Auxiliary diagnosis model of children with autism spectrum disorder based on random forest
-
摘要:
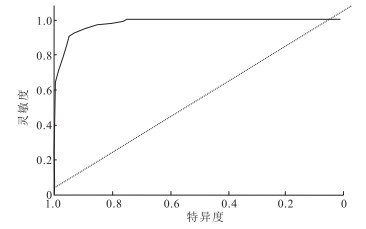
目的 利用随机森林算法构建孤独症谱系障碍(autism spectrum disorder, ASD)儿童快速辅助诊断模型,有助于ASD儿童的早期发现、早期诊断,减轻临床诊断及评估压力。 方法 采用机器学习中随机森林算法,应用社交反应量表(SRS)及文兰适应行为量表(VABS)对黑龙江省346名ASD儿童和90名健康儿童进行评估,并基于量表数据以及儿童基础信息构建预测模型,运用ROC曲线及准确率等指标评价模型拟合效果。 结果 得到的随机森林预测模型中,13个特征因素模型以及7个特征因素的预测模型准确率均达到0.9以上、灵敏度最高达到0.927,特异度最高达到0.936,AUC值为0.979;以年龄为筛选条件的模型准确率达到0.943,灵敏度达到0.959,特异度达到0.931,AUC值为0.978。3个模型的拟合和泛化效果都较为理想。 方法 采用社交及适应能力水平指标构建的随机森林模型可以较为精确辅助开展ASD的诊断,为开发快速筛查和诊断的辅助工具提供了科学依据。 Abstract:Objective The random forest algorithm was used to construct a rapid screening diagnostic prediction model for children with autism spectrum disorder, to provide the references for early detection, early diagnosis of ASD children, and to reduce the pressure of ASD clinical diagnosis and assessment. Methods The random forest algorithm of machine learning was applied to build the auxiliary diagnosis model. Totally 346 ASD children and 90 normal children were evaluated by Social Responsiveness Scale and Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales. ROC curve, and accuracy was used to evaluate the models. Results Among the models, the accuracy of 13 feature factors and 7 feature factors were above 0.9, the sensitivity was up to 0.927, the specificity was up to 0.936 and the AUC was up to 0.979. The accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and AUC of the model were 0.943, 0.959, 0.931 and 0.978 respectively. The fitting and generalization effects of the three models were all satisfactory. Conclusion A random forest model based on the SRS Scales and Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales can be used to diagnose ASD accurately and provide scientific basis for the development of rapid screening and diagnosis tools. -
Key words:
- Autistic disorder /
- Mental health /
- Models, structural /
- ROC curve /
- Child
-
表 1 ASD儿童随机森林预测模型评价指标
Table 1. Comparison of random forest prediction models evaluation indexes
模型输入特征 人数 准确率 灵敏度 特异度 AUC值 13特征变量模型 346 0.929 0.927 0.936 0.979 7特征变量模型 315 0.920 0.918 0.931 0.976 4~6岁特征变量模型 346 0.943 0.959 0.931 0.978 -
[1] SPIEGEL D. Dissociative disorders in DSM-5[J]. Depres Anx, 2011, 28(12): 1119. doi: 10.1002/da.20920 [2] MAENNER M J, SHAW K A, BAIO J, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years-autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, united states, 2016[J]. MMWR Surveill Summ, 2020, 69(4): 1-12. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6904a1 [3] ZWAIGENBAUM L, PENNER M. Autism spectrum disorder: advances in diagnosis and evaluation[J]. BMJ Clin Res, 2018, 361: k1674. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29784657 [4] 汤宜朗, 郭延庆, RICE C E, 等. 孤独症诊断的金标准之一《孤独症诊断观察量表》介绍[J]. 国际精神病学杂志, 2010, 37(1): 38-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYJ201001011.htmTANG Y L, GUO Y Q, RICE C E, et al. Introduction of autism diagnosis observation scale, one of the gold standard of autism diagnosis[J]. J Int Psychiatry, 2010, 37(1): 38-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYJ201001011.htm [5] THABTAH F. Machine learning in autistic spectrum disorder behavioral research: a review and ways forward[J]. Inform Health Soc Care, 2019, 44(3): 278-297. doi: 10.1080/17538157.2017.1399132 [6] BÖLTE S, POUSTKA F. The relation between general cognitive level and adaptive behavior domains in individuals with autism with and without co-morbid mental retardation[J]. Child Psychiatry Human Dev, 2002, 33(2): 165-172. doi: 10.1023/A:1020734325815 [7] ALDRIDGE F J, GIBBS V M, SCHMIDHOFER K, et al. Investigating the clinical usefulness of the Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS) in a tertiary level, autism spectrum disorder specific assessment clinic[J]. J Autism Dev Dis, 2012, 42(2): 294-300. doi: 10.1007/s10803-011-1242-9 [8] 龚俊, 邹时朴, 刘冬梅, 等. 社交反应量表的信效度分析[J]. 中国医学创新, 2019, 16(1): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.01.005GONG J, ZOU S P, LIU D M, et al. Reliability and validity of social responsiveness scale[J]. Med Innovat Chin, 2019, 16(1): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.01.005 [9] 张颖, 唐心蕊, 鲁萍, 等. 低功能孤独症谱系障碍患儿适应性行为的研究[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志, 2019, 27(9): 994-996, 1001. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO201909017.htmZHANG Y, TANG X R, LU P, et al. Adaptive behavior in children with low-functioning autism spectrum disorder[J]. Chin J Child Health Care, 2019, 27(9): 994-996, 1001. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ERTO201909017.htm [10] 张梁, 郭文斌, 王庭照. 文兰适应行为量表的发展及应用[J]. 现代特殊教育, 2017(22): 24-31, 38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDTS201722005.htmZHANG L, GUO W B, WANG T Z. Development and application of vineland adaptive behavior scales[J]. J Mod Spec Educ, 2017(22): 24-31, 38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDTS201722005.htm [11] RAHMAN R, MATLOCK K, GHOSH S, et al. Heterogeneity aware random forest for drug sensitivity prediction[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 11347. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11665-4 [12] LI N, CHEN G, SONG X, et al. Prevalence of autism-caused disability among Chinese children: a national population-based survey[J]. Epilepsy Behav, 2011, 22(4): 786-789. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2011.10.002 [13] 郭超, 赵艺皓, 郑晓瑛. 从罕见到高发: 对孤独症的重新审视[J]. 残疾人研究, 2020(2): 60-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0810.2020.02.007GUO C, ZHAO Y H, ZHENG X Y. From rare to high: a review of autism[J]. Disab Res, 2020(2): 60-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0810.2020.02.007 [14] 骆名进, 宋海东, 刘健, 等. 儿童孤独症社区早期综合干预现况及可行模式探讨[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2017, 32(1): 82-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2017.01.018LUO M J, SONG H D, LIU J, et al. A study on the status quo and feasible model of early comprehensive intervention for children with autism in community[J]. Chin J Rehabil Med, 2017, 32(1): 82-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2017.01.018 [15] JACOB S, WOLFF J J, STEINBACH M S, et al. Neurodevelopmental heterogeneity and computational approaches for understanding autism[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2019, 9(1): 63. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0390-0 [16] 柏冬, 王浩, 李璐, 等. 机器学习方法对前列腺癌的诊断价值[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2020, 43(2): 188-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYX202002002.htmBAI D, WANG H, LI L, et al. Diagnostic value of machine learning in prostate cancer[J]. J Mol Imag, 2020, 43(2): 188-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYX202002002.htm [17] KVPPER C, STROTH S, WOLFF N, et al. Identifying predictive features of autism spectrum disorders in a clinical sample of adolescents and adults using machine learning[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 4805. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61607-w [18] BONE D, BISHOP S L, BLACK M P, et al. Use of machine learning to improve autism screening and diagnostic instruments: effectiveness, efficiency, and multi-instrument fusion[J]. J Child Psychol Psychiatry, 2016, 57(8): 927-937. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12559 [19] 占锦敏, 赵知劲, 王李军. 基于随机森林的通信信号识别算法[J]. 杭州电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 40(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXDY202005001.htmZHAN J M, ZHAO Z J, WANG L J. Communication signal recognition algorithm based on random forest[J]. J Hangzhou Dianzi Univ(Natr Sci), 2020, 40(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXDY202005001.htm [20] BOTTEMA-BEUTEL K, KIM S Y, CROWLEY S. A systematic review and meta-regression analysis of social functioning correlates in autism and typical development[J]. Autism Res, 2019, 12(2): 152-175. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30575308 [21] FROST K M, HONG N, LORD C. Correlates of adaptive functioning in minimally verbal children with autism spectrum disorder[J]. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil, 2017, 122(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1352/1944-7558-122.1.1 -







 下载:
下载: