A longitudinal study on sex difference in weight growth and systolic blood pressure change among children and adolescents in Beijing
-
摘要:
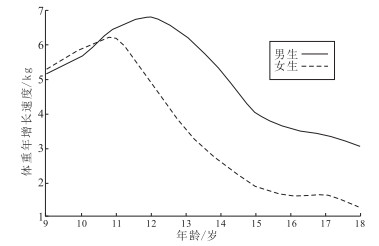
目的 探索北京市学龄儿童青少年体重增长与收缩压变化的性别差异,为控制体重和血压的快速增长提供依据。 方法 基于北京市顺义区2009—2018年中小学生体检资料,经匹配个人信息后形成70 288人具有完整体重、收缩压的纵向数据库,计算年龄别体重、收缩压及其增长速度,与以体重增速高峰年龄(PWA)为基点的收缩压增长速度,采用混合效应线性模型分析增速的性别差异。 结果 男、女生体重、收缩压均随年龄增长而升高,各年龄段男生体重、收缩压均高于女生。混合效应线性模型结果显示,体重和收缩压增长速度存在性别年龄交互作用(β值分别为-0.35,-0.40,P值均 < 0.01),即各年龄段体重、收缩压增长速度具有性别差异。年龄别增长速度曲线显示,男生分别于12和13岁达到体重增速高峰和收缩压增速高峰,比女生晚1年和3年,但增长速度高峰均高于女生。收缩压调整PWA后的增长速度曲线显示,PWA出现前2年,男、女生发生增速高峰,在PWA出现次高峰,在PWA后显著下降且男生收缩压增长速度始终高于女生。 结论 北京学龄儿童青少年体重与收缩压增长速度和规律存在性别差异,并且收缩压变化与体重增加密切相关。 Abstract:Objective To explore sex differences between weight and systolic blood pressure (SBP) changes among school-age children and adolescents in Beijing, and to provide a basis for priority intervention to control the rapid growth of body weight and blood pressure. Methods Anthropometric measurement data of 70 288 children and adolescents from primary and high schools in Shunyi District were collected from 2009 to 2018, and a longitudinal dataset with complete data related to weight and BP after individual data linkage was compiled. The age-specific weight and SBP growth rates were calculated, and a linear mixed-effects model was used to identify sex differences in chronological growth rates. Results Weight and SBP increased with age in both boys and girls, and the mean weight and SBP were higher in boys than in girls across all age groups. The result of the linear mixed-effects model indicated apparent sex differences in weight and SBP growth rates, with an age and sex interaction term(β=-0.35, -0.40, P < 0.01). The age at peak weight velocity (PWA) was 12 years old and the age at peak SBP velocity was 13 years old in boys, which occurred one and three years later than for girls, respectively. In addition, the peak weight and SBP velocity were higher in boys than in girls. The curves of the SBP growth rate adjusted for the PWA, showed that the peak SBP velocity occurred two years before PWA and the second peak SBP velocity occurred at the PWA, which indicated "double peaks" in both boys and girls. The SBP growth rate was always higher in boys than in girls, and the rates declined after PWA. Conclusion Sex differences in weight and SBP growth rates were persistent and obvious in school-age children and adolescents in Beijing and the change in SBP was highly time synchronized with the increase in weight. -
Key words:
- Weight gain /
- Blood pressure /
- Sex factors /
- Linear models /
- Child /
- Adolescent
1) 段军伟与李子昂为共同第一作者。 -
表 1 北京市顺义区8~18岁儿童青少年体重比较[M(P25,P75), kg]
Table 1. Comparison of sex difference in age-specific weight among children and adolescents aged 8-18 years in Shunyi District, Beijing[M(P25, P75), kg]
年龄/岁 男生 女生 Z值 P值 人数 体重 人数 体重 8 401 31.6(28.0, 37.8) 619 30.1(26.6, 35.4) 4.3 < 0.01 9 12 482 34.1(29.2, 42.0) 11 641 31.9(27.7, 38.0) -23.4 < 0.01 10 17 844 38.3(32.4, 47.4) 15 753 36.4(31.2, 43.9) -19.2 < 0.01 11 17 499 43.7(36.2, 54.0) 15 407 42.2(35.9, 50.1) -13.2 < 0.01 12 17 705 50.5(42.0, 61.2) 16 592 47.7(41.7, 55.4) -19.4 < 0.01 13 16 364 55.4(47.5, 66.5) 14 908 50.7(45.2, 58.1) -33.7 < 0.01 14 13 589 59.8(52.5, 71.2) 12 214 52.7(47.6, 59.6) -50.3 < 0.01 15 11 946 63.4(56.1, 74.6) 11 757 54.3(49.4, 60.8) -63.1 < 0.01 16 9 745 65.9(58.7, 76.8) 9 596 55.1(50.0, 61.5) -66.6 < 0.01 17 8 176 67.9(60.6, 78.2) 8 126 55.6(50.5, 61.8) -67.9 < 0.01 18 2 400 68.2(61.0, 77.6) 1 860 55.5(50.3, 61.1) -36.1 < 0.01 表 2 北京市顺义区8~18岁儿童青少年血压比较(x±s, mm Hg)
Table 2. Comparison of sex difference in age-specific blood pressure among children and adolescent aged 8-18 years in Shunyi District, Beijing (x±s, mm Hg)
年龄/岁 男生 女生 t值 P值 人数 收缩压 人数 收缩压 8 401 104.8±9.6 619 103.3±9.0 2.4 0.02 9 12 482 105.1±10.0 11 641 103.2±9.8 15.1 < 0.01 10 17 844 106.4±10.2 15 753 105.1±10.1 11.9 < 0.01 11 17 499 109.2±10.8 15 407 108.4±10.7 6.9 < 0.01 12 17 705 109.6±11.2 16 592 107.2±10.8 19.8 < 0.01 13 16 364 112.4±11.2 14 908 108.4±10.7 32.6 < 0.01 14 13 589 115.3±11.1 12 214 109.1±10.4 46.6 < 0.01 15 11 946 116.9±11.4 11 757 108.2±10.5 61.1 < 0.01 16 9 745 118.2±11.0 9 596 108.3±10.3 64.9 < 0.01 17 8 176 120.1±11.2 8 126 108.7±10.3 67.8 < 0.01 18 2 400 120.4±11.8 1 860 109.0±10.4 33.7 < 0.01 注: 1 mm Hg=0.133 kPa。 表 3 北京市顺义区8~18岁儿童青少年体重、收缩压增速混合效应线性模型分析(n=70 288)
Table 3. Linear mixed-effect models of weight and blood pressure growth rate among children and adolescents aged 8-18 in Shunyi District, Beijing (n=70 288)
参数 体重 收缩压 β值 标准误 P值 β值 标准误 P值 截距 9.94 0.07 < 0.01 -0.57 0.24 0.02 年龄 -0.34 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.23 0.02 < 0.01 女生a 3.22 0.09 < 0.01 3.89 0.34 < 0.01 年龄×女生b -0.35 0.01 < 0.01 -0.40 0.03 < 0.01 注: a表示以男生为参照组; b表示以年龄×男生为参照组。 -
[1] 孙伯庚, 高平, 刘泽军, 等. 临沂市7~18岁儿童生长发育水平和营养状况调查分析[J]. 中国社区医师, 2020, 36(23): 163-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2020.23.079SUN B G, GAO P, LIU Z J, et al. Investigation and analysis of growth and developmental level and. nutritional status of children aged 7 to 18 years in Linyi city[J]. Chin Commun Doctor, 2020, 36(23): 163-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2020.23.079 [2] 马军, 董彬. 儿童青少年血压与年龄、身高的关系研究[C]//中华预防医学会儿少卫生分会第九届学术交流会、中国教育学会体育与卫生分会第一届学校卫生学术交流会、中国健康促进与教育协会学校分会第三届学术交流会. 厦门: 中华预防医学会, 2011: 15-23.MA J, DONG B. Association between blood pressure, age and height in children and adolescents[C]//The 9th academic exchange conference of the Child and Adolescent Health Section of Chinese Preventive Medicine Association, the 1st academic exchange conference about school health of the Sports and Health Section of the Chinese Society of Education, the 3rd academic exchange conference of the School Section of China Health Promotion Association. Xiamen: Chinese Prevenive Medicine Association, 2011: 15-23. [3] LI M, MUSTILLO S, ANDERSON J. Childhood poverty dynamics and adulthood overweight/obesity: unpacking the black box of childhood[J]. Soc Sci Res, 2018, 76: 92-104. DOI: 10.1016/j.ssresearch.2018.05.009. [4] PETRICK J L, JENSEN B W, SØRENSEN T I A, et al. Overweight patterns between childhood and early adulthood and esophageal and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma risk[J]. Obesity(Silver Spring), 2019, 27(9): 1520-1526. doi: 10.1002/oby.22570 [5] GARLEHNER G, VANDER S E B, ORR C, et al. Screening for hypertension in children and adolescents: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force[J]. JAMA, 2020, 324(18): 1884-1895. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.11119 [6] HAGMAN E, DANIELSSON P, ELIMAM A, et al. The effect of weight loss and weight gain on blood pressure in children and adolescents with obesity[J]. Int J Obes(Lond), 2019, 43(10): 1988-1994. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0384-2 [7] JI H, KIM A, EBINGER J E, et al. Sex differences in blood pressure trajectories over the life course[J]. JAMA Cardiol, 2020, 5(3): 19-26. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_PM32489793 [8] SANTOS L P, SANTOS I S, MATIJASEVICH A, et al. Changes in overall and regional body fatness from childhood to early adolescence[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 1888. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38486-x [9] MOIN A, MOHANTY N, TEDLA Y G, et al. Under-recognition of pediatric hypertension diagnosis: examination of 1 year of visits to community health centers[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich), 2020, 23(2): 257-264. doi: 10.1111/jch.14148 [10] UNGER E S, KAWACHI I, MILLIREN C E, et al. Protective misperception?Prospective study of weight self-perception and blood pressure in adolescents with overweight and obesity[J]. J Adolesc Health, 2017, 60(6): 680-687. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.12.017 [11] 李子昂, 赵瑞兰, 赵芳芳, 等. 北京学龄儿童青少年身高增长与血压变化性别差异的10年纵向研究[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2020, 54(12): 1378-1382. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200612-00875LI Z A, ZHAO R L, ZHAO F F, et al. Sex difference in height growth and blood pressure change among Beijing school-age children and adolescents: a ten-year longitudinal study[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2020, 54(12): 1378-1382. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200612-00875 [12] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2005年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007.Chinese Students Physical Fitness and Health Research Group. Report on the physical fitness and health surveillance of Chinese school students[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007. [13] PHILIPPAERTS R M, VAEYENS R, JANSSENS M, et al. The relationship between peak height velocity and physical performance in youth soccer players[J]. J Sports Sci, 2006, 24(3): 221-30. doi: 10.1080/02640410500189371 [14] 潘思杏. 1985~2014年广西瑶族学生身高体重动态变化及体格与性发育相关性的研究[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学, 2018.PAN S X. The dynamic change of height and weight of YAO nationality students in Guangxi from 1985 to 2014 and the correlation between physical and sexual development[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Medical University, 2018. [15] 董彬. 青春期学生血压变化规律分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2012, 33(2): 137-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIWS201202002.htmDONG B. Research of the change in blood pressure during puberty[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2012, 33(2): 137-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIWS201202002.htm [16] HLAING W M, PRINEAS R J, ZHU Y. Trajectory of systolic blood pressure in children and adolescents[J]. Ann Epidemiol, 2006, 16(1): 11-8. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2005.03.006 [17] TU W, ECKERT G J, SAHA C, et al. Synchronization of adolescent blood pressure and pubertal somatic growth[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2009, 94(12): 5019-5022. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-0997 [18] MUNTHALI R J, KAGURA J, LOMBARD Z, et al. Childhood adiposity trajectories are associated with late adolescent blood pressure: birth to twenty cohort[J]. BMC Public Health, 2016, 16: 665. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-337-x. [19] SUGIANTO R I, SCHMIDT B M W, MEMARAN N, et al. Sex and age as determinants for high blood pressure in pediatric renal transplant recipients: a longitudinal analysis of the CERTAIN Registry[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2020, 35(3): 415-426. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04395-4 [20] ARIS I M, RIFAS-SHIMAN S L, LI L J, et al. Early-life predictors of systolic blood pressure trajectories from infancy to adolescence: findings from project viva[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2019, 188(11): 1913-1922. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwz181 -







 下载:
下载: