Design and construction of exercise prescription teaching mode in school physical education curriculum
-
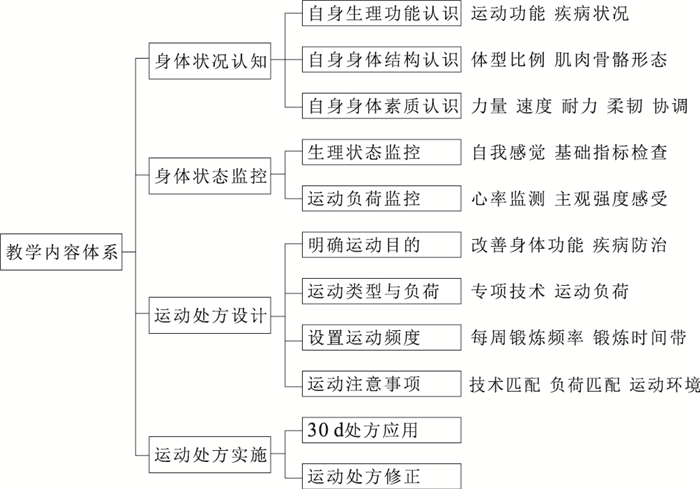
摘要: 围绕使学生学会制定符合自身特点的运动处方方案这一教学目标, 构建教学内容体系、成绩评价体系, 并设计教学实施路径。"运动处方教学模式"以学生身体状态认知、身体状况监控、运动处方设计、运动处方实施四方面知识或内容作为体育课程教学的主要内容。依据布鲁姆学习分类法设置保健知识学习、处方编制、处方实施、效果反馈及处方调整5个课程实施步骤。借助"互联网+教学"途径, 促进抽象运动技术与保健理论的教学效率, 并联通课内与课外, 拓展体育教学的时空条件。建立以保健知识掌握与应用、运动处方制定及实施、体育兴趣与习惯培养为主要内容的评价体系, 并融合定量与定性、过程与终结等多种评价手段, 增强成绩评价的公平性与准确性。"运动处方教学模式"具有健康教育主导性、运动与保健知识系统性、新兴教学方法与手段融合性、体育成绩评价公平性、尊重学生个性化与主体性等特点。Abstract: Objective Based on the teaching goal of "self-designed exercise prescription plans that meet their own characteristics", the teaching content and perfermance evaluation system are built, and the teaching implementation path is designed. The teaching mode of exercise prescription takes four aspects as the main contents of PE course teaching, namely, the cognition of students' physical state, the monitoring of physical state, the design of exercise prescription and the implementation of exercise prescription.According to Bloom's learning classification, five implementation steps of health care knowledge learning, prescription preparation, prescription implementation, effect feedback and prescription adjustment were set up.With the help of "Internet+teaching" approach, the teaching efficiency of abstract sports technology and health care theory is promoted, and the in-class and after-class connection is made to expand the space-time conditions of physical education teaching. In order to enhance the fairness and accuracy of performance evaluation, an evaluation system should be established with the main contents of mastering and applying health care knowledge, making and implementing sports prescription, and cultivating sports interest and habits. Exercise prescription teaching mode has the characteristics of health education leading, sports and health care knowledge system, new teaching methods and means integration, sports performance evaluation fairness, respect for students' individuality and subjectivity.
-
Key words:
- Curriculum /
- Sports /
- Education /
- Students
-
表 1 “运动处方教学”的成绩评价方式
Table 1. Performance evaluation methods of exercise prescription teaching mode
评价内容 评价指标 评价手段 评价目的 运动处方设计 1.反映自身状况认知程度;2.自身状态监控手段适应程度;3.选择运动技术的适宜程度;4.运动负荷与运动频率的匹配;5.运动处方内容的调整与总结。 1.组内讨论中的学生互评;2.学生运动保健知识测试;3.学生运动技术水平与功能性知识测试;4.学生运动处方方案与调整过程评分。 对学生运动保健知识体系,运动技术及运动处方设计能力的评价。 运动处方实施 1.锻炼打卡频率;2.锻炼打卡时长;3.锻炼负荷安排;4.锻炼过程与运动处方的一致性。 1.课下分组锻炼,组内同学间互相监督评分;2.处方执行日记记录情况评分;3.处方执行效果、体验报告评分。 对学生运动处方有效执行情况以及运动参与程度的评价。 锻炼兴趣培养 1.运动对人体健康促进的认识;2.对有计划性体育锻炼的认识;3.对运动处方执行效果的认识;4.对未来长期体育锻炼的期望。 1.教师对学生运动处方知识认知发展的过程性评价;2.处方执行中的体会评分;3.处方执行效果调查问卷;4.学生处方执行的总结与分析报告。 通过运动处方的实施体验,培养学生体育锻炼的兴趣、习惯与能力。 -
[1] 中共中央办公厅, 国务院办公厅. 关于全面加强和改进新时代学校体育工作的意见[J]. 西藏教育, 2020(12): 3-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5880.2020.12.003General Office of the CPC Central Committee, General Office of the State Council. Suggestions on comprehensively strengthening and improving school physical education in the New Era[J]. Educ Tibet, 2020(12): 3-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5880.2020.12.003 [2] 于佳祥, 徐英微. 高等学校体育教育中的运动处方教学理念探讨[J]. 体育与科学, 2009, 30(3): 105-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4590.2009.03.027YU J X, XU Y H. Discussion on the teaching Concept of exercise prescription in physical Education in colleges and universities[J]. Phys Educ Sci, 2009, 30(3): 105-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4590.2009.03.027 [3] 穆旭. 健身运动处方教学在高校体育教学中的应用研究[D]. 北京: 北京体育大学, 2007.MU X. Research on the application of fitness prescription teaching in college physical education[D]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University, 2007. [4] 于超. 论"体医结合"处方式的教学模式[J]. 当代体育科技, 2018, 8(19): 31-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYKJ201819017.htmYU C. On the teaching mode of combining physical and medical treatment[J]. Contemp Sports Tech, 2018, 8(19): 31-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYKJ201819017.htm [5] 王志华, 熊云新, 谢翔, 等. 健身运动处方教学模式与传统体育教学模式的比较研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2007(S1): 397-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD2007S1213.htmWANG Z H, XIONG Y X, XIE X, et al. A comparative study of fitness exercise prescription teaching mode and traditional physical education teaching mode[J]. J Beijing Univ Phys Educ, 2007(S1): 397-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJTD2007S1213.htm [6] 舒婷, 荆纯祥, 陈道睿, 等. 《运动处方》教学模式的革新与实践研究[J]. 体育科技, 2018, 39(4): 95-97, 99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1359.2018.04.042SHU T, JING C X, CHEN D R, et al. Research on innovation and Practice of teaching mode of exercise prescription[J]. Sports Sci Tech, 2018, 39(4): 95-97, 99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1359.2018.04.042 [7] 王正珍. 运动处方的研究与应用进展[J]. 体育学研究, 2021, 35(3): 40-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJTB202103006.htmWANG Z Z. Progress in research and application of exercise prescription[J]. Res J Phys Educ, 2021, 35(3): 40-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJTB202103006.htm [8] 祝莉, 王正珍, 朱为模. 健康中国视域中的运动处方库构建[J]. 体育科学, 2020, 40(1): 4-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX202001002.htmZHU L, WANG Z Z, ZHU W M. Construction of exercise prescription database from the perspective of Health China[J]. China Sports Sci, 2020, 40(1): 4-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX202001002.htm [9] 周登嵩. 学校体育学[M]. 北京: 人民体育出版社, 2005.ZHOU D S. School physical education[M]. Beijing: People's Sports Publishing House, 2005. [10] 王正珍. ACSM运动测试与运动处方指南(第十版)[M]. 北京: 北京体育大学出版社, 2015.WANG Z Z. ACSM Guide to Exercise Testing and Exercise Prescription(10th edition)[M]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University Press, 2015. [11] 罗曦娟, 王正珍, 李新, 等. 美国运动医学会运动风险筛查的演变和发展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2020, 39(5): 413-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2020.05.013LUO X J, WANG Z Z, LI X, et al. Evolution and development of exercise risk screening for the American College of Sports Medicine[J]. Chin J Sports Med, 2020, 39(5): 413-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2020.05.013 [12] 王瑞元, 苏全生. 运动生理学[M]. 北京: 人民教育出版社, 2012.WANG R Y, SU Q S, Exercise physiology[M]. Beijing: People's Education Press, 2012. [13] 美国运动医学学会. ACSM运动测试与运动处方指南[M]. 北京: 北京体育大学出版社, 2015.American Academy of Sports Medicine. ACSM'S guidelines for exercise testing and prescription[M]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University Press, 2015. [14] 范杰. 布鲁姆化学教育目标分类法及其应用[J]. 课程. 教材. 教法, 1987(7): 56-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJJF198707017.htmFAN J. Bloom's classification of chemical education objectives and its application[J]. Curriculum Teach Mate Teach Methods, 1987(7): 56-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJJF198707017.htm [15] 晋树利. 基于布鲁姆认知过程维度的深度学习评价研究[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2020.JIN S L. Deep learning evaluation based on Bloom's cognitive process dimension[D]. Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2020. [16] 荆雯, 李洋, 刘元国. "互联网+教育"背景下泛在化新型体育学习模式研究[J]. 体育学刊, 2019, 26(1): 120-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYXK201901019.htmJING W, LI Y, LIU Y G. A study of a new ubiquitous sports learning mode under the background of "Internet+Education"[J]. J Phys Educ, 2019, 26(1): 120-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYXK201901019.htm [17] 雷伯. 心理学词典[M]. 上海: 上海译文出版社, 1996.LEI B. Psychological dictionary[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Translation Publishing House, 1996. [18] 王铁. 中国大百科全书: 教育[M]. 北京: 中国大百科全书出版社, 1998.WANG T. Encyclopedia of China: education[M]. Beijing: Encyclopedia of China Publishing House, 1998. -







 下载:
下载: