增加, 40组, 运动时间4 min 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 6, 7 张立萌2020[22] 中国 10/10 20.60±0.91 超重 功率自行车 前3周, 90%VO2max运动1 min, 间歇1 min, 15组;后3周, 90%VO2max 3 min, 25%VO2max 2 min, 6组 3 6 不做干预 1, 3 张旭2014[23] 中国 16/10 21.44/21.00 肥胖 功率自行车 90%VO2peak运动4 min, 间歇不运动, 当RPE下降到13, 再运动4 min, 前2周克服200 kJ, 后10周克服300 kJ 3-4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7 张旭2014[23] 中国 16/10 21.31/21.00 肥胖 功率自行车 初始负荷0.5 kg, 全力冲刺6 s间歇9 s为1组, 80组 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7 Tong2018[24] 中国 16/14 21.3/20.7 肥胖 功率自行车 90%VO2max运动4 min, 间歇3 min, 前2周, 工作量200 kJ,后逐渐增加至400 kJ 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 6, 7 Tong2018[24] 中国 16/14 21.3/20.7 肥胖 功率自行车 全力冲刺踏车6 s后间歇9 s,80组 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 6, 7 Pour-Abdi2013[25] 伊朗 16/10 19~23 肥胖 跑步 75%HRR运动4 min 30 s, 积极性休息3 min, 4组 3 6 不做干预 1, 2, 3, 5 Zhang2017[26] 中国 15/13 18~22 肥胖 功率自行车 90%VO2max运动4 min,间歇3 min, 完成目标300 kJ 3~4 12 不做干预 1, 2, 4, 7 Sijie2012[27] 中国 17/19 19.8/19.5 超重 跑步 85%VO2max运动3 min, 间歇50%VO2max 3 min, 5组 5 12 不做干预 1, 2, 3, 注:1表示体重;2表示体脂率;3表示体质量指数(BMI);4表示全身脂肪量;5表示瘦体重;6表示腹部脂肪量;7表示躯干脂肪量;RPE表示主观体力感觉评分;HRmax表示最大心率;VO2peak表示峰值摄氧量;VO2max表示最大摄氧量。 -
[1] 中国肥胖问题工作组. 中国成人超重和肥胖症预防与控制指南(节录)[J]. 营养学报, 2004(1): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYXX200401004.htmWorking Group on Obesity in China. Guidelines for the prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults (Excerpt)[J]. Acta Nutr Sinica, 2004(1): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYXX200401004.htm [2] 卢桂兵, 董丹丹. 运动干预对肥胖大学生体质健康及心理指标的影响[J]. 吉林体育学院学报, 2018, 34(5): 59-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLTY201805011.htmLU G B, DONG D D. Effect of exercise intervention on physical health and psychological indexes of obese college students[J]. J Jilin Sport Univ, 2018, 34(5): 59-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLTY201805011.htm [3] 于芳, 巫国贵. 大学生超重、肥胖现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中北大学学报(社会科学版), 2005, 21(6): 91-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1646.2005.06.028YU F, WU G G. Current situation of overweight and obesity of college students and affecting factors[J]. J North Univ Chin(Soc Sci), 2005, 21(6): 91-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1646.2005.06.028 [4] ALLISON D B, FONTAINE K R, MANSON J E, et al. Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States[J]. JAMA, 1999, 282(16): 1530-1538. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.16.1530 [5] SLENTZ C A, DUSCHA B D, JOHNSON J L. Effects of the amount of exercise on body weight, body composition and measures of central obesity[J]. Arch Int Med, 2004, 164(1): 31-39. doi: 10.1001/archinte.164.1.31 [6] HEYDARI M, FREUND J, BOUTCHER S H. The effect of high-intensity intermittent exercise on body composition of overweight young males[J]. J Obes, 2012, 2012: 480467. DOI: 10.1155/2012/480467. [7] KRAUS W E, HOUMARD J A, DUSCHA B D, et al. Effects of the amount and intensity of exercise on plasma lipoproteins[J]. N Engl J Med, 2002, 347(19): 1483-1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020194 [8] RAMOS J S, DALLECK L C, RAMOS M V, et al. 12 min/week of high-intensity interval training reduces aortic reservoir pressure in individuals with metabolic syndrome: a randomized trial[J]. J Hypertens, 2016, 34(10): 1977-1987. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001034 [9] 黎涌明. 高强度间歇训练对不同训练人群的应用效果[J]. 体育科学, 2015(8): 59-75, 96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX201508009.htmLI Y M. Effect of high-intensity interval training on different training populations[J]. Chin Sport Sci, 2015(8): 59-75, 96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX201508009.htm [10] 高艳敏, 王光明, 杨文礼, 等. 高强度间歇训练和有氧运动对肥胖青年脂代谢及慢性炎症的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2017, 36(7): 628-632, 650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2017.07.011GAO Y M, WANG G M, YANG W L, et al. Effects of high intensity interval training and aerobic exercise on lipid metabolism and chronic inflammation in obese youth[J]. Chin J Sports Med, 2017, 36(7): 628-632, 650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2017.07.011 [11] 鲁鑫, 谢波. 功能性高强度间歇训练结合呼吸饮食对肥胖大学生的干预效果[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2021, 42(4): 569-573. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.04.021LU X, XIE B. Effect of functional high-intensity interval training combined with inhalation dietary intervention on obese college students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2021, 42(4): 569-573. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.04.021 [12] SHUSTER J J. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews for interventions, Version 5.1.0, published 3 /2011. Julian PT Higgins and Sally Green, Editors[J]. Res Synth Meth, 2011, 2(2): 126-130. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.38 [13] MOHE R D, LIBERATI A, TETZLAFF J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement[J]. Ann Int Med, 2009, 151(4): 264-269. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135 [14] 彭小红. 12周不同运动方式对超重女大学生干预研究[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2020.PENG X H. Intervention study of 12 weeks of different exercise patterns on overweight female college students[D]. Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2020. [15] 齐玉刚, 黄津虹, 谭思洁. HIIT和持续性有氧运动对肥胖女大学生减肥效果的比较研究[J]. 中国体育科技, 2013, 49(1): 30-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9826.2013.01.005QI Y G, HUANG J H, TAN S J. Comparison of weight loss effects carried out by hiit and continuous aerobic exercise of female obese college students[J]. Chin Sport Sci Technol, 2013, 49(1): 30-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9826.2013.01.005 [16] 韩涵. 高强度间歇和中强度持续训练对青年肥胖女性体脂分布的影响[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2014.HAN H. The Effect of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on body fat distribution in young obese women[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2014. [17] 林坚, 赵红勤, 黄雄昂, 等. 高强度间歇训练对肥胖女大学生体成分和血脂及空腹胰岛素水平的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2016, 19(18): 2139-2144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.18.007LIN J, ZHAO H Q, HUANG X A, et al. Effect of high intensity interval training on the body composition, blood lipid and fasting insulin level of obese female college students[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2016, 19(18): 2139-2144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.18.007 [18] 周广仁, 朱二刚, 陶志轩, 等. 健康教育和HIIT联合干预肥胖女大学生的减肥效果观察[J]. 石家庄学院学报, 2020, 22(3): 130-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1972.2020.03.024ZHOU G R, ZHU E G, TAO Z X, et al. Effect of joint intervention with health education and HIIT on weight loss of obese female college students[J]. J Shijiazhuang Univ, 2020, 22(3): 130-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1972.2020.03.024 [19] 曾帅. 中等强度持续和高强度间歇运动对肥胖青年女性心电QTc及血压影响以及训练适应[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2014.ZENG S. The effect of moderate intensity continuous and high intensity interval exericise on qtc、blood pressure and trailing adaptation in obese young women[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2014. [20] 曹文玲. 高强度间歇运动对肥胖青年女性血压、心率恢复和血清肌钙蛋白水平的影响及其训练适应[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2018.CAO W L. The effect of high intensity interval exercise on blood pressure, heart rate recovery and serum troponin level and training adaptation in obese young women[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2018. [21] 郑子威. 不同高强度间歇训练方案对肥胖青年女性腹部内脏脂肪量的影响[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2018.ZHENG Z W. Effects of different high-intensity interval training programs on abdominal visceral fat in obese young women[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2018. [22] 张立萌. 高强度间歇训练对超重青年循环骨钙素及其相关指标的影响[D]. 北京: 首都体育学院, 2020.ZHANG L M. Effect of high-intensity interval training on circulating osteocalcin and its related parameters in overweight youth[D]. Beijing: Capital University of Physical Education and Sports, 2020. [23] 张旭. 短时间大强度间歇训练对肥胖青年女性腹部脂肪的影响[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2016.ZHANG X. Effect of Short-term High-intensity interval training on abdominal fat in obese young women[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2016. [24] TONG T K, ZHANG H, SHI H, et al. Comparing time efficiency of sprint vs. High-intensity interval training in reducing abdominal visceral fat in obese young women: a randomized, controlled trial[J]. Front Physiol, 2018, 9: 1048. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01048 [25] POUR-ABDI K, SHAKERIAN S, POUR-ABDI Z, et al. Effects of short-term interval training courses on fitness and weight loss of untrained girls[J]. Annals Appll Sport Sci, 2013, 1(2): 1-9. http://aassjournal.com/article-1-39-en.pdf [26] ZHANG H, TONG T K, QIU W, et al. Comparable effects of high-intensity interval training and prolonged continuous exercise training on abdominal visceral fat reduction in obese young women[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2017, 2017: 5071740. DOI: 10.1155/2017/5071740. [27] SIJIE T, HAINAI Y, FENGYING Y, et al. High intensity interval exercise training in overweight young women[J]. J Sports Med Phys Fitness, 2012, 52(3): 255-262. http://www.lafitness.com.br/biblioteca/artigos/high-intensity-interval-exercise-training-in-overweight-young-women.pdf [28] 王京京, 张海峰. 高强度间歇训练运动处方健身效果研究进展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2013, 32(3): 246-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2013.03.011WANG J J, ZHANG H F. Research progress on fitness effect of exercise prescription of high intensity interval training[J]. Chin J Sports Med, 2013, 32(3): 246-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2013.03.011 [29] BARTLETT J D, CLOSE G L, MACLAREN D P, et al. High-intensity interval running is perceived to be more enjoyable than moderate-intensity continuous exercise: implications for exercise adherence[J]. J Sports Sci, 2011, 29(6): 547-553. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2010.545427 [30] 张歆然, 滕育松, 张龙. 对高校肥胖学生开展高强度间隙训练的可行性研究[J]. 文体用品与科技, 2020(10): 179-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8902.2020.10.077ZHANG X R, TENG Y S, ZHANG L. Feasibility study of carrying out high intensity interval training for obese college students[J]. Sci Technol Stationery Sport Goods, 2020(10): 179-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8902.2020.10.077 [31] RENTER A I, GARCÍA-SUREZ P C, MARTÍNEZ-CORONA D O, et al. Short-term high-Intensity interval training increases systemic brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in healthy women[J]. Eur J Sport Sci, 2020, 20(4): 516-524. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2019.1650120 [32] 童国元, 叶礼燕, 陈新民, 等. 单纯性肥胖儿童血清脑源性神经营养因子表达的变化及意义[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2006, 21(3): 197-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2224.2006.03.014TONG G Y, YE L Y, CHEN X M, et al. Changes and significance of the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in children with simple obesity[J]. Chin J Pract Pediatr, 2006, 21(3): 197-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2224.2006.03.014 [33] 顾新, 李京平, 陈刚, 等. 对肥胖者静息代谢率的研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2005(3): 200-202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2005.03.013GU X, LI J P, CHEN G, et al. Resting metabolic rate in obese and nonobese Chinese[J]. Chin J Rehabil Med, 2005(3): 200-202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2005.03.013 [34] TALANIAN J L, GALLOWAY S D, HEIGENHAUSER G J, et al. Two weeks of high-intensity aerobic interval training increases the capacity for fat oxidation during exercise in women[J]. J Appl Physiol (1985), 2007, 102(4): 1439-1447. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01098.2006 [35] 赵军, 梁晋裕, 郝亮. 中高强度运动对肥胖女大学生身体成分及心血管功能指标的影响[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2020, 41(5): 751-754. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.05.031ZHAO J, LIANG J Y, HAO L. Effects of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on body composition, arterial stiffness and serum resistin level in obese college female students[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2020, 41(5): 751-754. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.05.031 [36] WEWEGE M, VAN DEN BERG R, WARD R E, et al. The effects of high-intensity interval training vs. moderate-intensity continuous training on body composition in overweight and obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Obes Rev, 2017, 18(6): 635-646. doi: 10.1111/obr.12532 [37] 王京京, 韩涵, 张海峰. 高强度间歇训练对青年肥胖女性腹部脂肪含量的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2015, 34(1): 15-20, 30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX201501005.htmWANG J J, HAN H, ZHANG H F. Effects of high-intensity interval training and continuous training on abdominal fat in obese young women[J]. Chin J Sports Med, 2015, 34(1): 15-20, 30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX201501005.htm [38] TVRK Y, THEEL W, KASTELEYN M J, et al. High intensity training in obesity: a Meta-analysis[J]. Obes Sci Pract, 2017, 3(3): 258-271. doi: 10.1002/osp4.109 [39] DESPR S J P, LEMIEUX I, PRUD'HOMME D. Treatment of obesity: need to focus on high risk abdominally obese patients[J]. BMJ, 2001, 322(7288): 716-720. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7288.716 [40] TRAPP E G, CHISHOLM D J, BOUTCHER S H. Metabolic response of trained and untrained women during high-intensity intermittent cycle exercise[J]. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2007, 293(6): R2370-R2375. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00780.2006 [41] BOUDOU P, SOBNGWI E, MAUVAIS-JARVIS F, et al. Absence of exercise-induced variations in adiponectin levels despite decreased abdominal adiposity and improved insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic men[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2003, 149(5): 421-424. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1490421 [42] GREER B K, SIRITHIENTHAD P, MOFFATT R J, et al. EPOC comparison between isocaloric bouts of steady-state aerobic, intermittent aerobic, and resistance training[J]. Res Q Exerc Sport, 2015, 86(2): 190-195. doi: 10.1080/02701367.2014.999190 [43] BOUTCHER, STEPHEN H. High-intensity intermittent exercise and fat loss[J]. J Obes, 2011: 868305. DOI: 10.1155/2011/868305. [44] 苏利强, 陈海春, 温岱宗, 等. 生命科学新技术在体育科学领域的应用: 以UPLC-QTOF在HIIT减脂研究中的应用为例[J]. 上海体育学院学报, 2020, 44(10): 34-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STYB202010005.htmSU L Q, CHEN H C, WEN D Z, et al. Application of advanced detection technology of life science in sports science: effect of hiit in fat reduction using UPLC-QTOF[J]. J Shanghai Univ Sport, 2020, 44(10): 34-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STYB202010005.htm -







 下载:
下载: