Sex differences in the growth and physical development of Beijing school-aged children and adolescents
-
摘要:
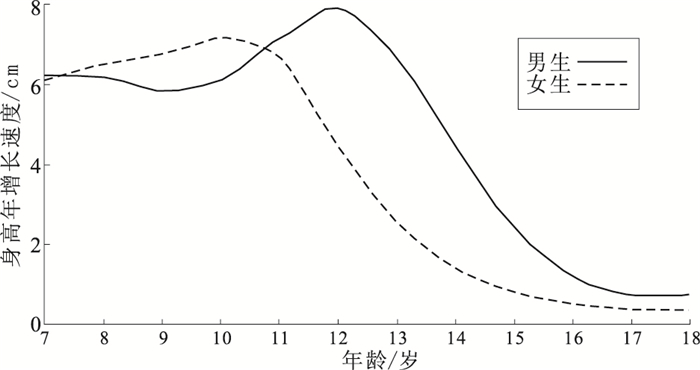
目的 探索学龄儿童青少年体格发育指标增长速度的性别差异,为明确中国儿童青少年的生长发育规律提供科学依据。 方法 基于北京市顺义区2009—2018年6~18岁学龄儿童及青少年健康体检资料,经匹配个人信息后共纳入94 122名学生,计算年龄别身高、体重、体质量指数(BMI)增长速度,以及以身高增速高峰年龄(PHA)为基点的体重和BMI增长速度,采用混合效应线性模型分析增长速度的性别差异。 结果 男、女生平均身高、体重和BMI随年龄增长而增长,除10~11岁男生平均身高低于女生外,其他年龄段男生平均身高均高于女生,各年龄段男生的平均体重和BMI均高于女生(P值均 < 0.01);混合效应线性模型结果显示身高、体重和BMI的增长速度存在性别年龄交互作用(t值分别为-67.56,-47.46,3.22,P值均 < 0.01),即每个年龄段身高、体重和BMI的增长速度具有性别差异;男生PHA为12岁,女生PHA为10岁,男生出现身高增速高峰较女生晚2年,但峰高高于女生。男生体重增长速度高峰年龄为12岁,女生为11岁。男生BMI增长速度曲线呈“双峰”状且最大增长速度年龄为10岁,女生为11岁,男生较女生早1年;调整PHA后的体重增长速度曲线均显示,男生和女生青春期体重增长与身高增长相一致,即体重增长速度在PHA前随年龄增加而升高,在PHA达到高峰,之后又下降;7~9岁男生可能出现青春期启动前脂肪堆积。 结论 青春期各年龄段男、女生身高、体重和BMI的增长速度存在性别差异,且体重的变化与身高增长密切相关。 Abstract:Objective The study aimed to explore sex differences in the growth and physical development of Beijing school-aged children and adolescents. Methods Data obtained from regular health examinations of 94 122 school-aged children and adolescents aged 6-18 years old were collected from primary and high schools in Shunyi District from 2009 to 2018, and a longitudinal dataset was compiled with complete anthropometric parameters including height, weight, and BMI levels after linkage of individual-level information. The age-specific growth rate was calculated and a linear mixed-effects model was used to identify sex differences according to chronological or relative age to peak height velocity (PHA). Results Height, weight, and BMI levels increased with age in both boys and girls. Girls were taller than boys in the 10-11-year-old age group, catch-up growth in height was observed in boys at age 12, whose height surpassed that of girls thereafter. Boys had a higher weight and BMI than girls in all age groups (P < 0.01). Sex differences were found in the growth rates of height, weight, and BMI levels(t=-67.56, -47.46, 3.22, P < 0.01), which was demonstrated by the interaction effect of sex and age in the linear mixed-effects model. The PHA in boys was 12 years old, which was two years later than the PHA in girls. Boys reached peak weight velocity at 12 years old, lagging one year behind girls who reached their peak at 11 years old. The curves of the BMI growth rate with age showed double peaks in boys and the first peak appeared at 10 years, which was one year earlier than girls. The change in weight was highly synchronized in time with the increase in height, after adjusting for the growth rate of weight by PHA. Weight velocity increased with age before the onset of puberty until PHA, and then it declined; boys presented with obvious fat accumulation before the onset of puberty. Conclusion Sex differences in the growth and physical development of school-aged children and adolescents were persistent and apparent, and the change in weight was highly synchronized in time with the increase in height. -
Key words:
- Growth and development /
- Body mass index /
- Physical examination /
- Chid /
- Adolescent
1) 赵瑞兰与李子昂为共同第一作者。 -
表 1 北京市顺义区2009—2018年6~18岁儿童青少年年龄别身高体重和BMI的性别比较
Table 1. Comparison of sex differences in age-specific height, weight and BMI among children and adolescents aged 6-18 years in Shunyi District, Beijing from 2009 to 2018
年龄/岁 男生 女生 t身高值 Z体重值 tBMI值 人数 身高/cm 体重/kg BMI/
(kg·m-2)人数 身高/cm 体重/kg BMI/
(kg·m-2)6 17 864 122.2±5.1 23.6(21.3, 27.1) 16.5±2.5 16 309 120.8±5.0 22.3(20.2, 25.1) 15.7±2.1 25.0 -32.3 30.2 7 24 839 127.6±5.6 26.3(23.5, 30.9) 17.0±2.8 21 859 126.2±5.5 24.7(22.2, 28.4) 16.1±2.4 26.6 -36.9 36.4 8 25 754 133.3±6.0 29.9(26.2, 36.2) 17.8±3.3 22 553 131.9±6.0 27.8(24.7, 32.6) 16.7±2.8 25.1 -38.4 40.5 9 24 051 138.6±6.3 33.9(29.1, 42.0) 18.7±3.7 21 007 137.9±6.6 31.6(27.6, 37.9) 17.4±3.1 11.5 -31.8 39.4 10 23 299 144.0±6.8 38.6(32.5, 48.1) 19.6±4.1 20 209 144.4±7.2 36.6(31.3, 44.3) 18.3±3.5 -6.9 -22.0 36.0 11 21 138 150.0±7.7 44.1(36.4, 54.7) 20.5±4.3 18 620 150.9±7.2 42.4(36.1, 50.5) 19.2±3.7 -12.7 -15.0 20.5 12 19 649 157.4±8.6 50.7(42.1, 62.0) 21.2±4.5 17 724 156.3±6.3 47.7(41.6, 55.6) 20.1±3.7 13.7 -21.6 25.6 13 18 430 164.4±8.1 56.1(48.0, 68.0) 21.6±4.5 16 222 159.2±5.7 50.8(45.3, 58.3) 20.7±3.7 69.5 -38.9 20.7 14 15 389 169.4±6.9 60.5(52.8, 73.0) 22.2±4.6 13 620 160.6±5.5 52.8(47.6, 59.7) 21.1±3.5 120.3 -56.2 21.8 15 12 925 172.5±6.2 63.7(56.3, 75.4) 22.5±4.4 12 830 161.5±5.5 54.4(49.4, 61.0) 21.5±3.4 149.5 -66.3 20.7 16 10 248 174.1±5.9 66.3(58.9, 77.8) 23.0±4.5 9 843 161.9±5.6 55.2(50.1, 61.7) 21.6±3.3 149.6 -68.3 23.5 17 8 592 174.8±6.0 68.4(60.9, 79.5) 23.3±4.4 8 323 162.2±5.5 55.7(50.6, 62.0) 21.7±3.3 144.2 -69.6 26.9 18 2 462 174.9±6.0 68.5(61.2, 78.1) 23.4±4.2 1 887 162.5±5.7 55.8(50.3, 61.1) 21.8±3.2 75.4 -36.5 12.7 注:体重为M(P25, P75),身高与BMI为(x±s);P值均 < 0.01。 表 2 北京市顺义区2009—2018年6~18岁儿童青少年身高、体重和BMI的增长速度混合效应线性模型(n=94 122)
Table 2. Linear mixed-effects models of the growth velocity of height, weight and BMI among children and adolescents aged 6-18 years in Shunyi District, Beijing from 2009 to 2018(n=94 122)
变量 身高 体重 BMI β值 标准误 t值 P值 β值 标准误 t值 P值 β值 标准误 t值 P值 常数项 9.98 0.04 259.75 < 0.01 4.16 0.04 100.07 < 0.01 -0.76 0.01 54.72 < 0.01 年龄 -0.39 < 0.01 -116.85 < 0.01 0.08 < 0.01 19.57 < 0.01 0.01 < 0.01 2.95 < 0.01 女a 2.81 0.06 50.37 < 0.01 1.74 0.06 27.70 < 0.01 -0.19 0.02 -8.18 < 0.01 年龄×女b -0.32 < 0.01 -67.56 < 0.01 0.24 0.01 -47.46 < 0.01 0.01 < 0.01 3.22 < 0.01 注: a表示以男为参照组;b表示以年龄×男为参照组。 -
[1] OHTA H. Growth spurts of the bone from infancy to puberty[J]. Clin Calcium, 2019, 29(1): 9-17. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30590354 [2] ALIMUJIANG A, COLDITZ G A, GARDNER J D, et al. Childhood diet and growth in boys in relation to timing of puberty and adult height: the longitudinal studies of child health and development[J]. Cancer Causes Control, 2018, 29(10): 915-926. doi: 10.1007/s10552-018-1068-2 [3] ELHAKEEM A, FRYSZ M, TILLING K, et al. Association between age at puberty and bone accrual from 10 to 25 years of age[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2019, 2(8): e198918. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8918 [4] RIMÁROVÁ K, DORKO E, DIABELKOVÁ J, et al. Anthropometric predictors of systolic and diastolic blood pressure considering intersexual differences in a group of selected schoolchildren[J]. Cent Eur J Public Health, 2018, 26(Suppl): s4-s11. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30817866 [5] AMOO-TELLA S, DANBORNO B, AKUYAM S, et al. Gender-and age-related differences in anthropometric and body composition parameters in Nigerians, Zaria, Nigeria[J]. J Exp Clin Anat, 2017, 16(2): 137-146. doi: 10.4103/jeca.jeca_4_17 [6] ZHANG J, ZHAI Y, FENG X Q, et al. Gender differences in the prevalence of overweight and obesity, associated behaviors, and weight-related perceptions in a national survey of primary school children in China[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2018, 31(1): 1-11. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895398818300151 [7] CURTIS V A, ALLEN D B. Male pubertal timing-boys will be men, but when?[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2019, 173(9): 819-820. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.2306 [8] HVIDT J J, BRIX N, ERNST A, et al. Size at birth, infant growth, and age at pubertal development in boys and girls[J]. Clin Epidemiol, 2019, 11: 873-883. DOI:10.2147/CLEP.SZ17388. [9] OHLSSON C, BYGDELL M, CELIND J, et al. Secular trends in pubertal growth acceleration in swedish boys born from 1947 to 1996[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2019, 173(9): 860-865. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.2315 [10] 张珊. 青春发动时相与儿童青少年肥胖发生发展关系的研究[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2011.ZHANG S. Study on relationship between pubertal timing and development of obesity in childhood and adolescence[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2011. [11] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2005年中国学生体质与健康调研报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007.Physical Fitness and Health Research Group of Chinese School Students. Report on the physical fitness and health surveillance of Chinese school students[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007. [12] ZHENG W, SUZUKI K, YOKOMICHI H, et al. Multilevel longitudinal analysis of sex differences in height gain and growth rate changes in Japanese school-aged children[J]. J Epidemiol, 2013, 23(4): 275-279. doi: 10.2188/jea.JE20120164 [13] 蔡赐河, 马军, 黄志达, 等. 广东省中山市5~19岁学生青春期身高增长规律的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2012, 33(7): 717-721. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2012.07.016CAI C H, MA J, HUANG Z D, et al. Study on growth of height among students during their adolescence in Zhongshan, Guangdong[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2012, 33(7): 717-721. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2012.07.016 [14] DABAS A, KHADGAWAT R, GAHLOT M, et al. Height velocity in apparently healthy north indian school children[J]. Indian J Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 22(2): 256-260. doi: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_638_17 [15] KELLY A, WINER K K, KALKWARF H, et al. Age-based reference ranges for annual height velocity in US children[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2014, 99(6): 2104-2112. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-4455 [16] GRANADOS A, GEBREMARIAM A, LEE J M. Relationship between timing of peak height velocity and pubertal staging in boys and girls[J]. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol, 2015, 7(3): 235-237. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.2007 [17] NEMBIDZANE C, LESAOANA M, MONYEKI K D, et al. Using the SITAR method to estimate age at peak height velocity of children in Rural South Africa: ellisras longitudinal study[J]. Children (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 7(3): 17. http://www.mdpi.com/2227-9067/7/3/17 [18] 林琬生, 侯启春, 吴南屏, 等. 儿童身高生长追踪研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2000, 19(2): 97-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RLXB200002001.htmLIN W S, HOU Q C, WU N P, et al. Longitudinal study on child height growth[J]. Acta Anthropol Sinica, 2000, 19(2): 97-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RLXB200002001.htm [19] 潘思杏. 1985—2014年广西瑶族学生身高体重动态变化及体格与性发育相关性的研究[D]. 桂林: 广西医科大学, 2018.PAN S X. The dynamic change of height and weight of YAO nationality students in Guangxi from 1985 to 2014 and the correlation between physical and sexual development[D]. Guilin: Guangxi Medical University, 2018. [20] ZIVICNJAK M, NARANCIĈ N S, SZIROVICZA L, et al. Gender-specific growth patterns for stature, sitting height and limbs length in Croatian children and youth (3 to 18 years of age)[J]. Coll Antropol, 2003, 27(1): 321-334. doi: 10.1525/aeq.2003.34.2.205 [21] DE MIGUEL-ETAYO P, MORENO LA, SANTABÁRBARA J, et al. Anthropometric indices to assess body-fat changes during a multidisciplinary obesity treatment in adolescents: EVASYON study[J]. Clin Nutr, 2015, 34(3): 523-528. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.06.004 [22] MARTIN-CALVO N, MORENO-GALARRAGA L, MARTINEZ-GONZALEZ M. Association between body mass index, waist-to-height ratio and adiposity in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Nutrients, 2016, 8(8): 512. doi: 10.3390/nu8080512 [23] BÖTTCHER Y, VERDUIN W M, VAN DEN HELDER R, et al. Dexa body composition assessment in 10-11 year healthy children[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(10): e0165275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165275 [24] MAFFEIS C, MORANDI A. Body composition and insulin resistance in children[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2018, 72(9): 1239-1245. doi: 10.1038/s41430-018-0239-2 -







 下载:
下载: