Factors influencing emotional and behavioral problems among firstborn children in transition to siblinghood: a systematic review
-
摘要:
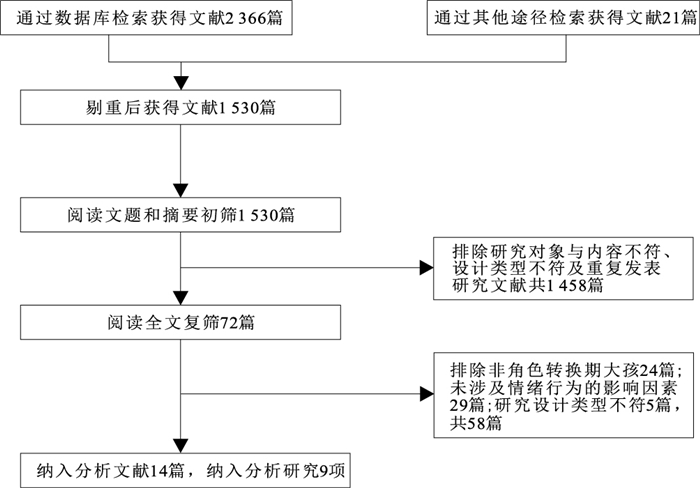
目的 系统评价影响角色转换期大孩情绪行为的相关因素,为角色转换期大孩情绪行为相关研究提供理论基础。 方法 通过计算机检索中国生物医学文献数据库、维普中文科技期刊数据库、中国知网期刊数据库、万方数据在线知识服务平台、PubMed、Web of Science、OVID和EBSCO数据库,搜集相关研究,检索时间为建库至2021年3月3日。由2名作者独立进行文献筛选、资料提取,评价纳入研究的偏倚风险,再采用定性分析方法归纳总结纳入研究的结果。 结果 共纳入9项研究,包括4项前瞻性队列研究和5项横断面研究。角色转换期大孩行为的影响因素研究主要涉及3大类,包括大孩自身因素(性别、年龄及气质类型),家庭因素(父母教养方式、家庭关系及家庭氛围、家庭社会经济、母亲行为、大孩获知二孩到来的时间)和社会因素(师生关系、同伴关系和生活变化)。情绪的影响因素主要为大孩自身因素(年龄和自身接纳度)。大孩消极气质类型,消极父母教养方式,消极家庭关系及家庭氛围,母亲的禁止行为,大孩在非备孕阶段获知二孩到来,不佳的师生关系、同伴关系、生活变化可能增加大孩情绪和行为问题的发生风险,其余影响因素的研究结果尚不十分确定。 结论 角色转换期大孩情绪行为的重要影响因素仍需进一步开展高质量的前瞻性队列研究加以证实,也可适当开展干预研究对其进行验证,从而为针对角色转换期大孩不同的情绪行为问题干预提供实证依据。 Abstract:Objective This study systematically reviewed the findings of studies on the factors influencing emotional and behavioral problems among firstborn children in transition to siblinghood, to provide a theoretical basis for the study of emotional behavior in firstborn children during role transition. Methods CBM, VIP, CNKI, WanFang Data, PubMed, Web of Science, OVID and EBSCO were electronically searched to collect studies on the relevant factors influencing the emotional and behavioral characteristics of firstborn children in transition to siblinghood (TTS) from inception to March 3rd, 2021. Literature screening and data extraction were conducted by two independent authors to evaluate the risk of bias in the included studies. The results of the included studies were summarized by qualitative analysis. Results A total of nine studies were included, comprising four prospective cohort studies and five cross-sectional studies. Systematic evaluation results indicated three main types of factor associated with behavioral problems among firstborn children: factors of firstborn children (gender, age and temperament), family factors (parents' upbringing, family relationships, family environment, social economy, maternal behavior and whether firstborn children knew that the second children would arrive), and social factors (relationships between teachers and students, peer relationships and life changes). The main factors affecting emotions were their own factors (age and self-acceptance). Negative temperament in firstborn children, negative parenting styles, negative family relationships and family environments, prohibited behaviors among mothers, whether the firstborn children were informed of the arrival of the second children during pregnancy, poor relationships between teachers and students, peer relationships and life changes may increase the risk of emotional and behavioral problems among firstborn children. Whether other factors might have affected the results of the study is unclear. Conclusion Important factors influencing firstborn children's emotions and behaviors during TTS, must be confirmed through a high-quality prospective cohort study. Intervention studies may be appropriate to verify the results and provide an empirical basis for behavioral interventions in firstborn children with different emotional problems. -
Key words:
- Emotions /
- Behavior /
- Mental health /
- Child
-
表 1 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 1. General characteristics of included studies
第一作者及年份 国家 地点 对象来源 大孩年龄 样本量 调查时间点 研究设计 数据收集方法 大孩情绪和行为 影响因素 大孩 独生子女 Gottlieb(1995)[22] 加拿大 家中 医院、学校 18~60月 20(男:10,女:10) 60 每月随访1次,随访3次 前瞻性队列 定量问卷 ③ 性别、年龄 Teti(1996)[23] 美国 家中 医院、社区 12~63月 194(男:92,女:102) 0 母亲孕晚期、产后4~8周 前瞻性队列 定量问卷 ③ 性别、年龄、家庭关系 Dunn(1981)[13]、Kendrick(1980)[14]、Kendrick(1982)[15]、Kendrick(1983)[16] 美国 家中 医院 18~43月 40(男:21,女:19) 0 母亲孕晚期、产后2~3周、8、14个月 前瞻性队列 定性观察、访谈母亲 ① 性别、年龄、母亲的行为 Kolak(2013)[17]、Oh(2015)[18]、Song(2015)[19] 美国 家中 医院、社区 12~69月 241(男:110,女:131) 0 母亲孕晚期、产后1,4,8,12个月 前瞻性队列 定量问卷、定性观察 ③ 性别、年龄、气质类型、父母教养方式、家庭关系、家庭社会经济 丁常聪(2018)[24] 中国 医院 2~6岁 96(男:43,女:53) 0 二孩2岁内 横断面调查 定量问卷 ① 性别、家庭社会经济 张星玮(2018)[20] 中国 3~6岁 30(男:15,女:15) 0 二孩出生前后1年 横断面调查 定量问卷、访谈母亲 ①④ 性别、年龄、父母教养方式 赵雪(2018)[21] 中国 咨询室 学校 8~12岁 8(男:4,女:4) 0 二孩出生后3个月~3岁 横断面调查 访谈大孩 ①④ 师生关系、同伴关系、生活变化、自身接纳度 孙雅(2020)[25] 中国 2~6岁 80(男:41,女:39) 0 二孩0~2岁 横断面调查 定量问卷 ①④ 性别、家庭社会经济 杨博(2020)[26] 中国 医院 1.5~5岁 882(男:397,女:483)a 329 母亲孕14周及以后 横断面调查 定量问卷 ③⑤ 性别、年龄、气质类型、父母教养方式、家庭关系及家庭氛围、大孩获知二孩到来的时间 注: ①发生相关行为的频率(自行设计调查工具);②相关行为得分(自行设计调查工具);③相关行为得分(量表);④发生相关情绪的频率(自行设计调查工具);⑤相关情绪得分(量表)。[13-16]为同一项研究、[17-19]为同一项研究。a存在性别样本缺失。 -
[1] FREUD A. Psychoanalytic treatment of children[M]. London: Imago Publishing Co., 1946. [2] HILL R. Families under stress; Adjustment to the crises of war separation and reunion[M]. New York: Harper& Brothers, 1949. [3] COWAN C P, COWAN P A. When partners become parents[M]. New York: Basic Books, 1992. [4] BRONFENBRENNER U. The ecology of human development: experiments by nature and design[M]. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1979. [5] WINNICOTT D W. The child, the family, and the outside world[M]. Reading, MA: Addison-wesley Publishing Company, 1964. [6] VOLLING B L. Family transitions following the birth of a sibling: an empirical review of changes in the firstborn's adjustment[J]. Psychol Bull, 2012, 138(3): 497-528. doi: 10.1037/a0026921 [7] 杨博, 刘琴, 盛露露, 等. 角色转换期大孩情绪行为特征及变化的系统评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2021, 21(2): 160-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXZ202102006.htmYANG B, LIU Q, SHENG L L, et al. Emotional and behavioral characteristics of firstborn children in transition to siblinghood: a systematic review[J]. Chin J Evid-Based Med, 2021, 21(2): 160-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXZ202102006.htm [8] NOYES J, BOOTH A, FLEMMING K, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series-paper 3: methods for assessing methodological limitations, data extraction and synthesis, and confidence in synthesized qualitative findings[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 2018, 97: 49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.06.020 [9] STNGH J J. Critical appraisal skills programme[J]. J Pharmacol Pharmacotner, 2013, 4(1): 76. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.107697 [10] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-ottawa Scale for the assessment of the quality of non randomized studies in meta analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9): 603-605. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z [11] 张若林, 帅兰军, 李晓燕, 等. 出生体重与慢性肾脏病关联性的系统评价和Meta分析[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2017, 12(2): 93-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2017.02.003ZHANG R L, SHUAI L J, LI X Y, et al. The relationship between birth weight and chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Evid Based Pediatr, 2017, 12(2): 93-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2017.02.003 [12] ROSTOM A, DUBE C, CRANNEY A, et al. Celiac disease (Evidence Reports/Technology Assessments, No. 104)[R]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2004. [13] DUNN J, KENDRICK C. Interaction between young siblings: association with the interaction between mother and firstborn child[J]. Dev Psychol, 1981, 17(3): 336-343. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.17.3.336 [14] KENDRICK C, DUNN J. Caring for a second baby: effects on interaction between mother and firstborn[J]. Dev Psychol, 1980, 16(4): 303-311. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.16.4.303 [15] KENDRICK C, DUNN J. Protest or pleasure? The response of first-born children to interactions between their mothers and infant siblings[J]. J Child Psychol Psychiatry, 1982, 23(2): 117-129. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1982.tb00057.x [16] KENDRICK C, DUNN J. Sibling quarrels and maternal responses[J]. Dev Psychol, 1983, 19(1): 62-70. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.19.1.62 [17] KOLAK A M, VOLLING B L. Coparenting moderates the association between firstborn children's temperament and problem behavior across the transition to siblinghood[J]. J Fam Psychol, 2013, 27(3): 355-364. doi: 10.1037/a0032864 [18] OH W, VOLLING B L, GONZALEZ R. Trajectories of children's social interactions with their infant sibling in the first year: a multidimensional approach[J]. J Fam Psychol, 2015, 29(1): 119-129. doi: 10.1037/fam0000051 [19] SONG J H, VOLLING B L. Coparenting and children's temperament predict firstborns' cooperation in the care of an infant sibling[J]. J Fam Psychol, 2015, 29(1): 130-135. doi: 10.1037/fam0000052 [20] 张星玮. 二孩出生前后一年内大孩的行为变化和家庭应对策略[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2018.ZHANG X W. Behavior changes and family coping strategies of two children in one year before and after birth[D]. Baoding: Hebei University, 2018. [21] 赵雪. 亲子依恋对8~12岁头胎儿童接纳二胎的影响: 共情和同伴关系的作用[D]. 成都: 四川师范大学, 2018.ZHAO X. The influence of parent-child attachment on acceptance of the second child by the first child aged 8-12: the role of empathy and peer relation[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Normal University, 2018. [22] GOTTLIEB L N, BAILLIES J. Firstborns' behaviors during a mother's second pregnancy[J]. Nurs Res, 1995, 44(6): 356-362. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/7501490 [23] TETI D M, SAKIN J W, KUCERA E, et al. And baby makes four: predictors of attachment security among preschool-age firstborns during the transition to siblinghood[J]. Child Dev, 1996, 67(2): 579-596. doi: 10.2307/1131833 [24] 丁常聪, 李红霞, 陈晓萍, 等. 二孩的出生对幼龄大孩的心理影响[J]. 重庆医学, 2018, 47(31): 106-108.DING C C, LI H X, CHEN X P, et al. The psychological impact of second children birth on young firstborn children[J]. Chongqing Med, 2018, 47(31): 106-108. [25] 孙雅, 付丽娟, 李明晶, 等. "二孩"政策下对"大孩"行为与心理的影响研究及其干预措施[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2020, 22(8): 1264-1266. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431274-20190607-00667SUN Y, FU L J, LI M J, et al. Study on the influence of "two-child" policy on the behavior and psychology of "firstborn children" and its intervention measures[J]. J Chin Physic, 2020, 22(8): 1264-1266. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431274-20190607-00667 [26] 杨博. 重庆市城区学龄前角色转换期大孩情绪行为特征及其相关因素的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2020.YANG B. The characteristics and related factors of emotional and behavioral problems of preschool firstborn children during transition to siblinghood in Chongqing[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2020. -







 下载:
下载: