Meta analysis of the effect of physical activity intervention on physical fitness in Chinese children aged 3-6 years
-
摘要:
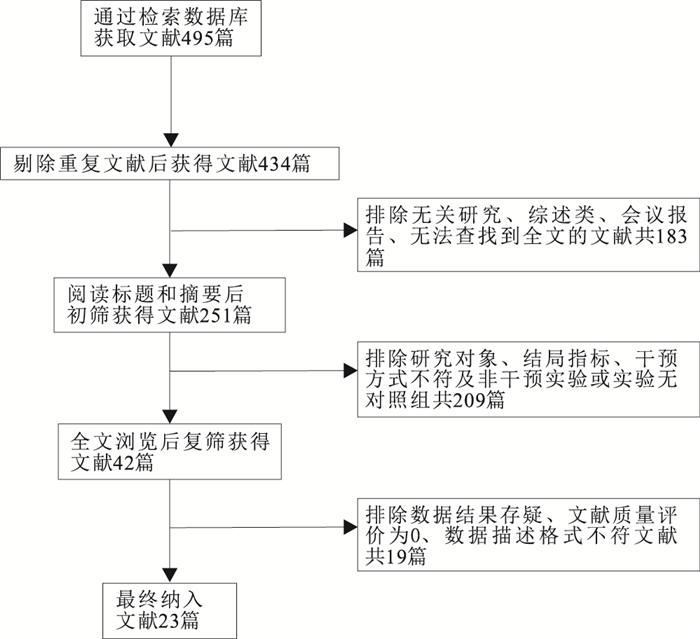
目的 系统量化评价1992—2020年有组织的体育活动对中国3~6岁幼儿身体素质的影响,为开展精准有效的干预实践、进一步提高幼儿身体素质提供方法参考。 方法 检索中国知网、万方数字资源、维普数据库、EBSCO运动数据库、Web of Science数据库,根据纳入与排除标准收集有关体育活动对中国3~6岁幼儿身体素质影响的随机对照实验。中文检索词包括:(幼儿OR学龄前儿童OR学前儿童)AND(身体素质OR体质)AND(干预实验OR干预研究OR随机对照实验)等,英文检索词包括:(preschool OR kindergarten OR young children OR nursery)AND(physical fitness)AND(randomized controlled trial)AND(Chinese OR China)等。 结果 共纳入23项研究2 386名幼儿。Meta分析结果显示,体育活动对于幼儿立定跳远(SMD=0.61,95%CI=0.46~0.76)、坐位体前屈(SMD=0.53,95%CI=0.36~0.70)、10 m折返跑(SMD=-0.84,95%CI=-1.08~-0.61)、双脚连续跳(SMD=-0.74,95%CI=-0.90~-0.58)、走平衡木(SMD=-0.54,95%CI=-0.70~-0.39)的成绩有中到高度的影响,而对网球掷远(SMD=0.39,95%CI=0.26~0.51)成绩影响较低。 结论 定期开展有针对性的体育活动能显著提高幼儿的身体素质,不同类型指标所反映的身体素质受体育活动内容、干预时长、锻炼频率、年龄等因素制约而影响不同。 Abstract:Objective To systematically review the efficacy of organized physical activity intervention from 1992 to 2020 on physical fitness of young children aged 3-6 in China. Methods Studies were searched in databases of CNKI, Wan Fang, VIP, EBSCO Sports and Web of Science. The randomized controlled trials of physical fitness of young children aged 3-6 in China were selected by using Chinese and English keywords: (preschool OR kindergarten OR young children OR nursery) AND (physical fitness) AND (randomized controlled trial) AND (Chinese OR China). Results Twenty-three studies were included, involving 2 386 young children. Meta-analysis showed that physical activity had a moderate-to-high effect on young children's standing long jump (SMD=0.61, 95%CI=0.46-0.76), sit and reach (SMD=0.53, 95%CI=0.36-0.70), 10-meter shuttle run (SMD=-0.84, 95%CI=-1.08- -0.61), continuous jumping on two feet (SMD=-0.74, 95%CI=-0.90- -0.58), and walking the balance beam (SMD=-0.54, 95%CI= -0.70- -0.39). On the other hand, physical activity had a small effect on young children's throwing ball (SMD=0.39, 95%CI=0.26-0.51). Conclusion Physical activity intervention shows significant effects on physical fitness of young children in China. Effecs on physical fitness indicated by different types of indicators depends on physical activity content, duration, frequency, child age and other factors. -
Key words:
- Motor activity /
- Physical fitness /
- Meta-analysis /
- Child
-
表 1 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 1. Baseline information of included study
第一作者及年份 年龄/岁 性别(男:女) 样本量 体育活动内容 锻炼频率 干预时长 教师来源 结局指标 Jaded得分 干预组 对照组 周喆啸(2017)[11] 无区分 119∶120 119 120 功能性动作练习 每周5次,小、中、大班幼儿每次练习时间依次为20~30,30~40,40~50 min 24周 经培训 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 江大雷(2015)[12] 5~6 无区分 30 31 足球运动 每周2次,每次35 min 8周 足球专业教练 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 徐婕(2018)[13] 5~6 31∶25 28 28 健身操 每周2次,每次35 min 3个月 幼儿教师 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 刘聪珊(2014)[14] 5~6 53∶34 45 42 体能训练 每周3次,每次40 min 3个月 幼儿教师 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 张春(2013)[15] 5~6 55∶43 49 49 武术 每周2次,每次30 min 16周 专业教师 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈 1 王旭(2018)[16] 5~6 26∶26 26 26 体育课程 每周3次,每次2 h 12周 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳 1 雷园园(2018)[17] 5~6 60∶66 61 65 功能性动作练习 每周3次,每次1 h 6周 幼儿教师 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 3 杨丽(2019)[18] 4~5 20∶20 20 20 体操 每周1次,每次2 h 1学期 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 厉余浩(2016)[19] 4~5 16∶14 15 15 敏捷梯训练 每周2次,每次20 min 2个月 立定跳远;网球掷远;10 m折返跑 1 桂聪(2019)[20] 5~6 30∶30 30 30 球类运动 每周3次,每次1 h 12周 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 吴志宝(2018)[21] 无区分 男性幼儿 120 120 跆拳道 每周2次,每次45 min 16周 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 2 王诚(2018)[22] 5~6 30∶30 30 30 体操 每周5次,每次1~1.5 h 6个月 坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑 1 肖艺(2011)[23] 4~5 30∶30 30 30 体育游戏 每周5次,每次45 min 12周 立定跳远;坐位体前屈;走平衡木 1 赫达(2009)[24] 无区分 无区分 30 30 体育游戏 每周5次,每次45 min 3个月 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 张鑫(2018)[25] 无区分 无区分 29 30 体智能课程 每周2次,每次30 min 3个月 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑 1 杨慧君(2016)[26] 4~5 无区分 30 30 体育活动干预 每周3次,每次30 min 4个月 幼儿教师 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 徐珊珊(2011)[27] 4~5 82∶94 87 89 健美操 每周5次,每次30 min 9个月 幼儿教师 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 2 潘娣(2013)[28] 4~5 无区分 33 27 健美操 每周3次,每次35 min 3个月 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 2 何东亮(2017)[29] 5~6 144∶96 120 120 篮球运动 每周5次,每次30 min 12周 体育教育专业 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑 1 黎细凤(2008)[30] 4~5 无区分 25 25 武术 每周5次,每次1 h 5个月 立定跳远;坐位体前屈 1 邓土军(2012)[31] 5~6 无区分 30 30 武术 每周2次,每次30 min 4个月 立定跳远;网球掷远;坐位体前屈;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 石少锋(2017)[32] 4~5 33∶35 33 35 户外运动 每周3次,每次30 min 8周 幼儿教师 立定跳远;10 m折返跑;双脚连续跳 1 王新晓(2019)[33] 5~6 51∶9 30 30 足球运动 每周2次,每次30 min 12周 足球教师 立定跳远;坐位体前屈;双脚连续跳;走平衡木 1 -
[1] 国家体育总局. 2014年国民体质监测公报[EB/OL]. [2015-11-25]. http://www.sport.gov.cn/n315/n329/c216784/content.html.General Administration of Sport of China. 2014 National physique monitoring bulletin[EB/OL]. [2015-11-25]. http://www.sport.gov.cn/n315/n329/c216784/content.html. [2] 刘万志, 刘丰彬. 幼儿体适能开展现状研究综述[J]. 湖北体育科技, 2019, 38(5): 419-422, 443. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-983X.2019.05.012LIU W Z, LIU F B. Summary of research on present situation of children's physical fitness[J]. Hubei Sports Sci, 2019, 38(5): 419-422, 443. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-983X.2019.05.012 [3] 夏诗洁, 唐玉成. 国内3~6岁幼儿体能训练研究综述[J]. 体育科技文献通报, 2019, 27(7): 116-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPOR201907050.htmXIA S J, TANG Y C. A review on strength and conditioning training of domestic kids aged 3 to 6[J]. Bull Sport Sci Technol, 2019, 27(7): 116-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPOR201907050.htm [4] DOWDA M, PATE R R, TROST S G, et al. Influences of preschool policies and practices on children's physical activity[J]. J Commun Health, 2004, 29(3): 183-196. doi: 10.1023/B:JOHE.0000022025.77294.af [5] WASENIUS N S, GRATTAN K P, HARVEY A L J, et al. The effect of a physical activity intervention on preschoolers' fundamental motor skills: a cluster RCT[J]. J Sci Med Sport, 2018, 21(7): 714-719. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2017.11.004 [6] PEDIATRICS A A O. Guidelines for health supervision III[M]. America: American Academy of Pediatrics, 2002. [7] MCENTIRE, NANCY. Active Start: a statement of physical activity guidelines for children birth to five years[J]. Childhood Educ, 2010, 86(3): 200. doi: 10.1080/00094056.2010.10523149 [8] RIETHMULLER A M, JONES R A, OKELY A D. Efficacy of interventions to improve motor development in young children: a systematic review[J]. Pediatr, 2009, 124(4): e782-e792. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-0333 [9] FOULKES J D, KNOWLES Z, FAIRCLOUGH S J, et al. Effect of a 6-week active play intervention on fundamental movement skill competence of preschool children: a cluster randomized controlled trial[J]. Percept Motor Skill, 2017, 124(2): 393-412. doi: 10.1177/0031512516685200 [10] JADAD A R, COOK D J, BROWMAN G P. A guide to interpreting discordant systematic reviews[J]. CMAJ, 1997, 156(10): 1411-1416. http://ije.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=cmaj&resid=156/10/1411 [11] 周喆啸. 3-6岁幼儿身体功能性动作体系的构建与实证研究[D]. 太原: 河北师范大学, 2017.ZHOU ZX. The Construction and empirical study of the physical function system among 3-6 years preschoolers[D]. Taiyuan: Hebei Normal University, 2017. [12] 江大雷, 曾从周. 8周中等强度足球运动游戏对学龄前儿童执行功能发展的影响[J]. 中国体育科技, 2015, 51(2): 43-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY201502005.htmJIANG D L, ZENG C Z. The effect of 8-week soccer exercise with medium intensity on executive function in preschool children[J]. Chin Sport Sci Technol, 2015, 51(2): 43-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY201502005.htm [13] 徐婕. 操舞类运动对幼儿园大班生体质健康影响的实验研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2018.XU J. An experimental study on the effect of dancing and dancing sports on the physical health of the big students in kindergarten[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2018. [14] 刘聪珊. 大班幼儿体能训练的实验研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2014.LIU C S. The experimental study of the physical fitness exercising for preschool children[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2014. [15] 张春. 德宏州州幼儿园武术基本功训练对幼儿体质影响比较研究[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2013.ZHANG C. A comparative study on the influence of Wushu basic skills training in Dehongzhouzhou kindergartens on children's physical fitness[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2013. [16] 王旭. 多样性体育课程对5-6岁儿童体适能的影响研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2018.WANG X. Research on the effect of diverse physical education curriculum on the physical fitness of 5-6 years old children[D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2018. [17] 雷园园, 周龙祥, 王国祥. 基于粗大动作发展的幼儿功能性动作训练方案设计研究[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2018, 44(1): 122-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SORT201801020.htmLEI Y Y, ZHOU L X, WANG G X. Research on the design of functional movement training program based on gross motor development for preschool children[J]. J Chengdu Sport Univ, 2018, 44(1): 122-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SORT201801020.htm [18] 杨丽, 苟淋玲. 快乐体操对幼儿体质健康影响的实验研究[J]. 当代体育科技, 2019, 9(16): 89-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYKJ201916057.htmYANG L, GOU L L. An experimental study on the influence of happy gymnastics on children's physical health[J]. Contemp Sports Technol, 2019, 9(16): 89-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYKJ201916057.htm [19] 厉余浩. 敏捷梯训练对学前儿童协调能力影响的实验研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2016.LI Y H. An experimental study on the influence of agility ladder training on the coordination ability of preschool children[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2016. [20] 桂聪. 球类游戏对5-6岁幼儿体能指标的影响研究[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学, 2015.GUI C. Study on the ball game effects on 5-6 years old children's physical fitness[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University, 2015. [21] 吴志宝. 跆拳道运动对4-6岁男性幼儿体能和智力的影响研究[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2018.WU Z B. Effects of Taekwondo on physical fitness and intelligence of 4 to 6 years male children[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal Unviersity, 2018. [22] 王诚. 体操对5-6岁幼儿身体素质及认知功能影响的实验研究[J]. 现代教育, 2018(7): 62-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDJU201807028.htmWANG C. An experimental study on the influence of gymnastics on the physical fitness and cognitive function of 5-6 year old children[J]. Mod Educ, 2018(7): 62-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDJU201807028.htm [23] 肖艺. 体育游戏对幼儿运动能力发展的实验研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2011.XIAO Y. An experimental study of sports games on the development of children's athletic ability[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2011. [24] 赫达. 体育游戏教学对学前儿童体质发展的研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2009.HE D. A study of the physical development of preschool children in the teaching of sports games[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2009. [25] 张鑫. 体智能课教学对幼儿健康体适能的影响[D]. 吉首: 吉首大学, 2018.ZHANG X. The effect of physical intelligence teaching on children's health and fitness[D]. Jishou: Jishou University, 2018. [26] 杨慧君, 黄茜. 武汉市城镇幼儿体质健康的实验干预研究[J]. 湖北体育科技, 2016, 35(10): 876-879, 913.YANG H J. An experimental intervention study on Wuhan urban infants' physical health[J]. Hubei Sports Sci, 2016, 35(10): 876-879, 913. [27] 徐珊珊. 幼儿健美操的创编与实施效果的实验研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳体育学院, 2011.XU S S. The experimental research in the creation and the results of aerobics for children[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Sport University, 2011. [28] 潘娣. 幼儿健美操对幼儿身体素质和执行功能影响的实验研究[D]. 北京: 北京体育大学, 2013.PAN D. An experimental study on the influence of infant aerobics on infant physical fitness and executive function[D]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University, 2013. [29] 何东亮. 幼儿篮球运动对6岁幼儿身心发展影响的研究[D]. 曲阜: 曲阜师范大学, 2017.HE D L. Research on the influence of infant basketball on the physical and mental development of 6-year-old infants[D]. Qufu: Qufu Normal University, 2017. [30] 黎细凤, 张云崖, 王洪宇. 幼儿武术游戏对幼儿身体素质的影响[J]. 武术研究, 2008(7): 65-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSKX200807032.htmLI X F, ZHANG Y Y, WANG H Y. The influence of children's martial arts games on children's physical fitness[J]. Wushu Stud, 2008(7): 65-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSKX200807032.htm [31] 邓土军. 幼儿武术游戏教学的实践研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2012.DENG S J. Practice of game teaching on children Wushu[D]. Chang-sha: Hunan Normal University, 2012. [32] 石少锋. 幼儿园户外区域体育活动的设计与实施[D]. 北京: 北京体育大学, 2017.SHI S F. The design and implementation of kindergarten outdoor area sports activities[D]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University, 2017. [33] 王新晓. 足球运动对5- 6岁幼儿身心发展的影响研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2019.WANG X X. A study on the influence of football on the physical and mental development of children aged 5 to 6[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2019. [34] 王佳丽, 马渝英, 董燕燕. 幼儿体操训练对改善儿童感觉机能和身体素质的作用[J]. 南京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 33(4): 110-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJSF201004021.htmWANG J L, MA Y Y, DONG Y Y. Function of child exercise training to improve children's sense and fitness [J]. J Nanjing Normal Univ(Natural Sci Edit), 2010, 33(4): 110-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJSF201004021.htm [35] MACALLUM L. HOWSON N, GOPU N. Designed to move: a physical activity action agenda[R]. Int J Physic Educ, 2012, 49(4): 38. [36] 关宏岩, 赵星, 屈莎等. 学龄前儿童(3 ~ 6岁)运动指南[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2020, 28(6): 714-720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO202006031.htmGUAN H Y, ZHAO X, QU S, et al. Physical activity guideline for Chi-nese preschoolers aged 3-6 years [J] Chin J Child Health Care, 2020, 28(6): 714-720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO202006031.htm [37] 何黎明, 盛群力. 5岁以下儿童身体活动、久坐行为与睡眠建议[J]. 数字教育, 2020, 6(4): 84-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEJY202004017.htmHE L M, SHENG Q L. Physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep advice for the children of less than 5 years old[J]. Digit Educ, 2020, 6(4): 84-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEJY202004017.htm -







 下载:
下载: